Vlan hierarchy – Allied Telesis AT-9000 Series User Manual
Page 804
Chapter 51: MAC Address-based VLANs
776
VLAN Hierarchy
The switch employs a VLAN hierarchy when handling untagged packets
that arrive on a port that is an egress port of a MAC address-based VLAN
as well as an untagged port of a port-based VLAN. (A port can be a
member of both types of VLANs at the same time.) The rule is that a MAC
address-based VLAN takes precedence over that of a port-based VLAN.
When an untagged packet arrives on a port, the switch first compares the
source MAC address of the packet against the MAC addresses of all the
MAC address-based VLANs on the device. If there is a match, the switch
considers the packet as a member of the corresponding MAC address-
based VLAN and not the port-based VLAN, and forwards it out the egress
ports defined for the corresponding MAC address-based VLAN.
If there is no match, the switch considers the packet as a member of the
port-based VLAN and forwards the packet according to the PVID assigned
to the port. For an explanation of a PVID, refer to “Port-based VLAN
Overview” on page 690.
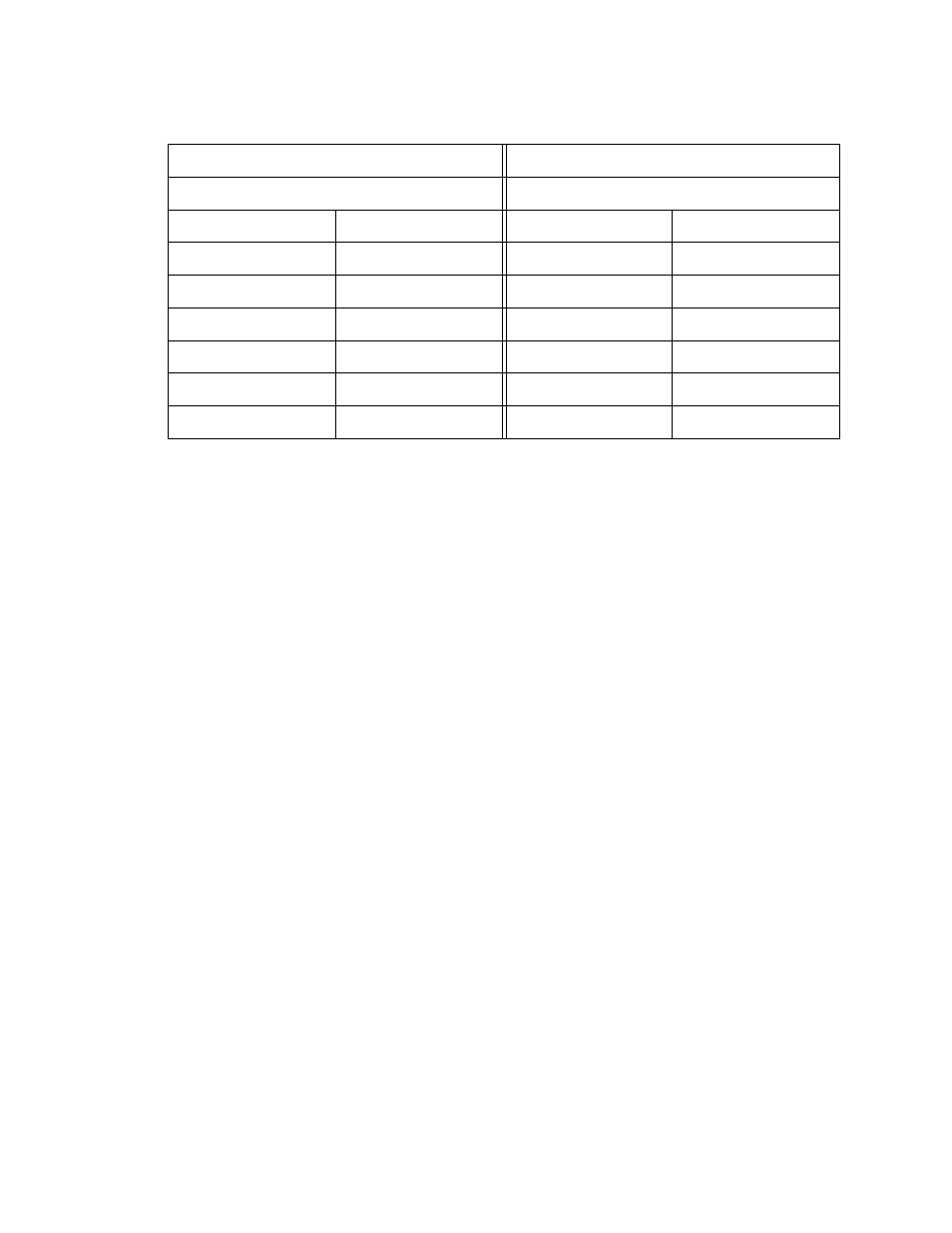
Table 76. Example of a MAC Address-based VLAN Spanning Switches
Switch A
Switch B
VLAN Name: Sales
VLAN Name: Sales
MAC Address
Egress Ports
MAC Address
Egress Ports
Address_1
1,3,4,5
Address_1
11,12,14,16
Address_2
1
Address_2
11
Address_3
1
Address_3
11
Address_4
1
Address_4
11
Address_5
1
Address_5
11
Address_6
1
Address_6
11
