Convergence in a complex 802.1w topology – Brocade FastIron Ethernet Switch Platform and Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 293
Next, the following happens:
• Port3/Switch 2, the Designated port, sends an RST BPDU, with a proposal flag to Port3/Switch 3.
• Port2/Switch 2 also sends an RST BPDU with an agreed flag to Port2/Switch 1 and then places itself
into a forwarding state.
When Port2/Switch 1 receives the RST BPDU with an agreed flag sent by Port2/Switch 2, it puts that
port into a forwarding state. The topology is now fully converged.
When Port3/Switch 3 receives the RST BPDU that Port3/Switch 2 sent, 802.1W algorithm determines
that these RST BPDUs are superior to those that Port3/Switch 3 can transmit. Therefore, Port3/Switch 3
is given a new role, that of an Alternate port. Port3/Switch 3 immediately enters a discarding state.
Now Port3/Switch 2 does not go into a forwarding state instantly like the Root port. It waits until the
forward delay timer expires twice on that port while it is still in a Designated role, before it can proceed
to the forwarding state. The wait, however, does not cause a denial of service, since the essential
connectivity in the topology has already been established.
When fully restored, the topology is the same as that shown on
on page 290.
Convergence in a complex 802.1W topology
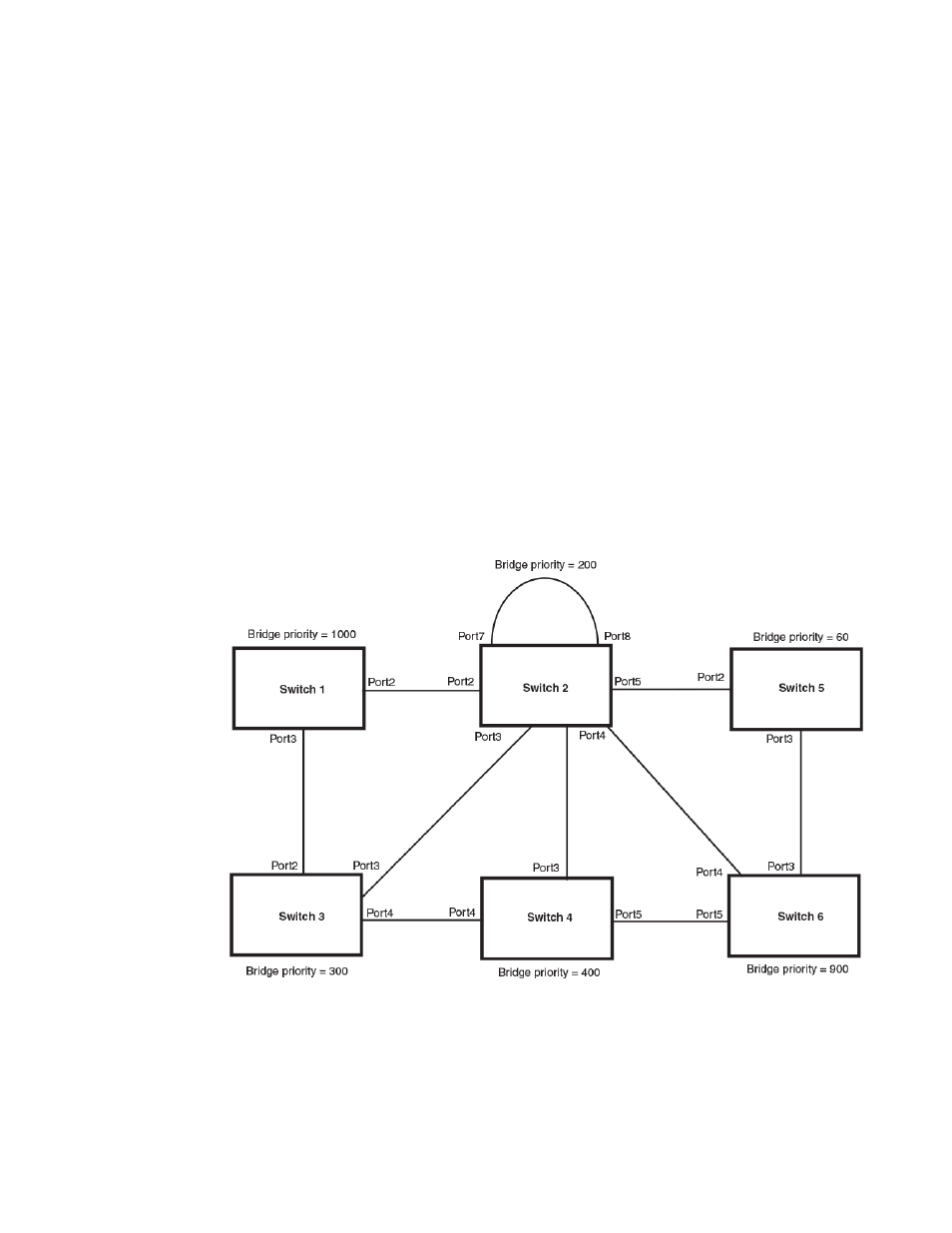
The following figure illustrates a complex 802.1W topology.
FIGURE 57 Complex 802.1W topology
In the above figure, Switch 5 is selected as the root bridge since it is the bridge with the highest priority.
Lines in the figure show the point-to-point connection to the bridges in the topology.
Switch 5 sends an RST BPDU that contains a proposal flag to Port5/Switch 2. When handshakes are
completed in Switch 5, Port5/Switch 2 is selected as the Root port on Switch 2. All other ports on Switch
2 are given Designated port role with discarding states.
Convergence in a complex 802.1W topology
FastIron Ethernet Switch Platform and Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide
293
53-1003086-04
