33 subroutines, Subprogram call: l"xx" v1 – HEIDENHAIN SW 548328-05 DIN Programming User Manual
Page 404
404
DIN programming
4.33 Subr
outines
4.33 Subroutines
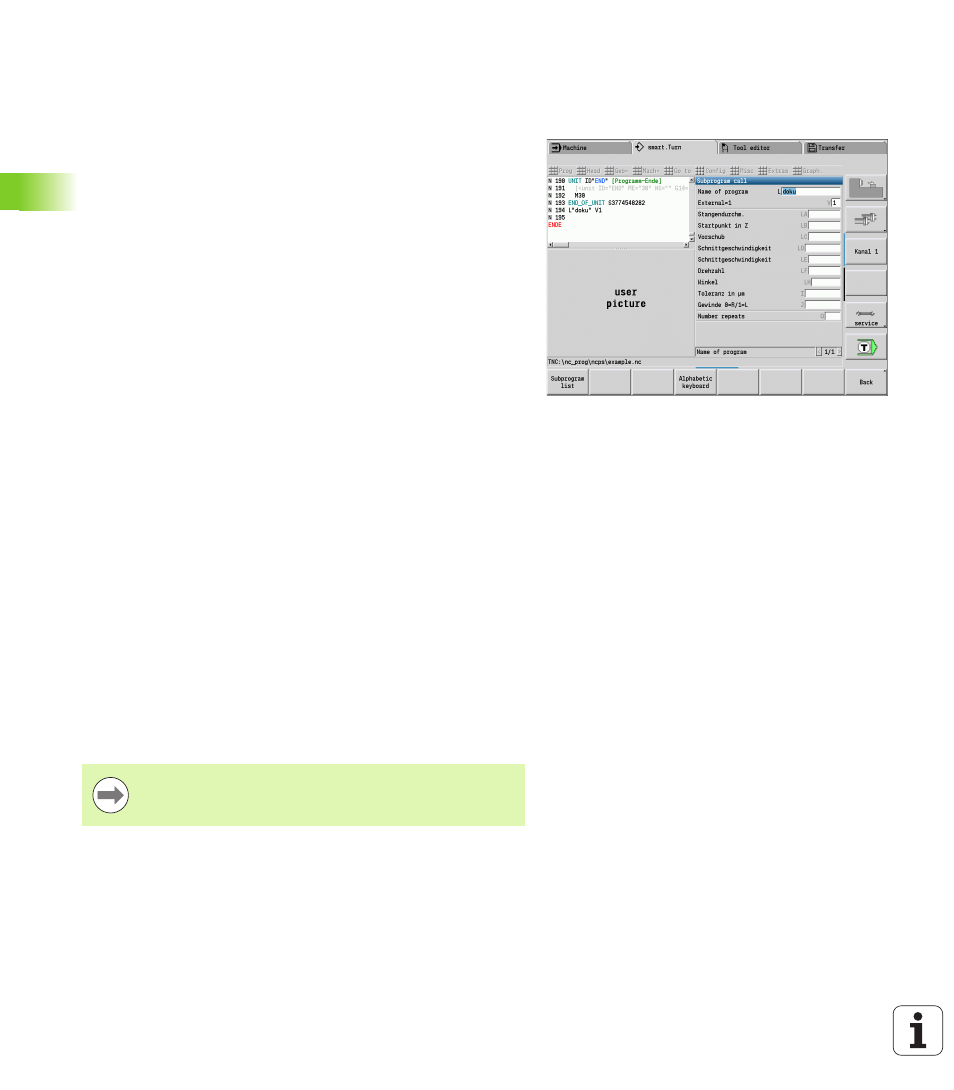
Subprogram call: L"xx" V1
The subprogram contains the following elements:
L: Identifying letter for subprogram call
"xx": Name of the subprogram—file name for external subprograms
(max. 16 letters or numbers)
V1: Identification code for external subprograms—omitted for local
subprograms
Note on using subprograms:
External subprograms are defined in a separate file. They can be
called from any main program or other subprogram.
Local subprograms are in the main program file. They can be called
only from the main program.
Subprograms can be nested up to 6 times. Nesting means that
another subprogram is called from within a subprogram.
Recursion should be avoided.
You can add up to 29 transfer values to a subprogram.
Designations: LA to LF, LH, I, J, K, O, P, R, S, U, W, X, Y, Z, BS,
BE, WS, AC, WC, RC, IC, KC and JC
The identification code within the subprogram is: #__.., followed
by the parameter designation in lowercase letters (for example:
#__la).
Use the transfer values when programming with variables within
the subprogram.
String variables: ID and AT
The variables #l1 – #l30 are available in every subprogram as local
variables.
To transfer a variable to the main program, program the variable
after the fixed word RETURN. In the main program, the information
is available in #i99.
If a subprogram is to be executed repeatedly, define in the "number
of repeats" Q parameter the number of times the subprogram is to
be repeated.
A subprogram ends with RETURN.
The parameter LN is reserved for the transfer of block
numbers. This parameter may receive a new value when
the NC program is renumbered.
