2 serial audio interface internal architecture, 1 baud-rate generator, Figure61 sai baud-rate generator block diagram – Motorola DSP56012 User Manual
Page 182: Serial audio interface internal architecture 6-4, Baud-rate generator -4, Figure 6-1, Sai baud-rate generator block diagram -4
6-4
DSP56012 User’s Manual
MOTOROLA
Serial Audio Interface
Serial Audio Interface Internal Architecture
• User programmable to support a wide variety of serial audio formats
• Three receive interrupt vectors: Receive Left Channel, Receive Right Channel,
and Receive with Exception
• Three transmit interrupt vectors: Transmit Left Channel, Transmit Right
Channel, and Transmit with Exception
6.2
SERIAL AUDIO INTERFACE INTERNAL ARCHITECTURE
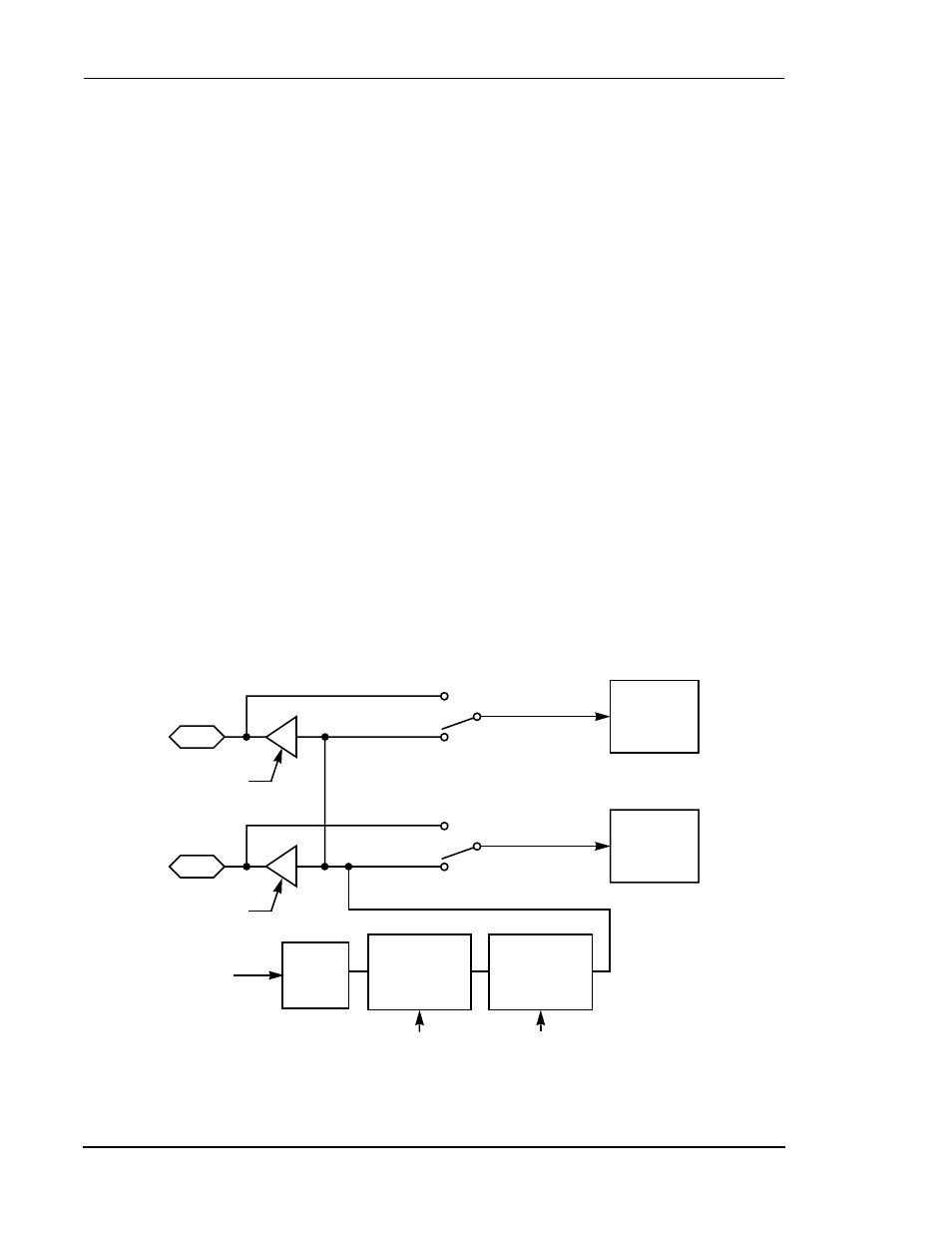
The SAI is functionally divided into three parts: the baud-rate generator, the receiver
section, and the transmitter section. The receive and transmit sections are completely
independent and can operate concurrently or separately. The following paragraphs
describe the operation of these sections.
6.2.1
Baud-Rate Generator
The baud-rate generator produces the internal serial clock for the SAI if either or both
of the receiver and transmitter sections are configured in the Master mode. The
baud-rate generator is disabled if both receiver and transmitter sections are
configured as slaves. Figure 6-1 illustrates the internal clock path connections. The
receiver and transmitter clocks can be internal or external depending on the
configuration of the Receive Master (RMST) and Transmit Master (TMST) control
bits.
Figure 6-1 SAI Baud-Rate Generator Block Diagram
Tx
TMST
TMST = 0
TMST = 1
SCKT
Rx
RMST
RMST = 0
RMST = 1
SCKR
Divider
Divide By 1
or
Divide By 8
Divide By 1
To
Divide By 256
Prescale
PSR
PM0–PM7
RClock
TClock
F
OSC
Internal Clock
Divide
By 2
AA0427k
