Optional, Optional paps position number – IAI America XSEL-KX User Manual
Page 230
214
Part 4 Commands
PAPS (Set palletizing positions)
Extension condition
(LD, A, O, AB, OB)
Input condition
(I/O, flag)
Command, declaration
Output
(Output, flag)
Command,
declaration
Operand 1
Operand 2
Optional
Optional
PAPS
Position
number
(Palletizing
position
setting type)
CP
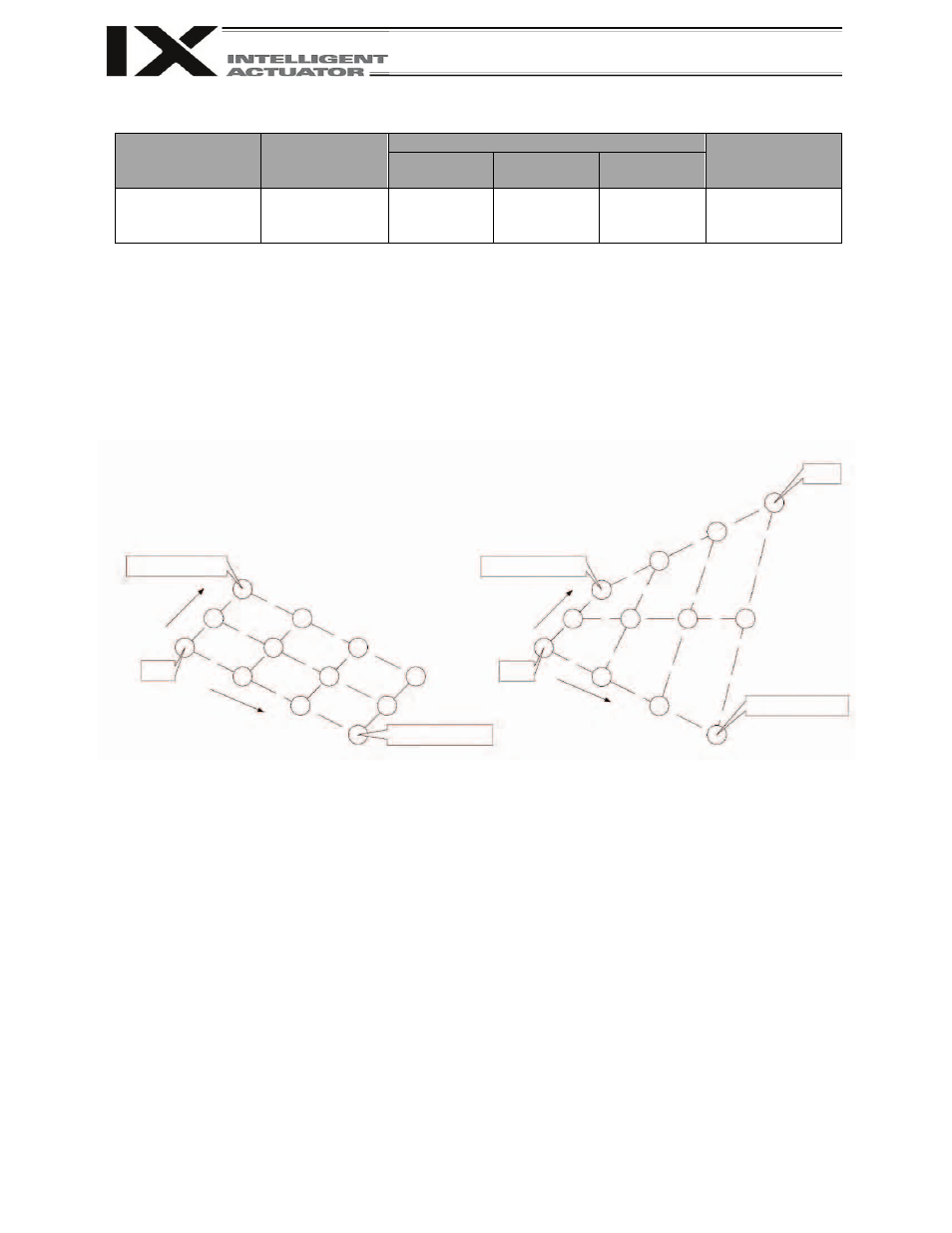
Set palletizing positions based on 3-point teaching.
In operand 1, specify the first of the position numbers in which the coordinate values for start point, end point
in PX-axis direction and end point in PY-axis direction (hereinafter referred to as “Point Data”), which are
required when setting palletizing positions based on 3-point teaching, are stored.
In main application version 0.40 or later, palletizing positions can be set based on 4-point teaching, meaning
that the pallet surface can be set to any quadrangle other than square, rectangle or parallelogram.
If No. n is set as the position number in operand 1, point n represents the start point, point n+1 represents the
end point in PX-axis direction, and point n+2 represents the end point in PY-axis direction (in the case of 4-
point teaching, there is also point n+3 representing the end point). Fig. 1 shows the arrangement of palletizing
positions.
(a) 3-point teaching
(b) 4-point teaching
Fig. 1 Arrangement of Palletizing Positions
In main application version 0.40 or later specify the palletizing position setting type in operand 2.
[Palletizing position setting type]
0, or nothing is specified = 3-point teaching
Palletizing positions are arranged on a quadrangular pallet surface determined by the three points of
start point, end point in PX-axis direction and end point in PY-axis direction, as shown in Fig. 1-(a).
1 = 4-point teaching (planar type)
Palletizing positions are arranged on a planar quadrangular pallet surface determined by the four points
of start point, end point in PX-axis direction, end point in PY-axis direction, and point achieved by moving
the end point in parallel in the direction of the palletizing Z-axis (hereinafter referred to as “PZ-axis”) and
placing it on the plane determined by the aforementioned three points other than the end point, as shown
in Fig. 2-(a). Take note that if the three points other than the end point meet any of the conditions in
Table 1, the moving direction of the end point becomes different.
2 = 4-point teaching (non-planar type)
Palletizing positions are arranged on a quadrangular pallet surface determined by the four points of start
point, end point in PX-axis direction, end point in PY-axis direction, and end point, as shown in Fig. 1-(b).
Take note that whether the shape is planar or not varies depending on the point data of the end point.
End
point
End point in PX-axis
direction
Preferential axis
(PX-axis)
Start
point
PY-axis
End point in PY-axis
direction
End point in PX-axis
direction
Preferential axis
(PX-axis)
Start
point
PY-axis
End point in PY-axis
direction
