Measurement Computing TempScan/1100 User Manual
Page 264
B-6 IEEE 488, Serial, & ASCII
889597
TempScan/MultiScan,
Appendix
B
…… A-
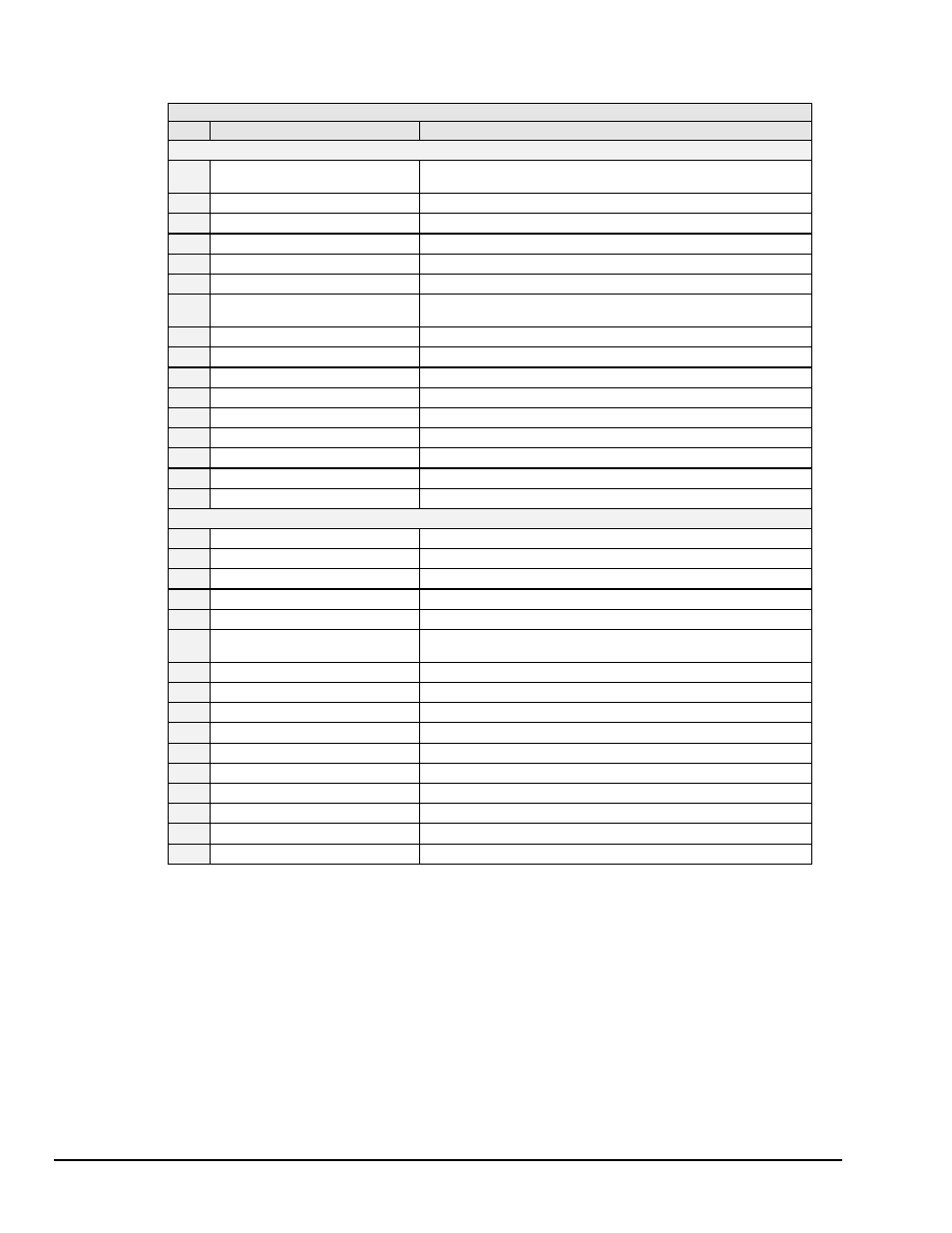
Decimal Values 00 to 31 – ACG & UCG Descriptions
ASCII Control Codes (00 to 31)
Dec
Name
Description
Addressed Command Group (
ACG
)
00
Null (
NUL
)
Space filler character. Used in output timing for some device
drivers.
01
Start of Header (
SOH
)
Marks beginning of message header.
02
Start of Text (
STX
)
Marks beginning of data block (text).
03
End of Text (
ETX
)
Marks end of data block (text).
04
End of Transmission (
EOT
)
Marks end of transmission session.
05
Inquiry (
ENQ
)
Request for identification or information.
06
Acknowledgment (
ACK
)
“Yes” answer to questions or “ready for next transmission.” Used in
asynchronous protocols for timing.
07
Bell (
BEL
)
Rings bell or audible alarm on terminal.
08
Backspace (
BS
)
Moves cursor position back one character.
09
Horizontal Tab (
HT
)
Moves cursor position to next tab stop on line.
10
Line Feed (
LF
)
Moves cursor position down one line.
11
Vertical Tab (
VT
)
Moves cursor position down to next “tab line.”
12
Form Feed (
FF
)
Moves cursor position to top of next page.
13
Carriage Return (
CR
)
Moves cursor to left margin.
14
Shift Out (
SO
)
Next characters do not follow ASCII definitions.
15
Shift In (
SI
)
Next characters revert to ASCII meaning.
Universal Command Group (
UCG
)
16
Data Link Escape (
DLE
)
Used to control transmissions using “escape sequences.”
17
Device Control 1 (
DC1
)
Not defined. Normally used for ON controls.
18
Device Control 2 (
DC2
) Usually
user-defined.
19
Device Control 3 (
DC3
)
Not defined. Normally used for OFF controls.
20
Device Control 4 (
DC4
) Usually
user-defined.
21
Negative Acknowledgment (
NAK
)
“No” answer to questions or “errors found, re-transmit.” Used in
asynchronous protocols for timing.
22
Synchronous Idle (
SYN
)
Sent by asynchronous devices when idle to insure sync.
23
End of Transmission Block (
ETB
)
Marks block boundaries in transmission.
24
Cancel (
CAN
)
Indicates previous transmission should be disregarded.
25
End of Medium (
EM
)
Marks end of physical media, as in paper tape.
26
Substitute (
SUB
)
Used to replace a character known to be wrong.
27
Escape (
ESC
)
Marks beginning of an Escape control sequence.
28
File Separator (
FS
)
Marker for major portion of transmission.
29
Group Separator (
GS
)
Marker for submajor portion of transmission.
30
Record Separator (
RS
)
Marker for minor portion of transmission.
31
Unit Separator (
US
)
Marker for most minor portion of transmission.
Notes:
ASCII control codes are sometimes used to “formalize” a communications session between
communication devices.
DC1, DC2, DC3, DC4, FS, GS, RS,
and
US
all have user-defined meanings, and may
vary in use between sessions or devices.
DC4
is often used as a general “stop transmission character.”
Codes used to control cursor position may be used to control print devices, and move the
print head accordingly. However, not all devices support the full set of positioning codes.
