Fig. 8.22, Cst and ist of mstp (1) – Siemens S223 User Manual
Page 210
UMN:CLI User Manual
SURPASS hiD 6615 S223/S323 R1.5
210 A50010-Y3-C150-2-7619
Operation
Here explains how STP/MSTP differently operates on the LAN. Suppose to configure 100
of VLAN from Switch A to B, C. In case of STP, there’s only a STP on all of VLAN and it
does not provide multiple instances.
While existing STP is a protocol to prevent Loop in a LAN domain establishes STP per
VLAN in order to realize routing suitable to VLAN environment.
It does not need to calculate all STP for several VLAN so that traffic overload could be
reduced. By reducing unnecessary overload and providing multiple transmission route for
data forwarding, it realizes load balancing and provides many VLAN through Instances.
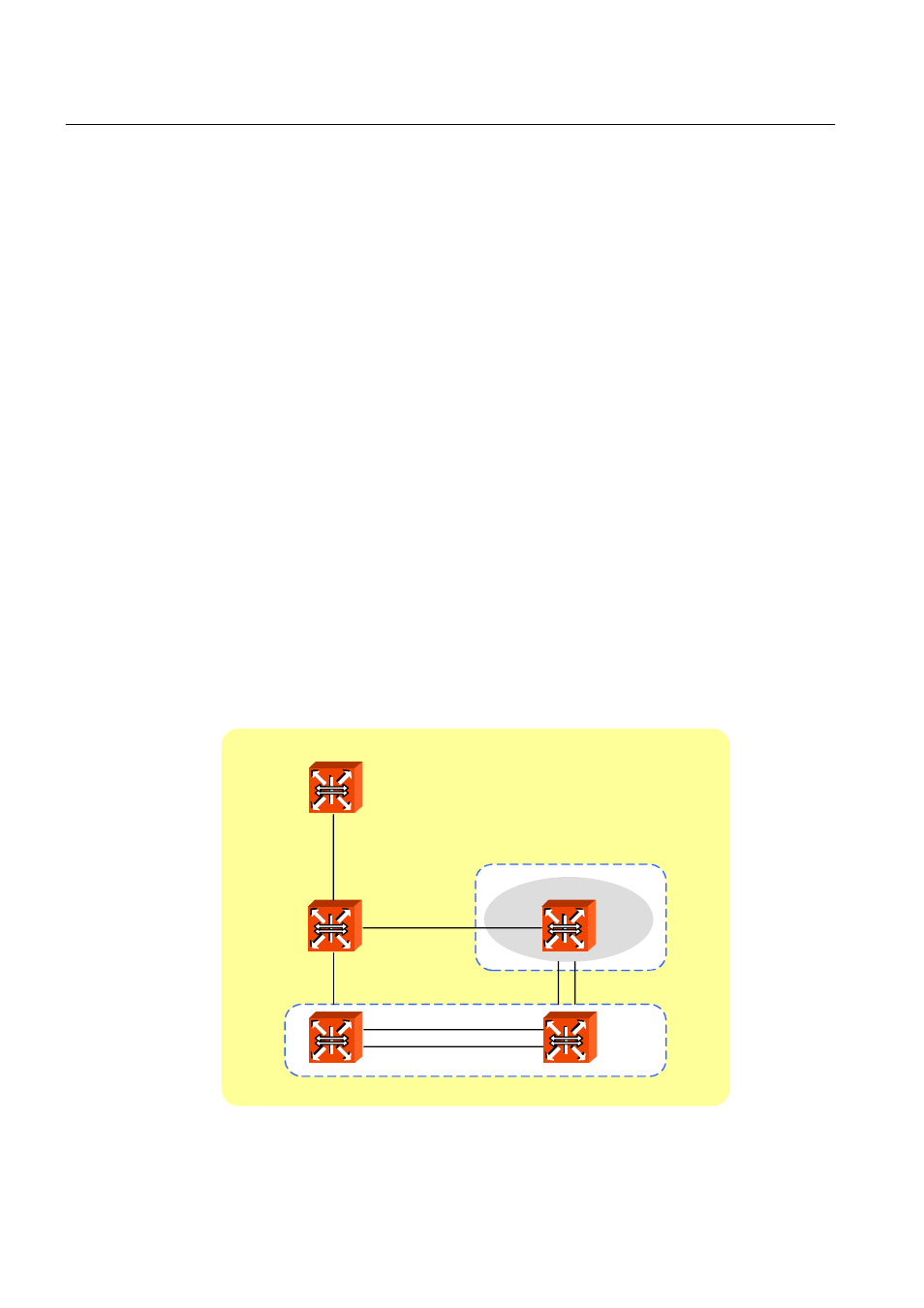
MSTP
In MSTP, VLAN is classified to groups with same Configuration ID. Configuration ID is
composed of Revision name, Region name and VLAN/Instance mapping. Therefore, to
have same configuration ID, all of these tree conditions should be the same. VLAN classi-
fied with same configuration ID is called MST region. In a region, there’s only a STP so
that it is possible to reduce the number of STP comparing to PVSTP. There’s no limitation
for region in a network environment but it is possible to generate Instances up to 64.
Therefore instances can be generated from 1 to 64. Spanning-tree which operates in
each region is IST (Internal Spanning-Tree). CST is applied by connecting each span-
ning-tree of region. Instance 0 means that there is not any Instance generated from
grouping VLAN, that is, it does not operate as MSTP. Therefore Instance 0 exists on all
the ports of the equipment. After starting MSTP, all the switches in CST exchanges BPDU
and CST Root is decided by comparing their BPDU. Here, the switches that don’t operate
with MSTP have instance 0 so that they can also join BPUD exchanges. The operation of
deciding CST Root is CIST (Common & Internal Spanning-Tree).
Legacy 802.1d
Legacy 802.1d
CST Root & IST Root
Switch A
Switch B
Switch D
Switch C
Switch E
Instance 2
Instance 3
Instance 2
Instance 1
Region B (IST)
IST Root
CST
Region A (IST)
Fig. 8.22
CST and IST of MSTP (1)
