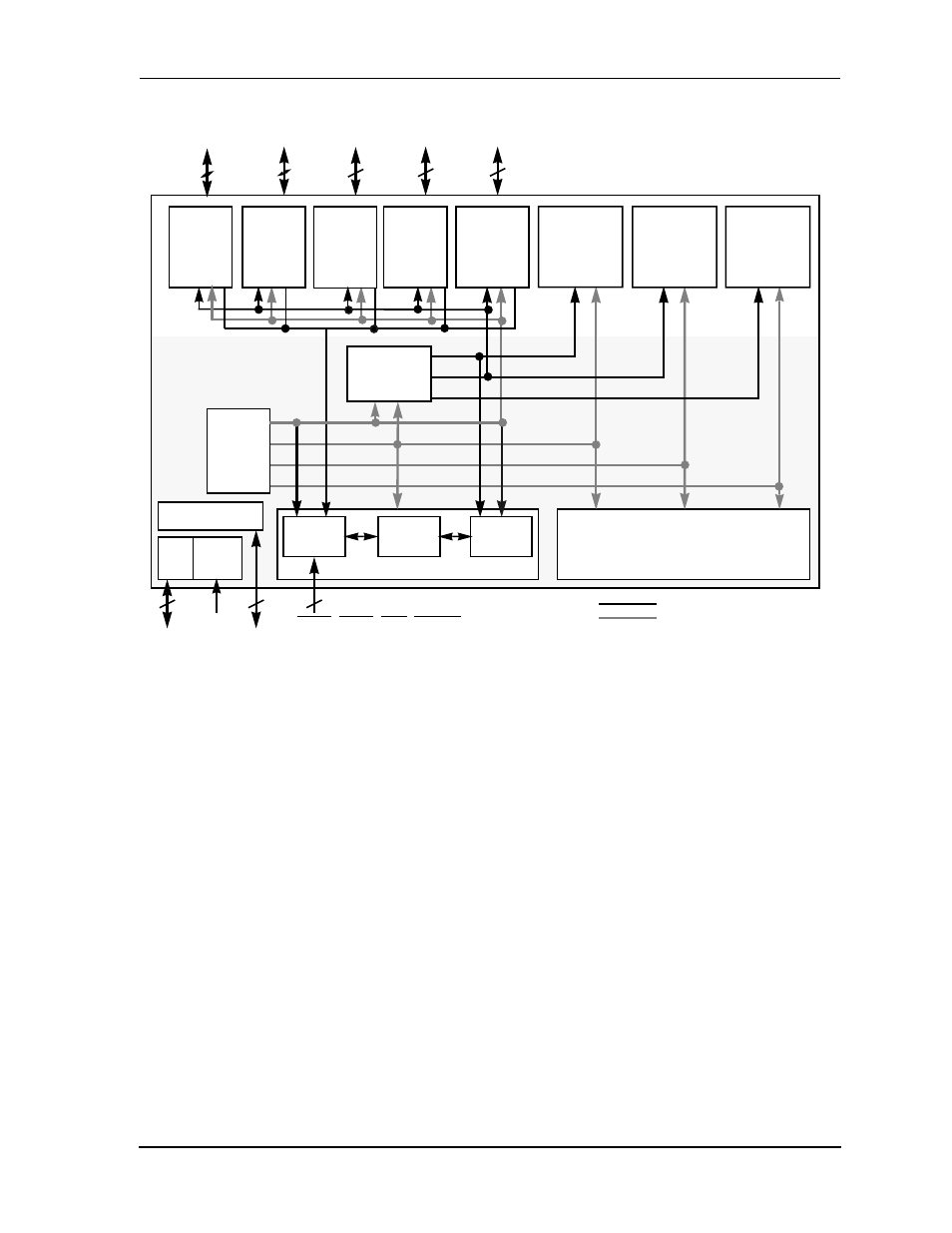
Figure11 dsp56012 block diagram, Figure 1-1, Dsp56012 block diagram -9 – Motorola DSP56012 User Manual
Page 29
Overview
DSP56012 Architectural Overview
MOTOROLA
DSP56012 User’s Manual
1-9
The DSP56000 core is dual-natured in that there are two independent data memory
spaces, two address arithmetic units, and a Data ALU that has two accumulators and
two shifter/limiters. The duality of the architecture makes it easier to write software
for DSP applications. For example, data is naturally partitioned into coefficient and
data spaces for filtering and transformations, and into real and imaginary spaces for
performing complex arithmetic.
Note:
Although the DSP56000 core has built-in support for external memory
expansion, the DSP56012 does not implement this function. For DSP56012
applications, external memory expansion is a function of the host processor.
The DSP56000 architecture is especially suited for audio applications since its
arithmetic operations are executed on 24-bit or 48-bit data words. This is a significant
advantage for audio over 16-bit and 32-bit architectures—16-bit DSP architectures
have insufficient precision for CD-quality sound, and while 32-bit DSP architectures
possess the necessary precision, with extra silicon and cost overhead they are not
suitable for high-volume, cost-driven audio applications
Figure 1-1 DSP56012 Block Diagram
Y Data
Memory
X Data
Memory
Program
Memory
Program Control Unit
24-Bit
DSP56000
Core
OnCE
TM
Port
PLL
Clock
Gen.
8
9
5
2
16-Bit Bus
24-Bit Bus
Data ALU
24
×
24 + 56
→
56-Bit MAC
Two 56-Bit Accumulators
Program
Interrupt
Controller
Program
Decode
Controller
Program
Address
Generator
4
IRQA, IRQB, NMI, RESET
4
3
Internal
Data
Bus
Switch
Address
Generation
Unit
PAB
XAB
YAB
GDB
PDB
XDB
YDB
General
Purpose
I/O
(GPIO)
Digital
Audio
Transmitter
(DAX)
Serial
Audio
Interface
(SAI)
Serial
Host
Interface
(SHI)
Parallel
Host
Interface
(HI)
15
EXTAL
Expansion
Area
