Comparison protocols 76. protocol key, Appendix a. comparison of protocols, Protocol comparison table – IBM SC30-3865-04 User Manual
Page 463: Key to protocols
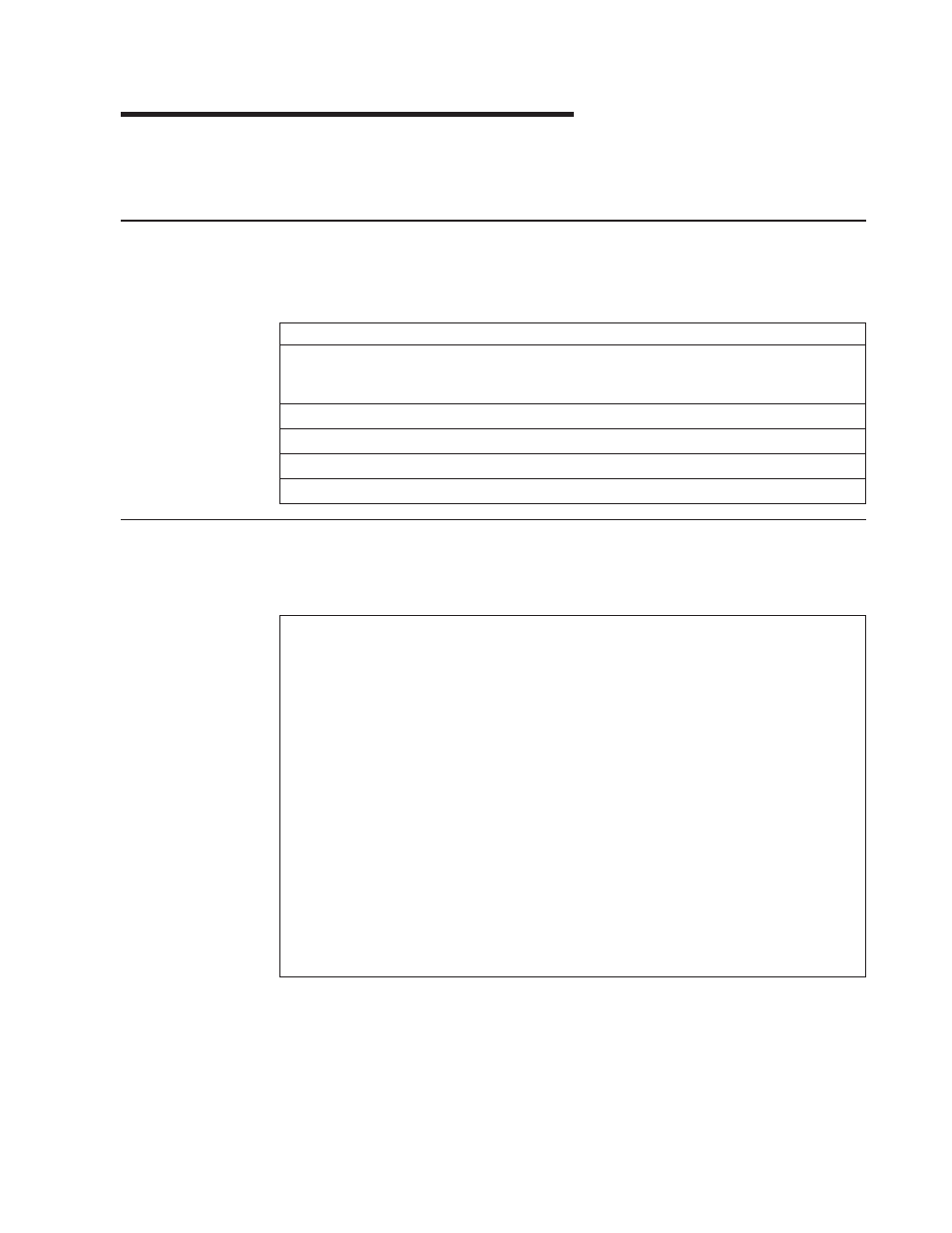
Appendix A. Comparison of Protocols
This appendix compares some of the well-known protocols that your router
supports. It is provided as a memory aid and is not meant as a reference.
Protocol Comparison Table
The following table compares the protocols.
Table 75. Comparison Protocols
ISO OSI Model
TCP/IP
IPX
Other
7 Application 6
Presentation 5
Session
Telnet, FTP, TFTP,
SGMP
4 Transport
TCP, UDP
PXP, SPX
3 Network
IP, RIP, BGP, ICMP
RIP, SAP
2 Data Link
Local Net
HDLC
1 Physical
Key to Protocols
Table 76 is a key to the protocols.
Table 76. Protocol Key
Protocol
Description
BGP
Border Gateway Protocol. An IP external routing protocol.
FTP, TFTP
File Transfer Protocol; Trivial File Transfer Protocol.
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol. Used to send network level error
and control messages between routers and hosts.
IP
Internet protocol. IP is a widely used standard transport protocol. IP is
the 2210 routers’ basic protocol. IP leaves some error-checking to
higher-level (end-to-end) protocols.
IPX
Internet Packet Exchange Protocol.
RIP
Routing Information Protocol (Routing protocols are used to determine
network topology and data paths). RIP is the most common IP routing
protocol.
SGMP
Simple Gateway Monitoring Protocol. Used to obtain statistics in
machine-readable form from 2210 routers.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol. Used to obtain statistics in
machine-readable form from 2210 routers.
TCP
Transport Control Protocol. An end-to-end (host-to-host) protocol that is
often used with IP. Useful for sending streams of data. Uses checksums,
acknowledgments, and timeouts to ensure the correct delivery and
sequence of data.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1994, 1998
433
