Figure423 hi configuration—host side, Figure 4-22, Hi initialization—host side, polling mode -46 – Motorola DSP56012 User Manual
Page 126: Figure 4-23, Hi configuration—host side -46
4-46
DSP56012 User’s Manual
MOTOROLA
Parallel Host Interface
Host Interface (HI)
10
The basic data transfer process from the host processor’s view (see
on page 4-40) is for the host to:
1. Assert HOREQ when the HI is ready to transfer data.
2. Assert HACK (if the interface is using HACK).
3. Assert HR/W to select whether this operation will read or write a register.
4. Assert the HI address (HOA2, HOA1, HOA0) to select the register to be read
or written.
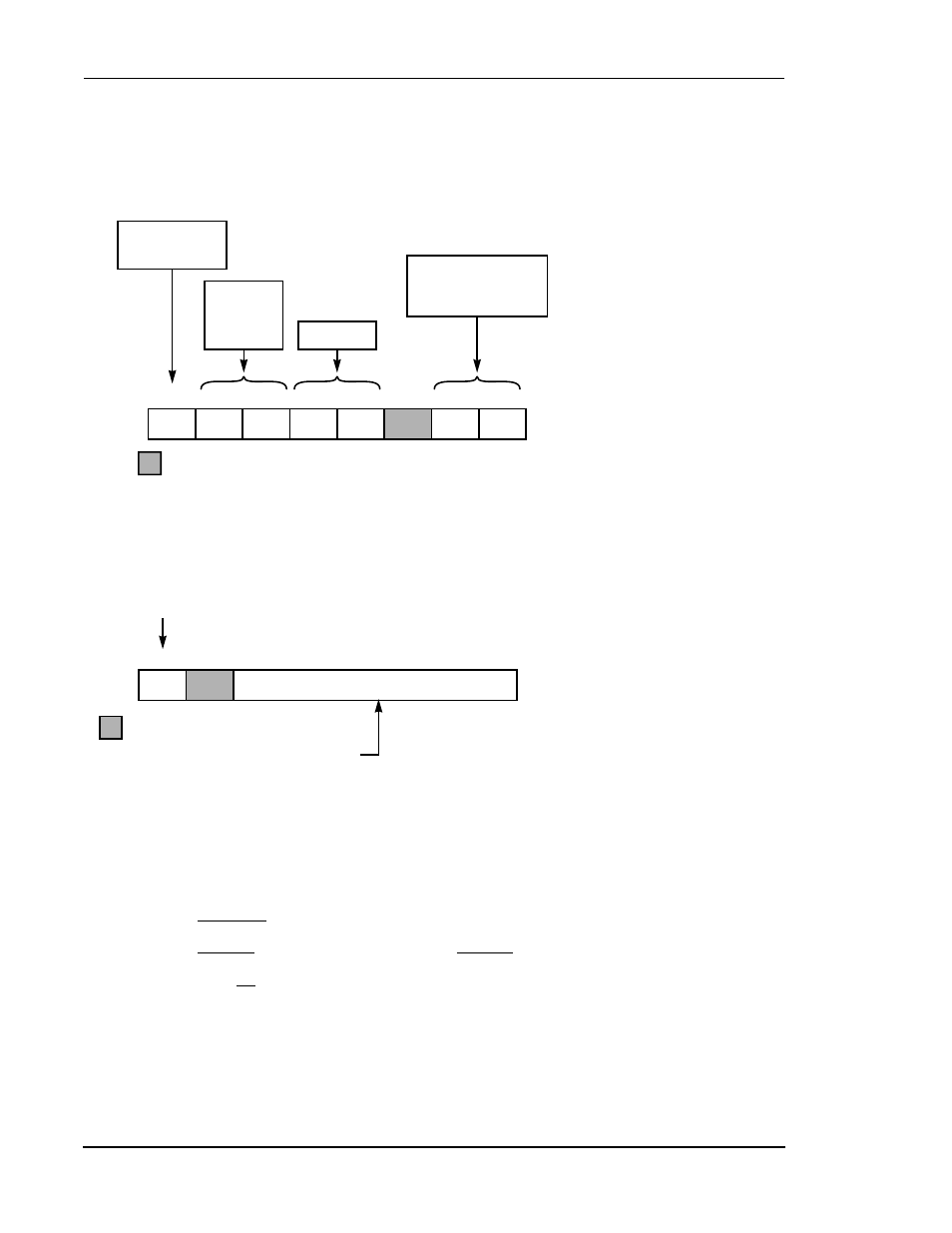
Figure 4-22 HI Initialization—Host Side, Polling Mode
Figure 4-23 HI Configuration—Host Side
Reserved; write as 0.
Step 2 of HI Port configuration
2. Option 2: Select polling mode for Host-to-DSP communication
Initialize DSP
And HI Port
DMA Off
Bit 5 = 0
Bit 6 = 0
Optional
Disable Interrupts
Bit 0 = 0
Bit 1 = 0
Interrupt Control Register (ICR)
(Read/Write)
AA0330k
$0
INIT
HF1
HF0
TREQ RREQ
7
0
HM0
HM1
6
5
4
3
2
1
Step 2 Of HI Port Configuration
1. Clear Host Command bit (HC):
2. Option 1: Select Host Vector (HV)
Optional since HV can be set any time before the host command is executed. DSP Interrupt Vector = The
Host vector multiplied by 2. Default (upon DSP reset): HV = $17
⇒
DSP Interrupt Vector $0034
Command Vector Register (CVR)
(Read/Write)
$1
HC
RREQ
7
0
6
Reserved; write as 0.
AA0331k
Bit 7 = 0
