Appendix e: alarm and status codes, Alarm code definitions al command, F” data register – Applied Motion RS-232 User Manual
Page 253
253
920-0002 Rev. I
2/2013
Host Command Reference
Appendix E: Alarm and Status Codes
One of a drive’s diagnostic tools is its ability to send alarm and status codes back to a host. The AL (Alarm
code) and SC (Status Code) commands can be used by a host to query a drive at any time. If a drive faults or
sets an alarm, the AL command allows the host to find out what alarm, or alarms, has been set. Similarly, the SC
command allows a host to find out what the status code of a drive is at any time during drive operation. A status
code provides information as to whether the drive is running, in position, disabled, homing, and other conditions.
Both alarm and status codes can be very useful when initially setting up and integrating a servo system into your
machine.
The Alarm and Status codes are hexadecimal equivalents of 16 bit binary “words”. Each bit in each binary
word is assigned a meaning, and therefore a code word can actually show information about more than one alarm
or status condition.
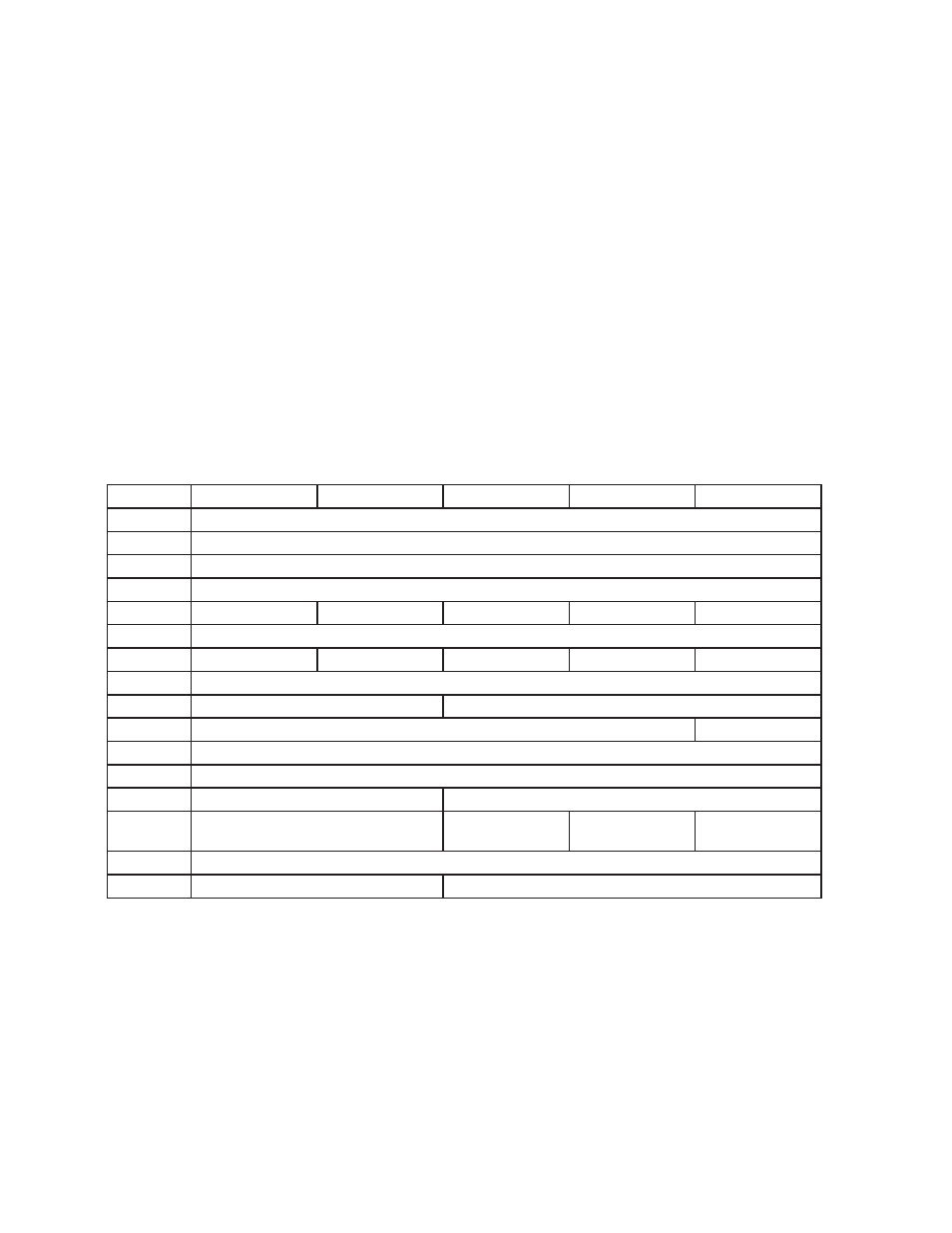
Alarm Code Definitions
AL command
When a host sends the AL command, the response from the drive will be the Hexadecimal equivalent of a
16-bit word. This hexadecimal value is considered the Alarm Code, and the hexadecimal value for each of the bits
in the Alarm Code is given below.
Hex Value
BLu
SV
STAC6
ST
STM
0001
Position Limit
0002
CCW Limit
0004
CW Limit
0008
Over Temp
0010
Excess Regen*
Internal Voltage
Excess Regen
Internal Voltage
Internal Voltage
0020
Over Voltage
0040
Under Voltage*
Under Voltage
Under Voltage
Under Voltage
Under Voltage
0080
Over Current
0100
Bad Hall Sensor
Open Motor Winding
0200
Bad Encoder
(not used)
0400
Comm Error
0800
Bad Flash
1000
Wizard Failed
No Move
2000
Current Foldback
Motor Resistance
Out of Range
(not used)
(not used)
4000
Blank Q Segment
8000
No Move
(not used)
* BLuAC drives only
NOTE: Items in
bold italic represent Drive Faults, which automatically disable the motor. Use the OF
command in a Q Program to branch on a Drive Fault.
Example: The drive has hit the CW limit (0004), there is an under voltage condition (0040), and an encoder
wiring connection has been lost resulting in an encoder fault (0200). The resulting Alarm Code is 0244, and when
the host sends the “AL” command the drive will respond with “AL=244”.
“f” data register
Another way to retrieve the Alarm Code is to use the “f” data register. If the host sends the RLf command,
the response from the drive will be the decimal equivalent of the 16-bit Alarm Code word. The diagram below
