Shielding, Tc common mode – Measurement Computing DBK Part 2 User Manual
Page 184
pg. 10, DBK90
907492
DBK Option Cards and Modules
Shielding
Using shielded TC wire with the shield connected to analog common [DBK90’s ACOM jack] will result in further
noise reduction. Using a shielded ribbon cable to connect the DBK90’s male P1 connector to the P1 connector of
the primary data acquisition device will also help minimize noise. CA-143-7 and CA-143-18 are female-to-female,
DB37 shielded ribbon cables of 7-inch and 18-inch lengths, respectively.
If a thermocouple shield is connected to the DBK90 module, leave the shield unconnected at the
other end of the thermocouple. Connecting the shield to common at both ends will result in a
ground loop.
TC Common Mode
The maximum common-mode voltage for the DBK90 is ±10 volts. Common-mode voltage is the DC or AC voltage
signal that is applied equally to both sides of a differential input.
If a thermocouple is connected directly to a component in the vehicle at a potential that is over the maximum
common-mode voltage, then very noisy or incorrect readings will be seen. Thermocouple connections that are
made directly to the alternator or engine block may also result in high noise. Two methods of reducing noise are:
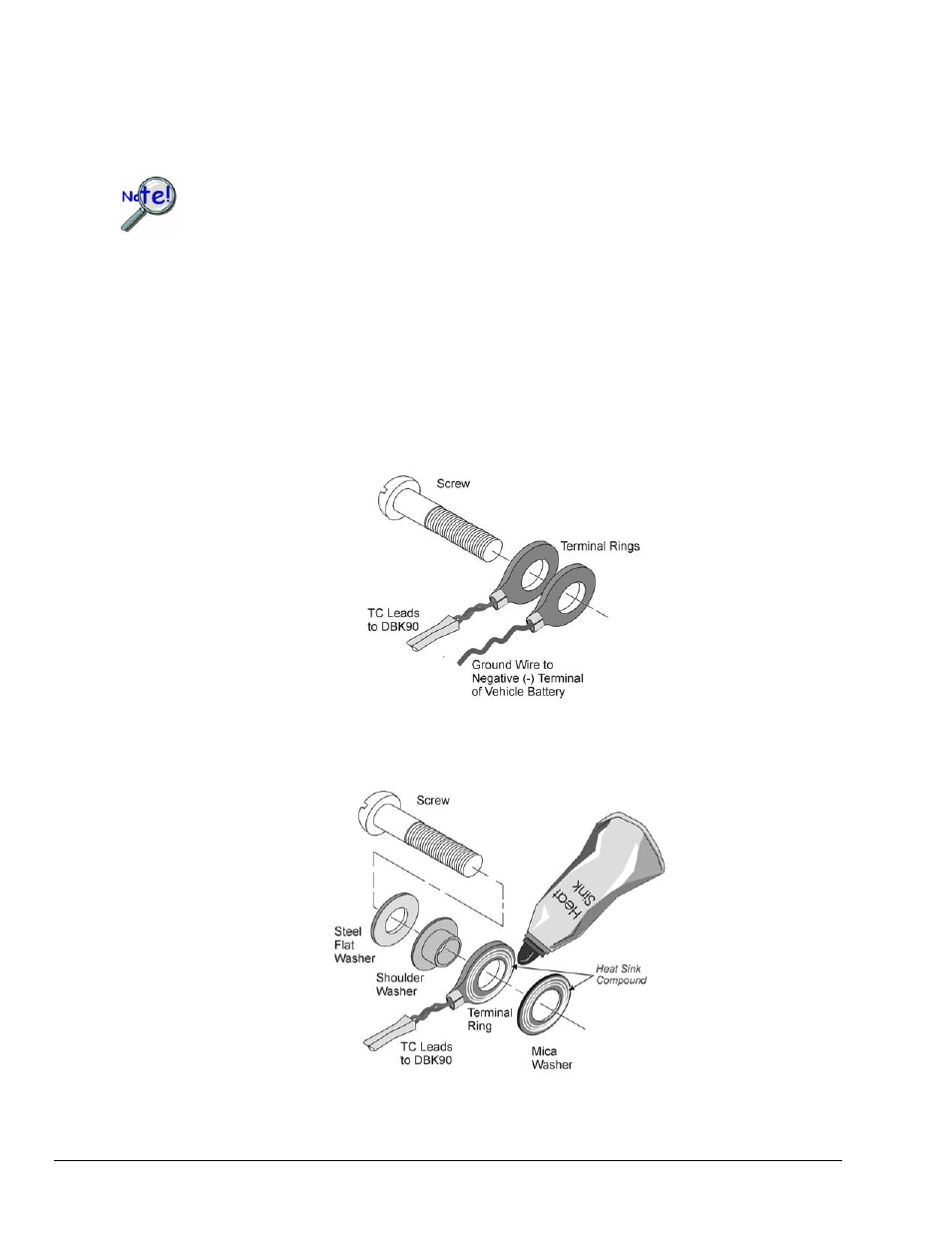
(a) Run a ground line from the bolt, as indicated in the first figure.
(b) Isolate the thermocouple leads with a set of washers, one of which is mica.
This is indicated in the second figure.
Running a Ground Wire to the Battery’s Negative Terminal
Using a Washer Set and Heat Sink to Isolate the Thermocouple
A thin layer of heat-sink
compound on the indicated
surfaces will improve
thermal conductivity.
The length of the shoulder
washer’s hub must not exceed
the combined thickness of the
terminal ring and mica washer.
