6 characteristics of the i2c bus, 1 overview, Figure57 i2c bit transfer – Motorola DSP56012 User Manual
Page 168: Characteristics of the i, Overview -20, Figure 5-7, Characteristics of the i2c bus -20, 6 characteristics of the i, C bus
5-20
DSP56012 User’s Manual
MOTOROLA
Serial Host Interface
Characteristics Of The I
2
C Bus
5.6
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE I
2
C BUS
The I
2
C serial bus consists of two bi-directional lines, one for data signals (SDA) and
one for clock signals (SCL). Both the SDA and SCL lines must be connected to a
positive supply voltage via a pull-up resistor.
Note:
Within the I
2
C bus specifications, a low-speed mode (2 kHz clock rate) and a
high-speed mode (100 kHz clock rate) are defined. The SHI operates in the
high-speed mode only.
5.6.1
Overview
The I
2
C bus protocol must conform to the following rules:
• Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not busy.
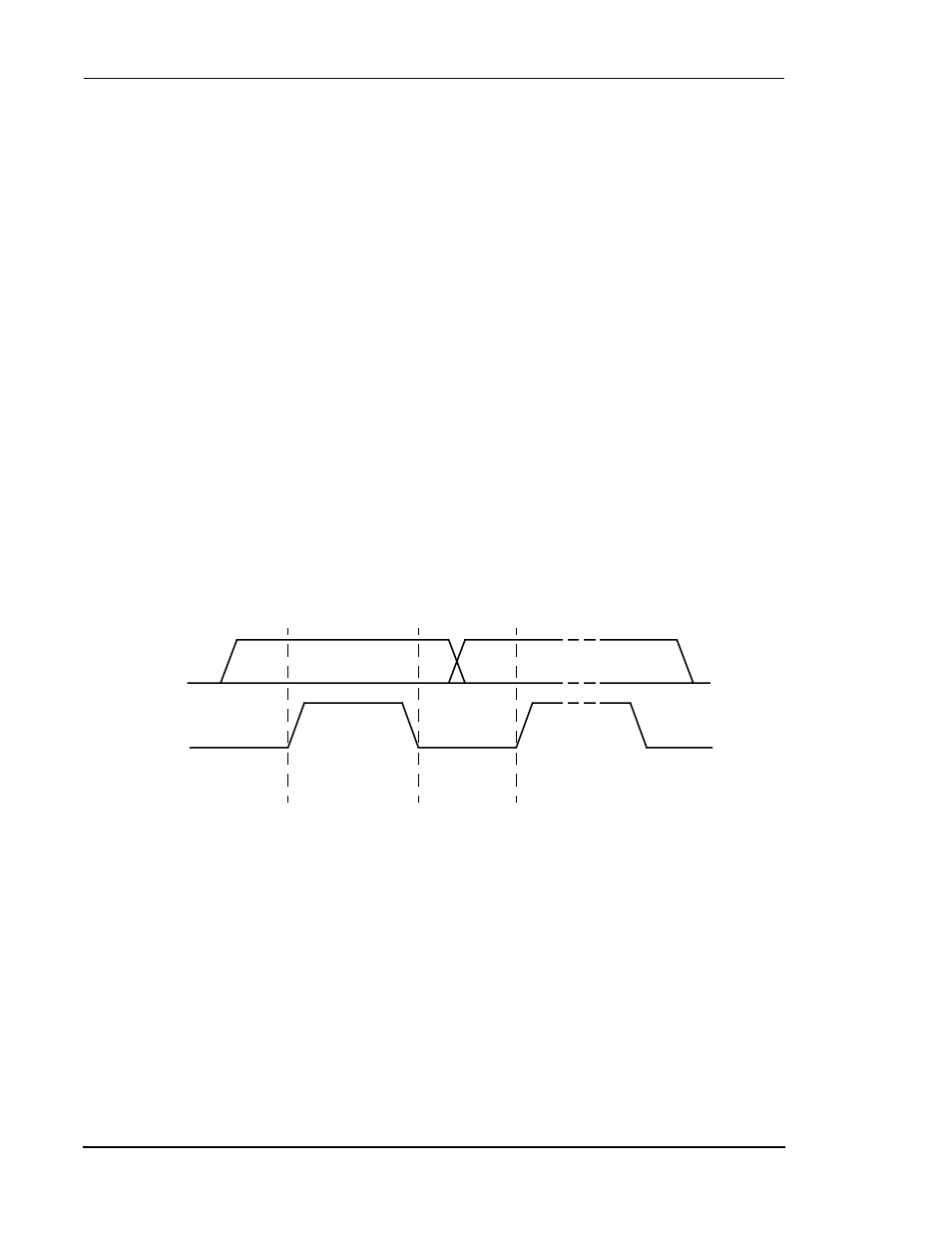
• During data transfer, the data line must remain stable whenever the clock line
is high. Changes in the data line when the clock line is high will be interpreted
as control signals (see
Accordingly, the I
2
C bus protocol defines the following events:
• Bus not busy—Both data and clock lines remain high.
• Start data transfer—The start event is defined as a change in the state of the
data line, from high to low, while the clock is high (see
• Stop data transfer—The stop event is defined as a change in the state of the
data line, from low to high, while the clock is high (see
Figure 5-7 I
2
C Bit Transfer
SDA
SCL
Data Line
Stable:
Data Valid
Change
of Data
Allowed
AA0422
