3 spanning-tree protocol (stp), Spanning-tree protocol (stp), Fig. 8.8 – Siemens S223 User Manual
Page 200: Example of loop, Fig. 8.9, Principle of spanning tree protocol
UMN:CLI User Manual
SURPASS hiD 6615 S223/S323 R1.5
200 A50010-Y3-C150-2-7619
8.3
Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP)
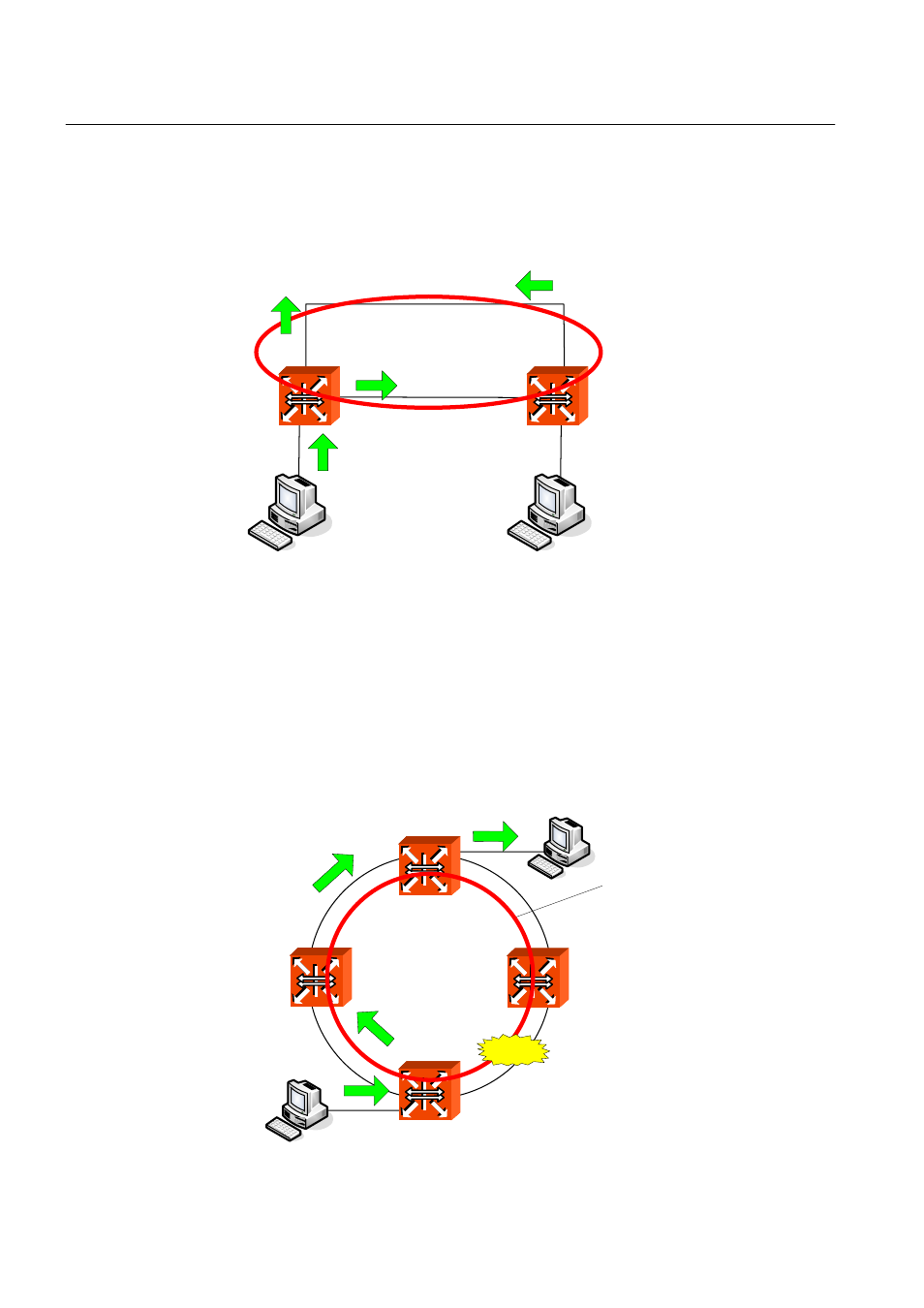
LAN, which is composed of double-path like token ring, has the advantage that it is pos-
sible to access in case of disconnection with one path. However, there is another problem
named Loop when you always use the double-path.
Switch A
Switch B
PC-A
PC-B
Fig. 8.8
Example of Loop
Loop is when there are more than one path between switches (SWITCH A, B), PC A
sends packet through broadcast or multicast and then the packet keeps rotating. It
causes superfluous data-transmission and network fault.
STP (Spanning-Tree Protocol) is the function to prevent Loop in LAN with more than two
paths and to utilize the double-path efficiently. It specify in IEEE 802.1d. If STP is config-
ured, there is no Loop since it chooses more effective path of them and closes the other
path. In other words, when SWITCH C in the below figure sends packet to SWITCH B,
path 1 is chosen and path 2 is blocked.
Switch B
Switch C
Switch D
Switch A
Path 1
Path 2
VLAN 1
PC-A
PC-B
Blocking
Fig. 8.9
Principle of Spanning Tree Protocol
