Zilog Z80230 User Manual
Page 114
SCC/ESCC
User Manual
UM010903-0515
Data Communication Modes
107
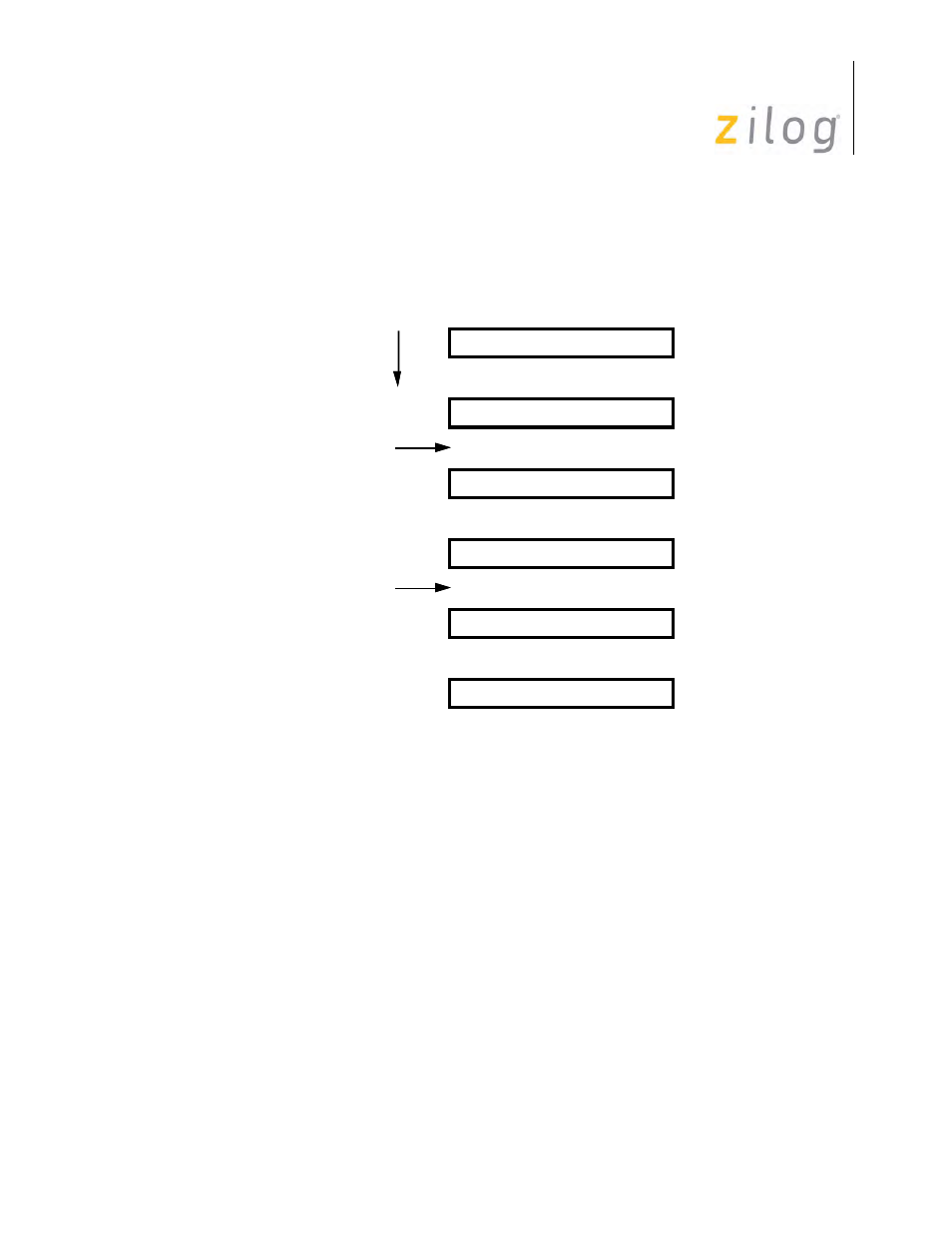
The character length can be changed at any time before the new number of bits has been assem-
bled by the receiver, but, care should be exercised as unexpected results may occur. A representa-
tive example would be switching from five bits to eight bits and back to five bits (
).
Changing Character Length
Either of two CRC polynomials are used in Synchronous modes, selected by bit D2 in WR5. If this
bit is set to 1, the CRC-16 polynomial is used, if this bit is set to 0, the CRCCCITT polynomial is
used. This bit controls the polynomial selection for both the receiver and transmitter.
The initial state of the generator and checker is controlled by bit D7 of WR10. When this bit is set
to 1, both the generator and checker have initial values of all ones; if this bit is set to 0, the initial
values are all 0. The SCC presets the checker whenever the receiver is in Hunt mode so a CRC
reset command is not necessary. However, there is a Reset CRC Checker command in WR0. This
command is encoded in bits D7 and D6 of WR0. If the CRC is used, the CRC checker is enabled
by setting bit D0 of WR3 to 1.
Sync characters can be stripped from the data stream any time before the first non-sync character
is received. If the sync strip feature is not being used, the CRC is not enabled until after the first
data character has been transferred to the receive data FIFO. As previously mentioned, 8-bit sync
characters stripped from the data stream are automatically excluded from CRC calculation.
6 5 4 3 2 1
Receive Data Buffer
7
8
11 10 9 8 7 6
12
13
19 18 17 16 15 14
20
21
27 26 25 24 23 22
28
29
32 31 30 29 28 27
33
34
37 36 35 34 33 32
38
39
Time
Change from Five to Eight
Change from Eight to Five
5 Bits
5 Bits
5 Bits
8 Bits
8 Bits
