4 hi transmit data register (hotx), 5 register contents after reset, Hi transmit data register (hotx) -19 – Motorola DSP56012 User Manual
Page 99: Register contents after reset -19, Table 4-1, Hi registers after reset—dsp cpu side -19
Parallel Host Interface
Host Interface (HI)
MOTOROLA
DSP56012 User’s Manual
4-19
(TXDE) and DSP HI Receive Data Full (HRDF) bits are cleared. This transfer
operation sets TXDE and HRDF. The HORX register contains valid data when the
HRDF bit is set. Reading HORX clears HRDF. The DSP can program the HRIE bit to
cause a host-receive-data interrupt when HRDF is set.
Note:
Resets do not affect HORX.
4.4.4.4
HI Transmit Data Register (HOTX)
The HI Transmit data register (HOTX) is used for DSP-to-host data transfers. The
HOTX register is viewed as a 24-bit write-only register by the DSP CPU. Writing the
HOTX register clears HTDE. The DSP can program the HTIE bit to cause a host
transmit data interrupt when HTDE is set. The HOTX register is transferred as 24-bit
data to the Receive byte registers (RXH:RXM:RXL) if both the DSP-side HTDE bit
and host-side Receive Data Full (RXDF) status bits are cleared. This transfer
operation sets RXDF and HTDE. Data should not be written to the HOTX until HTDE
is set to prevent the previous data from being overwritten.
Note:
Resets do not affect HOTX.
4.4.4.5
Register Contents After Reset
shows the results of four reset types on bits in each of the HI registers, as
seen by the DSP CPU. The Hardware reset (HW) is caused by the deasserting the
RESET pin; the Software reset (SW) is caused by executing the RESET instruction; the
Individual Reset (IR) is caused by clearing PBC register bits 0 and 1, and the Stop
reset (ST) is caused by executing the STOP instruction.
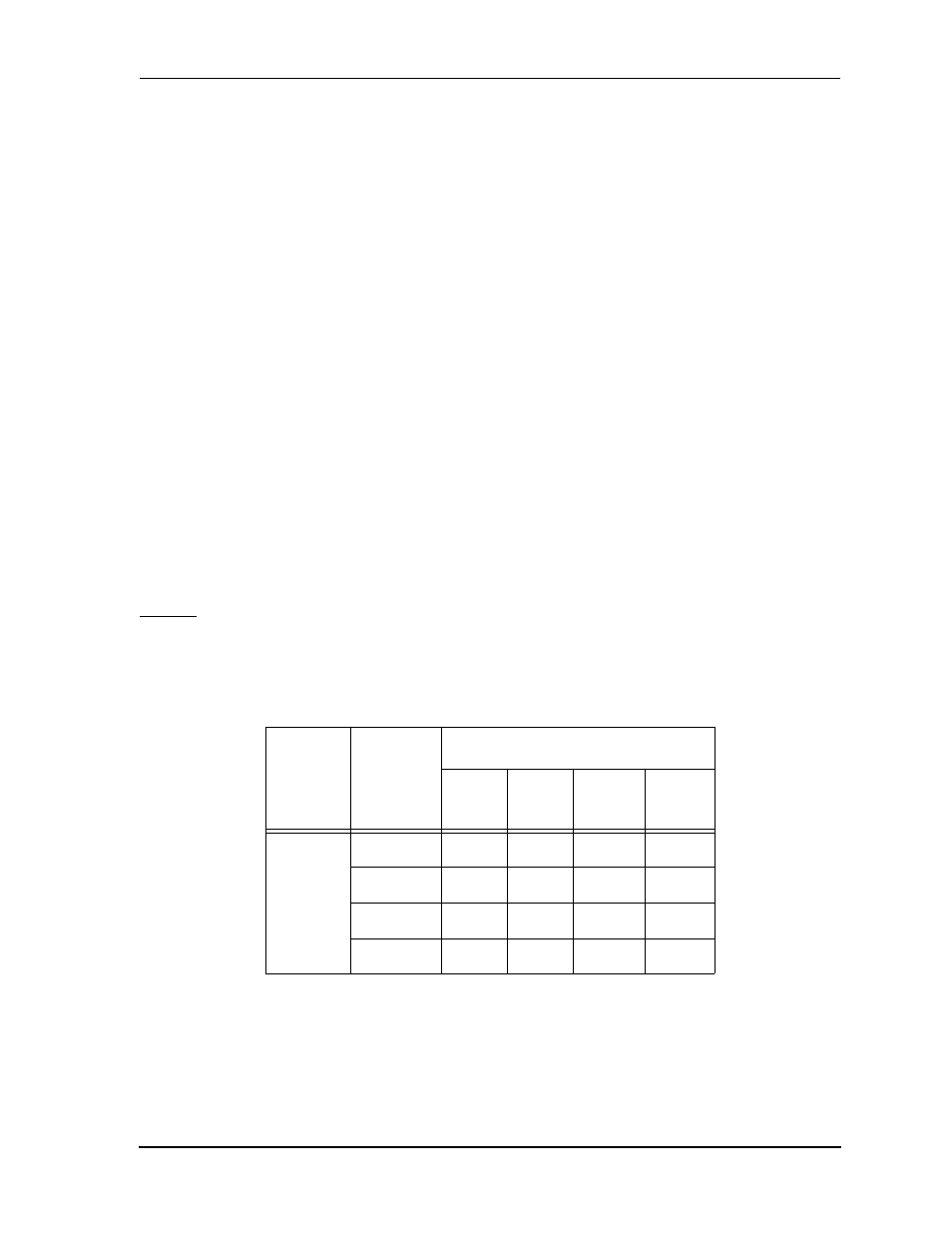
Table 4-1
HI Registers after Reset—DSP CPU Side
Register
Name
Register
Data
Reset Type
HW
Reset
SW
Reset
IR
Reset
ST
Reset
HCR
X:$FFE8
HF[3:2]
0
0
—
—
HCIE
0
0
—
—
HTIE
0
0
—
—
HRIE
0
0
—
—
