7 serial host interface (shi), Serial host interface (shi) -13, Table 2-7 – Motorola DSP56012 User Manual
Page 53: Serial host interface (shi) signals -13
Signal Descriptions
Serial Host Interface (SHI)
MOTOROLA
DSP56012 User’s Manual
2-13
2.7
SERIAL HOST INTERFACE (SHI)
The SHI has five I/O signals that can be configured to allow the SHI to operate in
either SPI or I
2
C mode.
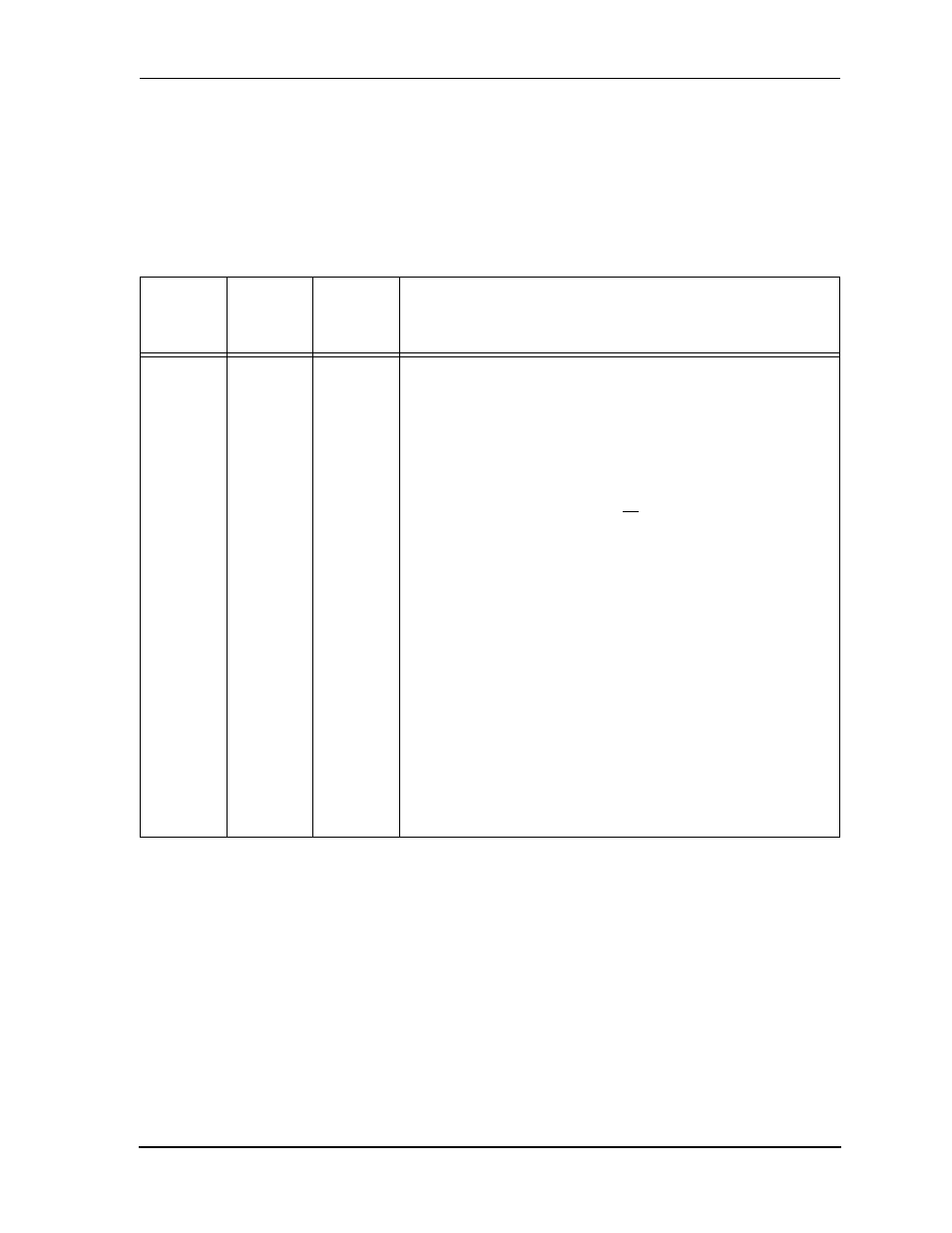
Table 2-7
Serial Host Interface (SHI) Signals
Signal
Name
Signal
Type
State
during
Reset
Signal Description
SCK/
SCL
Input or
Output
Tri-stated
SPI Serial Clock/I
2
C Serial Clock
—The SCK signal is an
output when the SPI is configured as a master, and a
Schmitt-trigger input when the SPI is configured as a slave.
When the SPI is configured as a master, the SCK signal is
derived from the internal SHI clock generator. When the SPI
is configured as a slave, the SCK signal is an input, and the
clock signal from the external master synchronizes the data
transfer. The SCK signal is ignored by the SPI if it is defined
as a slave and the Slave Select (SS) signal is not asserted. In
both the master and slave SPI devices, data is shifted on one
edge of the SCK signal and is sampled on the opposite edge
where data is stable. Edge polarity is determined by the SPI
transfer protocol. SCL carries the clock for I
2
C bus
transactions in the I
2
C mode. SCL is a Schmitt-trigger input
when configured as a slave, and an open-drain output when
configured as a master. SCL should be connected to V
CC
through a pull-up resistor.
The maximum allowed internally generated bit clock
frequency is f
osc
/4 for the SPI mode and f
osc
/6 for the I
2
C
mode where f
osc
is the clock on EXTAL. The maximum
allowed externally generated bit clock frequency is f
osc
/3 for
the SPI mode and f
osc
/5 for the I
2
C mode
An external pull-up resistor is not required.
