Proportional and integral control (pi), Proportional and integral control (pi) 113, Figure 5.2—proportional control 113 – Watlow Series D8 User Manual
Page 131: Figure 5.3—proportional and integral control 113
Series D8 User’s Guide
Chapter 5: Tuning and Control
Doc. 0600-3120-2000
Watlow Anafaze
113
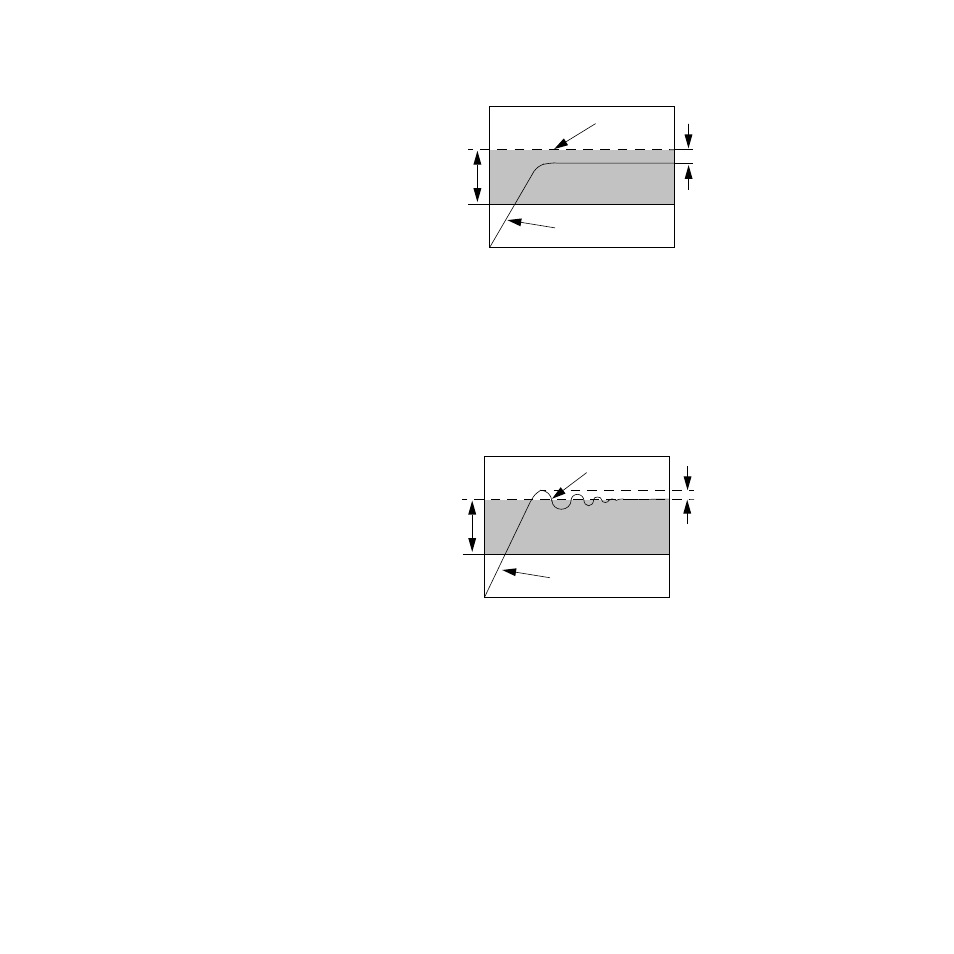
Figure 5.2
Proportional Control
Proportional and Integral Control (PI)
With proportional and integral control, the integral term cor-
rects for offset by repeating the proportional band’s error cor-
rection until there is no error. For example, if a process tends
to settle about 5° F below the set point, appropriate integral
control brings it to the desired setting by gradually increasing
the output until there is no deviation.
Figure 5.3
Proportional and Integral Control
Proportional and integral action working together can bring a
process to set point and stabilize it. However, with some pro-
cesses the user may be faced with choosing between parame-
ters that make the process very slow to reach set point and
parameters that make the controller respond quickly, but in-
troduce some transient oscillations when the set point or load
changes. The extent to which these oscillations cause the pro-
cess variable to exceed the set point is called overshoot.
Offset
Proportional
Set Point
Process Variable
Band
Proportional
Set Point
Process Variable
Band
Overshoot
