Grass Valley K2 Storage System Instruction Manual v.3.2 Sep.24 2007 User Manual
Page 213
September 7, 2007
K2 Storage System Instruction Manual
213
Configuring RAID
NOTE: Binding destroys all user data on the disks.
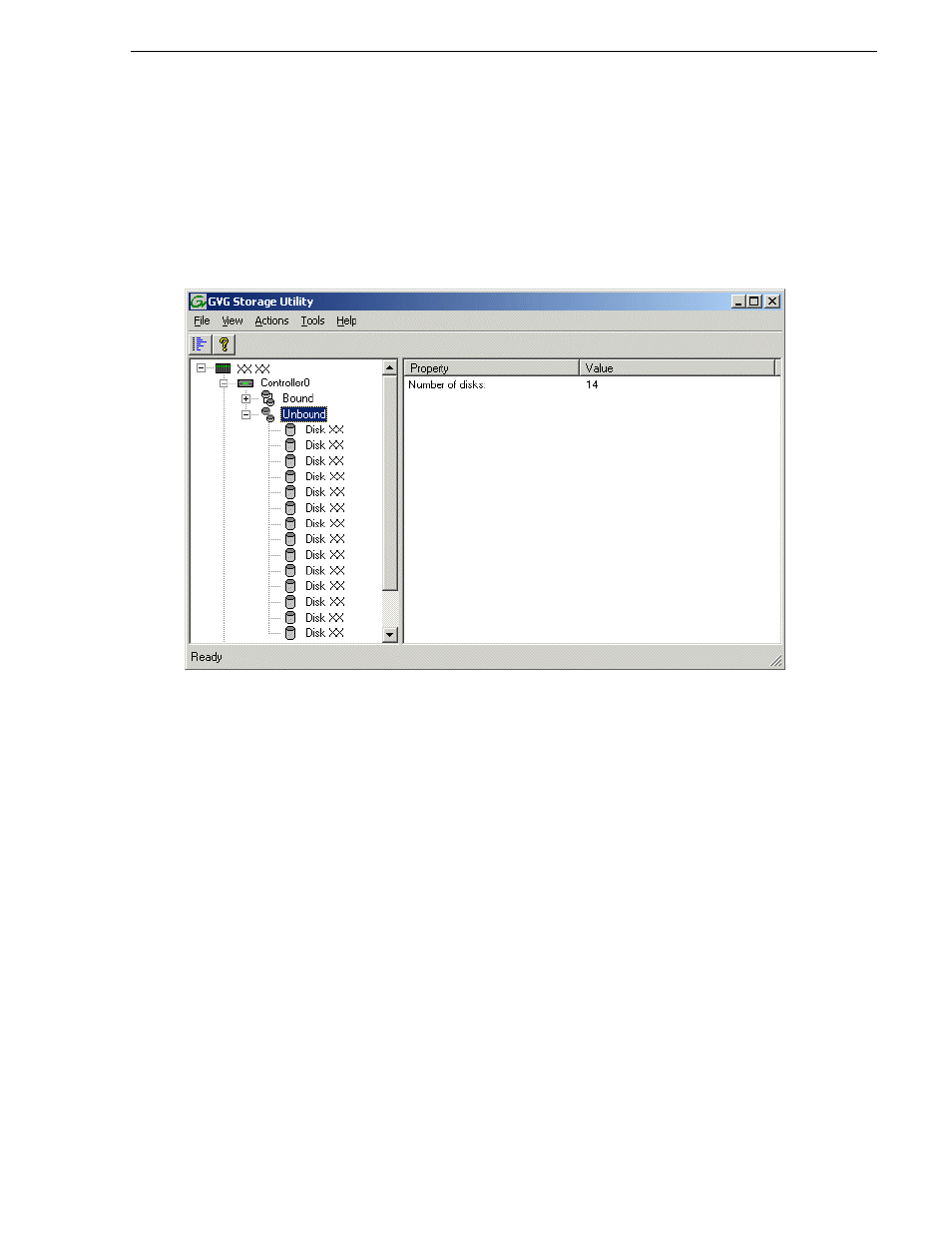
1. In the Storage Utility main window, identify bound RANKs and unbound disks by
their placement in the hierarchy of the tree view. In the following illustration, disk
numbers are represented by “XX”. Refer to
“Identifying disks” on page 744
for an
explanation of how disks are actually numbered in Storage Utility.
Redundant systems store metadata files and journal files on the primary RAID
chassis, which requires a RAID 1 RANK (two disks) for metadata storage and a
RAID 1 RANK (two disks) for journal storage. The RAID 1 RANKs must be
bound from the first four disks (counting from left to right as you face the front of
the RAID chassis) in the primary RAID chassis. These disks must be 15K rpm
drives. In addition, the fifth disk in the primary RAID chassis (also a 15K drive) is
bound as a Hot Spare. This fifth 15K disk then provides Hot Spare functionality for
the other four 15K disks (the RAID 1 RANKs) only. Optionally, you can also use
some of your other 10K disks (in groups of five) as Hot Spares for your media
storage RANKs. Refer to
“Binding Hot Spare drives” on page 751
for more
information.
View disk properties and identify the four disks you will use for the RAID 1
RANKs, the one 15K Hot Spare disk, any other disks that you intend to use for
media RANK Hot Spares, and the remainder of the disks that are available for
media storage RANKs. Make sure you select disks appropriately as you bind
RANKs in the remainder of this procedure.
View disk properties and identify the four disks you will use for the metadata/
journal RAID 1 RANKs, the one metadata/journal Hot Spare disk, any other disks
that you intend to use for Hot Spares, and the remainder of the disks that are
available for media storage. Make sure you select disks appropriately as you bind
disks in the remainder of this procedure.
