On/off control, Proportional control (p), On/off control 112 – Watlow Series D8 User Manual
Page 130: Proportional control (p) 112, Figure 5.1—on/off control 112
Chapter 5: Tuning and Control
Series D8 User’s Guide
112
Watlow Anafaze
Doc. 0600-3120-2000
On/Off Control
On/off control is the simplest way to control a process. The
controller turns an output on or off when the process variable
reaches limits around the desired set point. This limit is adjust-
able.
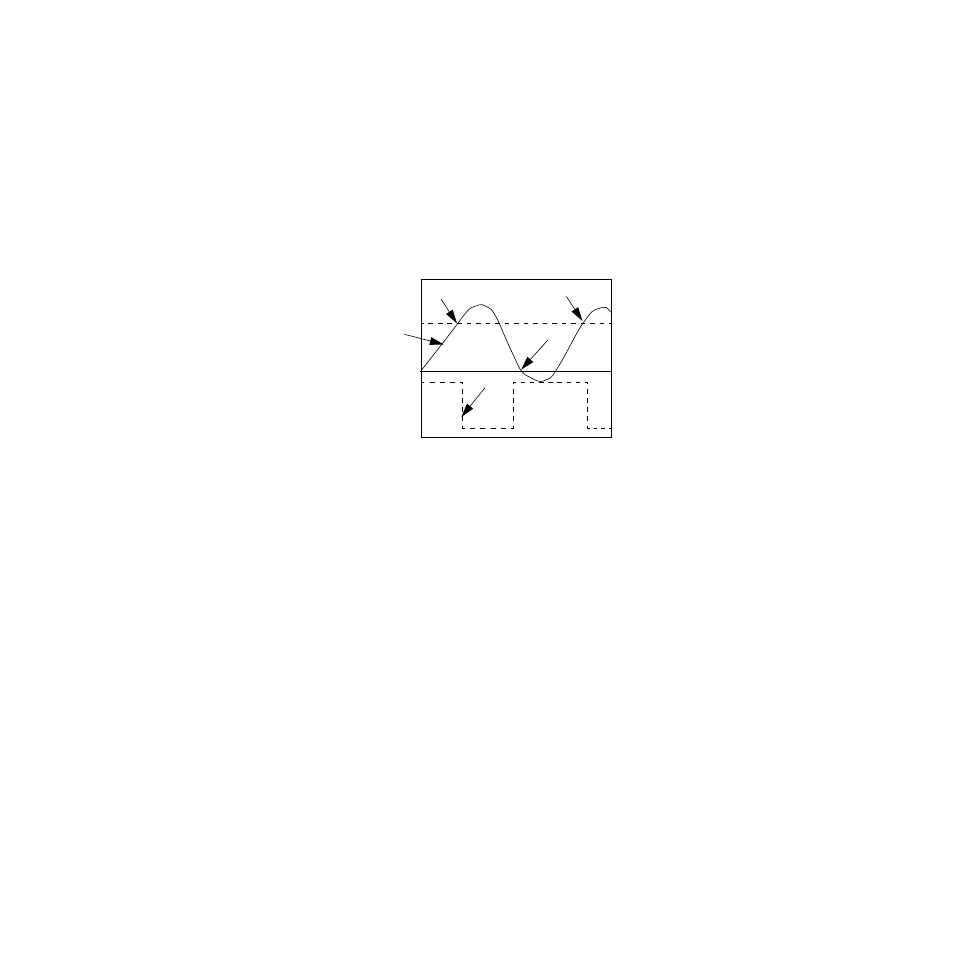
For example, if the set point is 1000° F and the control hyster-
esis is 20° F, the heat output switches on when the process
variable drops below 980° F and off when the process rises
above 1000° F. A process using on/off control cycles around
the set point. Figure 5.1 illustrates this example.
Figure 5.1
On/Off Control
Proportional Control (P)
Proportional control eliminates cycling by increasing or de-
creasing the output proportionally with the process variable’s
deviation from the set point.
The magnitude of proportional response is defined by the pro-
portional band. Outside this band, the output is either 100 per-
cent or 0 percent. Within the proportional band the output
power is proportional to the process variable’s deviation from
the set point.
For example, if the set point is 1000° F and the proportional
band is 20° F, the output power is as follows:
•
0 percent when the process variable is 1000° F or above
•
50 percent when the process variable is 990° F
•
75 percent when the process variable is 985° F
•
100 percent when the process variable is 980° F or below
However, a process that uses only proportional control settles
at a point above or below the set point; it never reaches the set
point. This behavior is known as offset or droop. When using
proportional control, configure the manual reset parameter for
the power level required to maintain set point.
Heat Off
Heat On
Set Point
Set Point - Hysteresis
Process
On
Heat Off
Output
Off
Variable
980
°
F
1000
°
F
