4 slave-to-slave communications, 1 general information – Efficient Networks Siemens Sinamics S120 User Manual
Page 421
Communication PROFIBUS DP/PROFINET IO
10.2 Communication via PROFIBUS DP
Drive Functions
Function Manual, (FH1), 07/2007 Edition, 6SL3097-2AB00-0BP4
421
10.2.4
Slave-to-slave communications
10.2.4.1 General information
Description
For PROFIBUS-DP, the master addresses all of the slaves one after the other in a DP cycle.
In this case, the master transfers its output data (setpoints) to the particular slave and
receives as response the input data (actual values). Fast, distributed data transfer between
drives (slaves) is possible using the "slave-to-slave communications" function without
involving the master.
The following terms are used for the functions described here:
● Slave-to-slave communications
● Data Exchange Broadcast (DXB.req)
● Slave-to-slave communications (is used in the following)
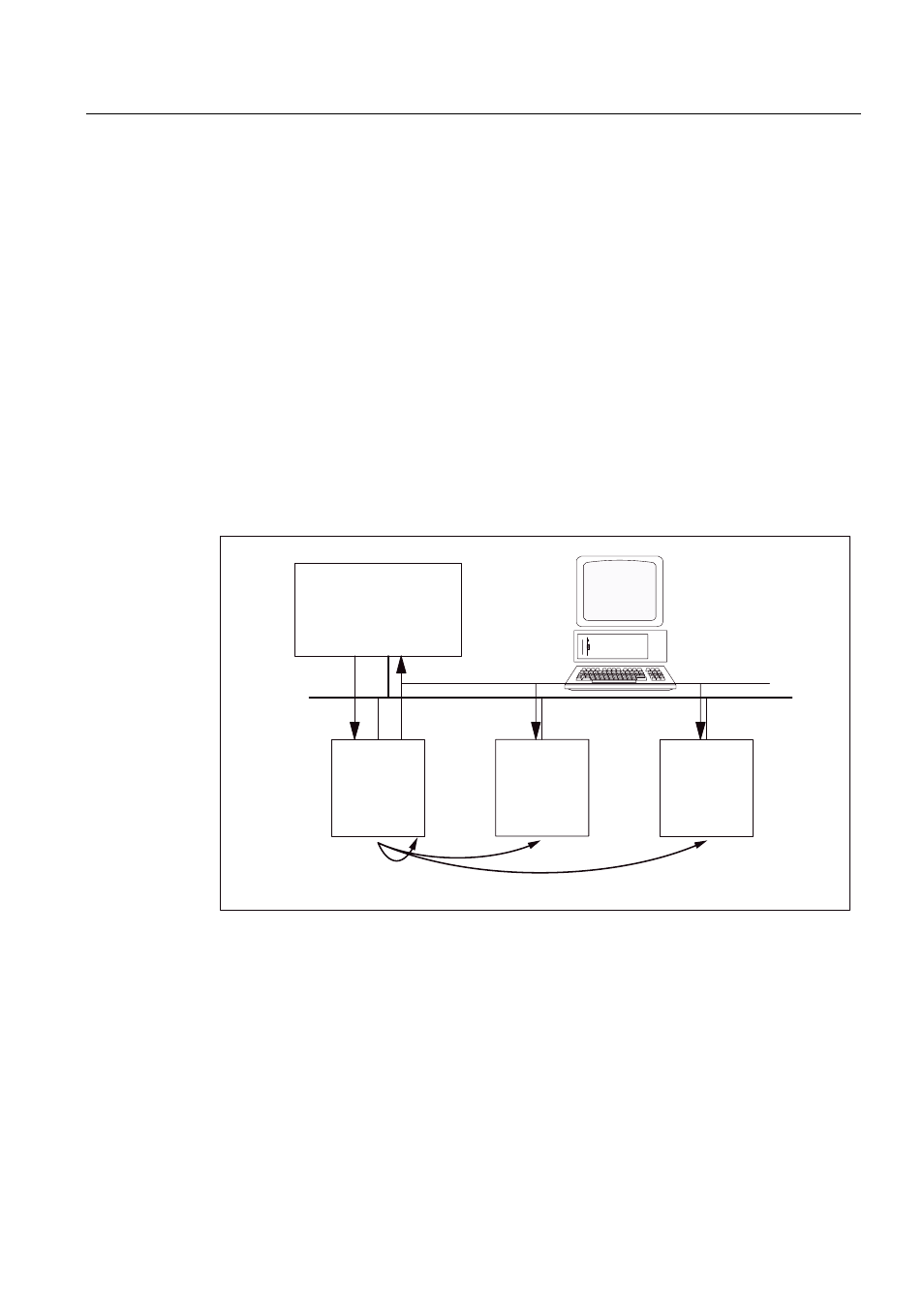
3*3&
)URPWKHSHUVSHFWLYHRIWKH&ODVVPDVWHU
$QVZHU
,QSXWGDWD
2XWSXWGDWD
0DVWHU&ODVV
HJ6,0$7,&6
3DUDPHWHUDVVLJQPHQW
PDVWHU
&\FOHJHQHUDWRU
+:&RQILJ
&RQILJXUDWLRQ
6ODYH
6,1$0,&6
3XEOLVKHU
6ODYH
6,1$0,&6
6XEVFULEHU
6ODYH
6,1$0,&6
6XEVFULEHU
/LQNV
'ULYH(6%DVLF
Figure 10-29 Slave-to-slave communications with the publisher-subscriber model
Publisher
With the "slave-to-slave communication" function, at least one slave must act as the
publisher.
The publisher is addressed by the master when the output data is transferred with a different
layer 2 function code (DXB.req). The publisher then sends its input data to the master with a
broadcast telegram to all bus nodes.
