Camming, Camming introduction, Camstate – Yaskawa MotionWorks IEC User Manual
Page 361
PLCopenPlus Function Blocks for Motion Control 2013-04-13
353
Camming
Camming Introduction
At its core, an electronic cam is simply a list of master and slave positions
that describe the synchronized relationship of two axes. For a given
master position, the slave is commanded at the corresponding position in
the table. Surrounding this core are many functional elements, including
methods to load cam data, configuration for the type of data, engage &
disengage methods, on-the-fly adjustments, and the possibility to switch
cam tables on the fly.
CamState
Similar to the Motion State Diagram for general motion, the camming
mode has a CamState, parameter 1540. This value indicates the slave’s
current mode of operation, and is very useful for debugging and program
logic flow. Possible values are:
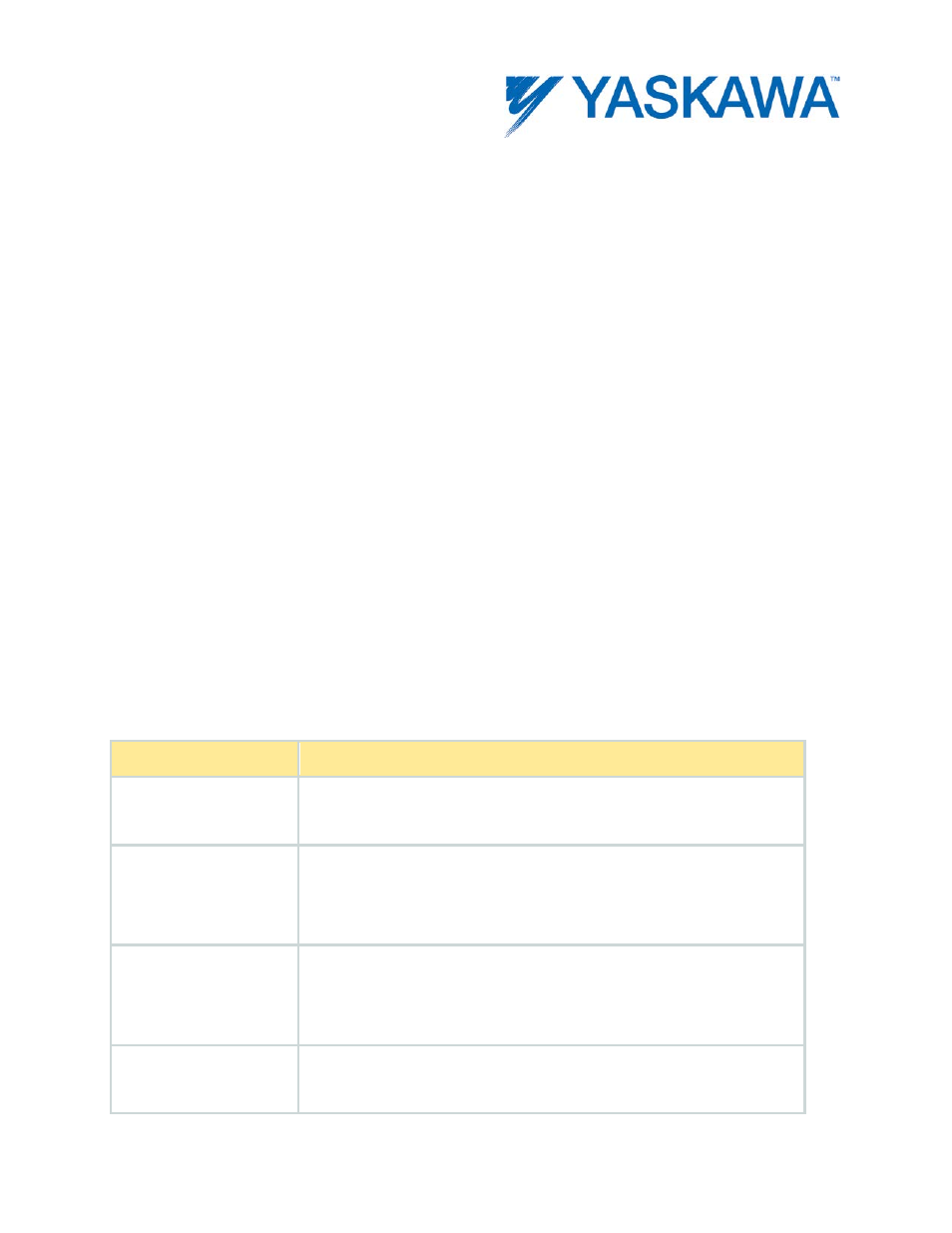
CamState
Meaning
0 = Not
Engaged
Axis is not involved in a cam operation
1 = Waiting to
Engage
Y_CamIn has been executed, but the slave is not
yet following the master because it has not
passed into the engage window.
2 = Engaging
The very short time the master is within the
window and the slave is moving to the very first
commanded cam position.
3 = Engaged
The slave's commanded position is dictated by the
cam function as the master moves through the
