Escc/scc differences – Zilog Z16C35 User Manual
Page 269
Application Note
Boost Your System Performance Using The Zilog ESCC
™
13-2
ESCC/SCC DIFFERENCES
The differences between the ESCC and SCC are shown
below:
The differences between the ESCC and SCC are
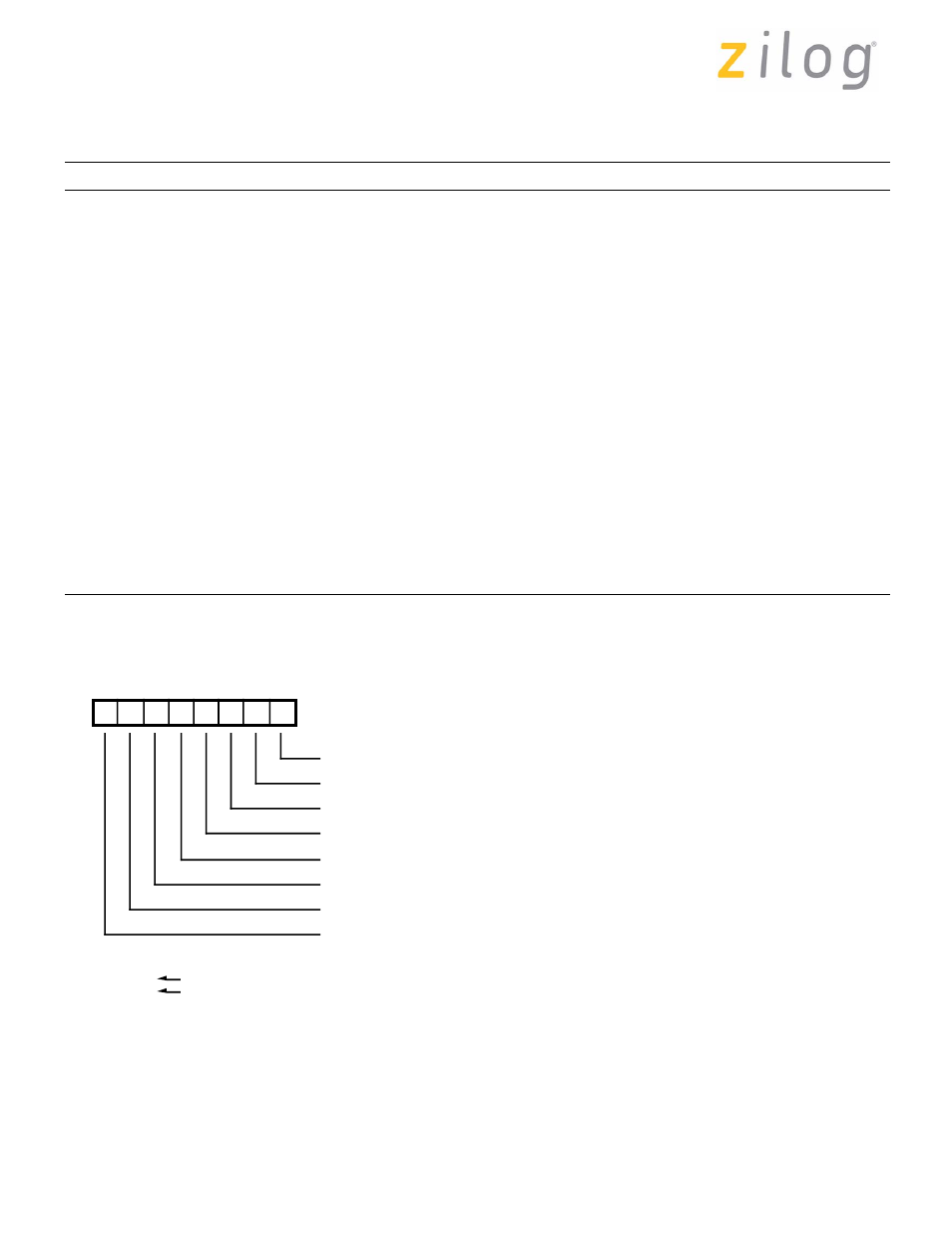
summarized by a new register, WR7' (Figure 1).
The advantages of the new features are illustrated in the
following examples.
One of the features that is offered by the ESCC, but not the
SCC, is Extended Read Enable. Write Register values
from the WR3, WR4, WR5, WR7', and WR10 can be
examined in the ESCC but not the SCC. This feature
improves system testability. It is also crucial for
SCC/ESCC differentiation and allows generic software
structures for all SCC/ESCC devices.
Flowchart 1 (Figure 2) shows a generic software structure
applicable for all SCC/ESCC initializations. Flowchart 2
(Figure 3) suggests a method for determining which type
of SCC/ESCC™ device is in the socket. This software
structure helps the development of software drivers
independent of the device type.
ESCC ENHANCEMENT
PERFORMANCE BENEFITS
1. Extended Read Enable of Write Registers
- Improves Testability
- Ability to examine SDLC status on-the-fly
2. Hardware Improvement
- Modified WRITE Timing
- Improves Interface to 80X86 CPU
- Modified DMA Request on
- Improves Interface DMA-driven system
- Transmit Deactivation Timing
3. Throughput improvement
- Deeper Transmit FIFO
- Reduces TBE Interrupt Frequency by 3/4
- Deeper Receive FIFO
- Reduces RCA Interrupt Frequency by 3/4
- FIFO Interrupt Level
- Flexibility in Adapting CPU Workload
4 SDLC End Of Frame Improvement
- Automatic RTS Deassertion after Closing Flag
- Reduces CPU and DMA Controller Overhead after
End Of Frame
- Automatic Opening Flag Transmission
- Automatic TxD Forced High in SDLC with NRZI Encoding
When Marking Idle After End Of Frame
- Allows Optimal SDLC Line Utilization
- Improvement to Allow Transmission of Back-to-Back
Frames with a Shared Flag
- Status FIFO Anti-Lock Feature in DMA-Driven System
Figure 1. WR7' Definition
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Auto Tx Flag
RR7' Prime
Auto EOM Reset
Auto RTS Deactivate
Rx FIFO Int Level
DTR/REQ Timing
Extended RD Enable
Not Used, Always 0
Tx FIFO Int Level
Addressing:
WR15 D0 '1'
WR7 'XX'
Page 263 of 316
UM011002-0808
