5 link aggregation – Interlogix NS3550-8T-2S User Manual User Manual
Page 91
91
4.5 Link Aggregation
Port Aggregation optimizes port usage by linking a group of ports together to form a single Link Aggregated Groups (LAGs). Port
Aggregation multiplies the bandwidth between the devices, increases port flexibility, and provides link redundancy.
Each LAG is composed of ports of the same speed, set to full-duplex operations. Ports in a LAG, can be of different media types
(UTP/Fiber, or different fiber types), provided they operate at the same speed.
Aggregated Links can be assigned manually (Port Trunk) or automatically by enabling Link Aggregation Control Protocol
(LACP) on the relevant links.
Aggregated Links are treated by the system as a single logical port. Specifically, the Aggregated Link has similar port attributes
to a non-aggregated port, including auto-negotiation, speed, Duplex setting, etc.
The device supports the following Aggregation links :
Static LAGs
(Port Trunk) – Force aggregared selected ports to be a trunk group.
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
(LACP) LAGs - LACP LAG negotiate Aggregated Port links with other LACP
ports located on a different device. If the other device ports are also LACP ports, the devices establish a LAG
between them.
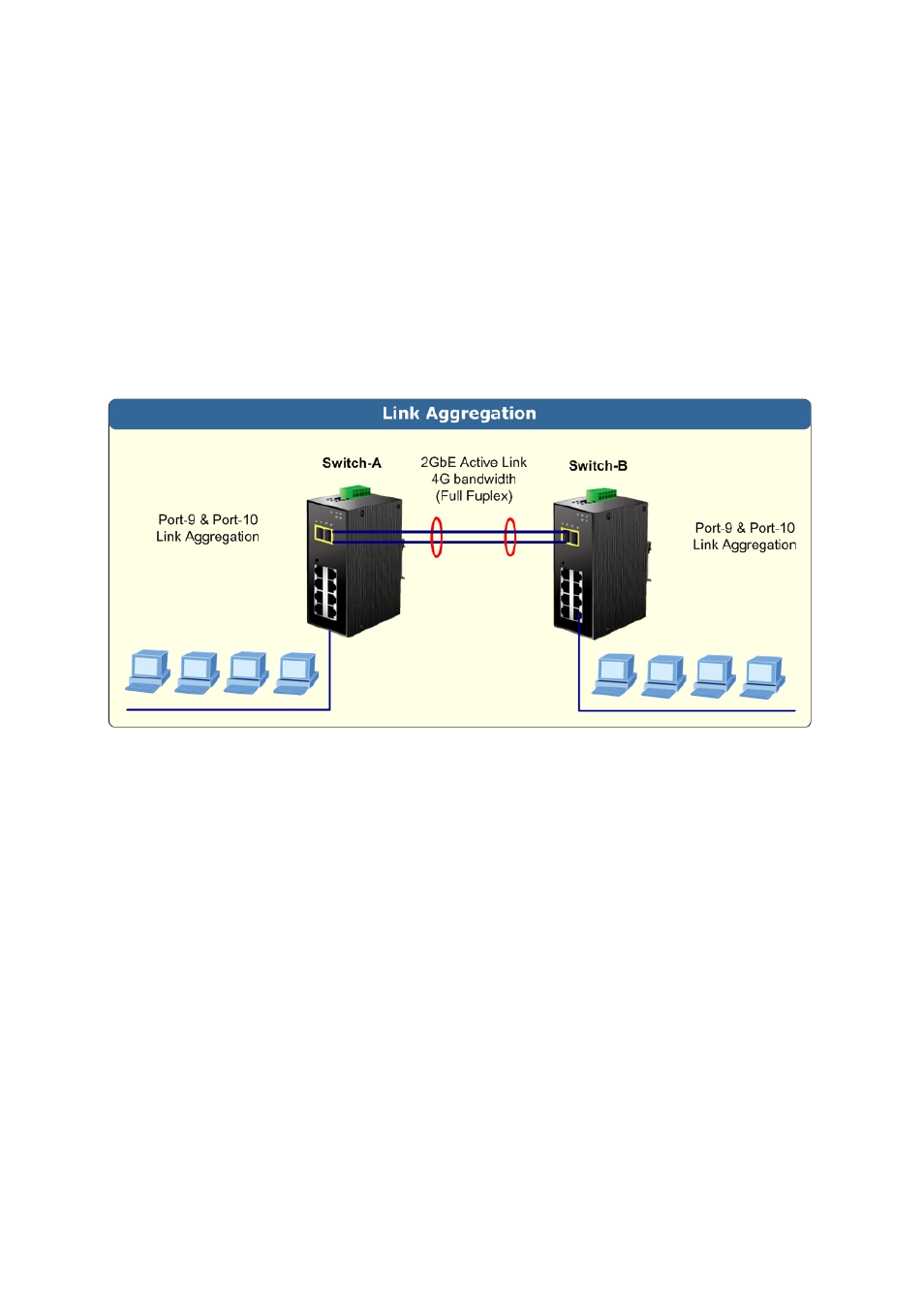
Figure 4-5-1:
Link Aggregation Topology
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardized means for exchanging information between Partner
Systems that require high speed redundant links. Link aggregation lets you group up to eight consecutive ports into a single
dedicated connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the network. LACP operation requires full-duplex mode,
more detail information refer to the IEEE 802.3ad standard.
Port link aggregations can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or to ensure fault recovery. Link
aggregation lets you group up to 4 consecutive ports into a single dedicated connection between any two the Switch or other
Layer 2 switches. However, before making any physical connections between devices, use the Link aggregation Configuration
menu to specify the link aggregation on the devices at both ends. When using a port link aggregation, note that:
The ports used in a link aggregation must all be of the same media type (RJ-45, 100 Mbps fiber).
The ports that can be assigned to the same link aggregation have certain other restrictions (see below).
Ports can only be assigned to one link aggregation.
The ports at both ends of a connection must be configured as link aggregation ports.
None of the ports in a link aggregation can be configured as a mirror source port or a mirror target port.
All of the ports in a link aggregation have to be treated as a whole when moved from/to, added or deleted from a VLAN.
The Spanning Tree Protocol will treat all the ports in a link aggregation as a whole.
Enable the link aggregation prior to connecting any cable between the switches to avoid creating a data loop.
Disconnect all link aggregation port cables or disable the link aggregation ports before removing a port link aggregation to
avoid creating a data loop.
It allows a maximum of 10 ports to be aggregated at the same time. The Managed Switch support Gigabit Ethernet ports (up to 5
groups). If the group is defined as a LACP static link aggregationing group, then any extra ports selected are placed in a standby
mode for redundancy if one of the other ports fails. If the group is defined as a local static link aggregationing group, then the
number of ports must be the same as the group member ports.
The aggregation code ensures that frames belonging to the same frame flow (for example, a TCP connection) are always
forwarded on the same link aggregation member port. Reording of frames within a flow is therefore not possible. The
aggregation code is based on the following information:
