2 the pt table, 3 motion, Management – ElmoMC SimplIQ Digital Servo Drives-Bell Command Reference User Manual
Page 260: 3 motion management
0
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.1
-1000
-800
-600
-400
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
Interpolated path
PvtPlan output
Time (seconds)
Motion path in counts
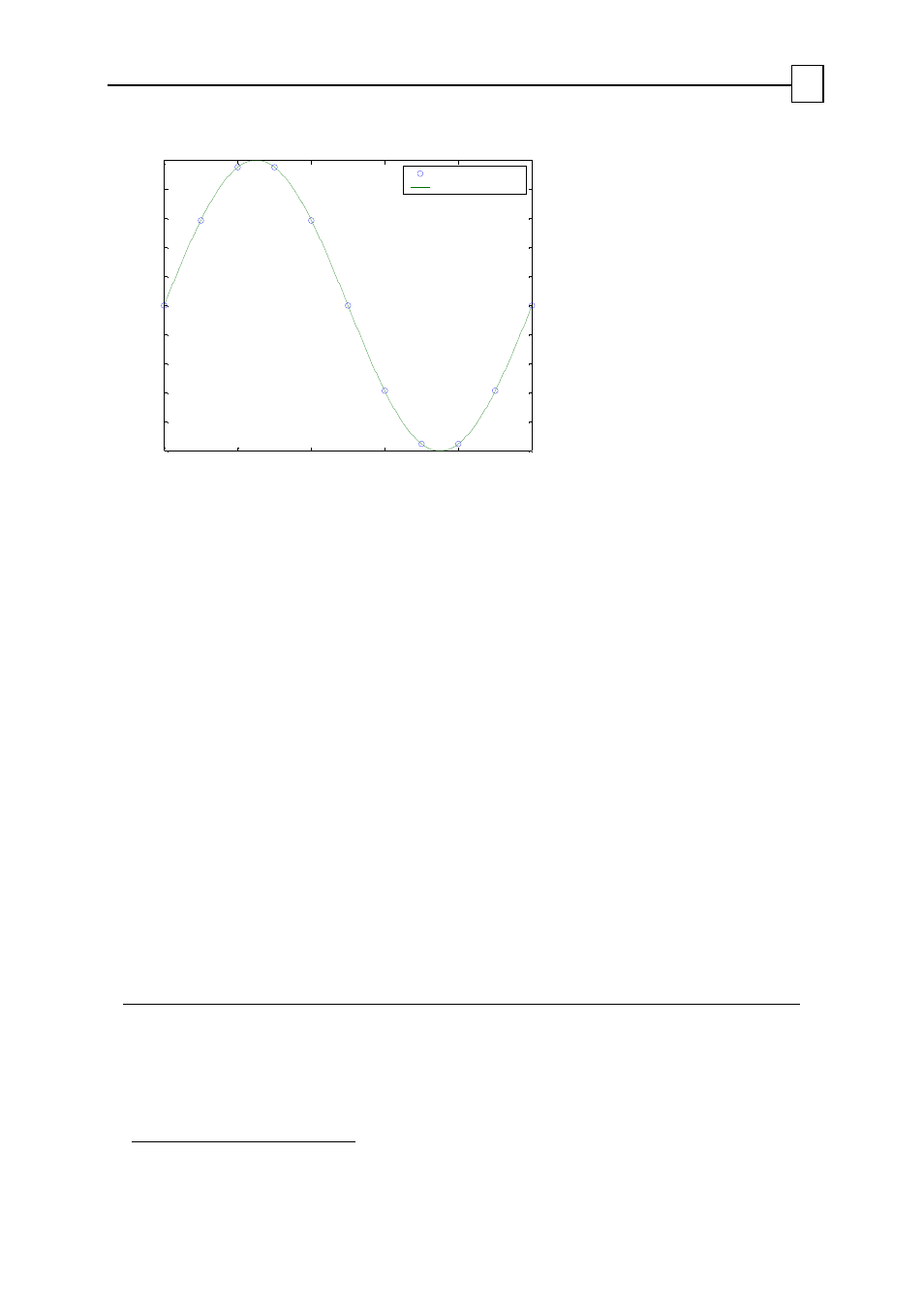
6.1.7.2 The PT Table
The vector QP[N] defines the position points for PT motion. Each element of the vector
defines the position at a given time. The QP vector has 1024 elements, and can therefore
specify up to 1023 consecutive PT motion segments, or 1024 PT motion segments in
cyclical mode.
The first PT point must be within the range XM[1]…XM[2]. The remaining PT points
need not be within modulo range; but the difference between consecutive PT position
points must be less than (XM[2] - XM[1])/2. For example, suppose that XM[1] = 0 and
XM[2] = 1000. If the PT describes a trajectory beginning at 0 and ending at 10,000, the
motor will travel 10,000 counts, completing its position range 10 times.
6.1.7.3 Motion Management
In PT mode, the drive manages a “read pointer” for the QP[N] vector. When the read
pointer is N, the present motion segment starts at position QP[N] and ends at QP(N+1)
9
.
After MP[4] control sampling times, the drive increments the read pointer to N+1, and
reads QP[N+2] to calculate the parameters of the next motion segment.
The entire PT table need not be used for a given motion.
The parameters of a PT motion are summarized in the following table:
Parameter Use
Comment
MP[1]
Lowest valid element of QP vector.
MP[2]
Highest valid row of QP vector.
9
The PT mode may be cyclical, according to [MP3]. In this case, N+1 must be interpreted in
the modulo sense.
SimplIQ for Steppers Application Note
The Position Reference Generator
MAN-STECR (Ver. 1.1)
61
