3 can operations -47, 1 frame types -47, Figure 4-3. can2.0a (standard) format -47 – Maxim Integrated MAXQ7666 User Manual
Page 177: Figure 4-4. can2.0b (extended) format -47, 3 can operations, 1 frame types, 1 data frame
MAXQ7665/MAXQ7666 User’s Guide
4-47
4.3 CAN Operations
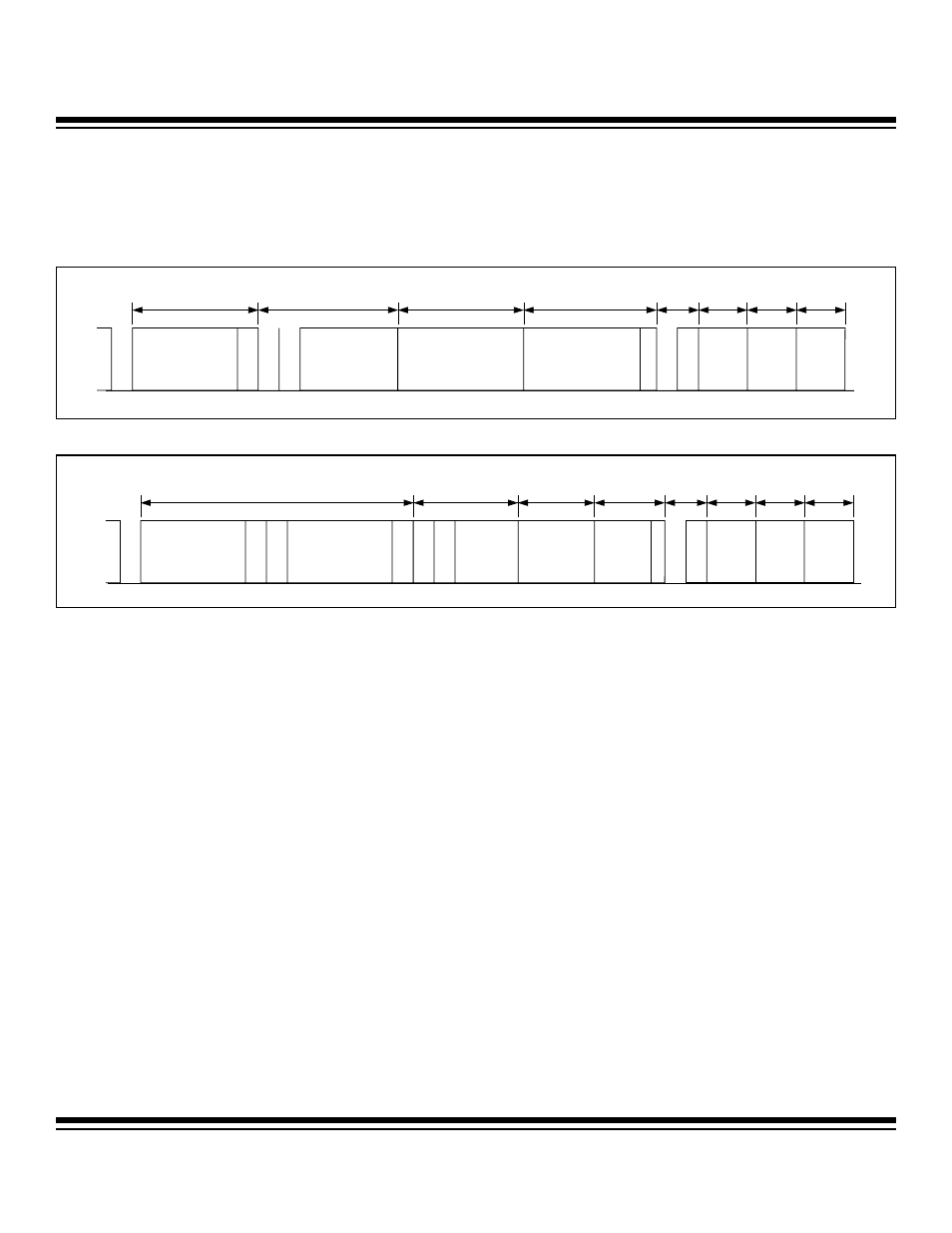
The CAN2.0B protocol specifies two different message formats: the standard 11-bit (CAN2.0A) and the extended 29-bit (CAN2.0B),
and four different frame types for CAN bus communications. The standard format, as shown in Figure 4-3, makes use of an 11-bit iden-
tifier. The extended format, as shown in Figure 4-4, makes use of a 29-bit identifier.
4.3.1 Frame Types
The four different frame types for CAN bus communications are data frame, remote frame, error frame, and overload frame.
4.3.1.1 Data Frame
The data frame is formulated to carry data from a transmitter to a receiver. Figure 4-3 and Figure 4-4 show examples of data frames in
the standard and extended formats. The data frame is composed of seven fields that include the start of frame, arbitration field, con-
trol field, data field, CRC field, acknowledge field, and an end of frame. A description of these fields follows.
4.3.1.1.1 Start of Frame (SOF)
(Standard and extended format.) The start of frame (SOF) is a dominant bit that signals the start of a data or remote frame. The dom-
inant bit forces a hard synchronization, initiating the CAN controller receive mode.
4.3.1.1.2 Arbitration Field
(Standard and extended format.) The arbitration field contains the identifier of the message and a dominant remote request (RTR) bit.
The identifier is composed of one field in the standard 11-bit format or two fields in the extended 29-bit format. Two additional bits, the
substitution remote request (SRR) bit and the identifier extension (IDE) bit, separate the two fields in the extended format.
• Remote Request (RTR) Bit: (Standard and extended format.) The remote request (RTR) bit is a dominant bit in data frames
and a recessive bit in remote frames.
• Substitution Remote Request (SRR) Bit: (Extended format.) The substitution remote request (SRR) bit is a recessive bit and
is substituted for the RTR bit when using the extended format.
• Identifier Extension (IDE) Bit: (Extended format.) The identifier extension (IDE) bit is a dominant bit in the standard format and
a recessive bit in the extended format. The IDE bit is located in the control field in the standard format and is located in the arbi-
tration field in the extended format.
Figure 4-3. CAN2.0A (Standard) Format
7
BITS
3
BITS
S
O
F
R
T
R
I
D
E
r
o
11-BIT IDENTIFIER
0 TO 8 BYTES
15-BIT CRC
DLC
ARBITRATION FIELD
CONTROL FIELD
DATA FIELD
CRC FIELD
ACK
FIELD
INTER
BUS
IDLE
END OF
FRAME
Figure 4-4. CAN2.0B (Extended) Format
7
BITS
3
BITS
S
O
F
R
T
R
S
R
R
I
D
E
r
1
r
0
11-BIT IDENTIFIER
18-BIT IDENTIFIER
0 TO 8 BYTES
15-BIT CRC
DLC
ARBITRATION FIELD
CONTROL FIELD
DATA FIELD
CRC FIELD
ACK
FIELD
INTER
BUS
IDLE
END OF
FRAME
Maxim Integrated
