5 p ath cont ours — p olar coor dinat es – HEIDENHAIN TNC 426B (280 472) ISO programming User Manual
Page 131
115
HEIDENHAIN TNC 410, TNC 426, TNC 430
Y
X
Z
25=J
40=I
5
270°
R3
6.5 P
ath Cont
ours — P
olar Coor
dinat
es
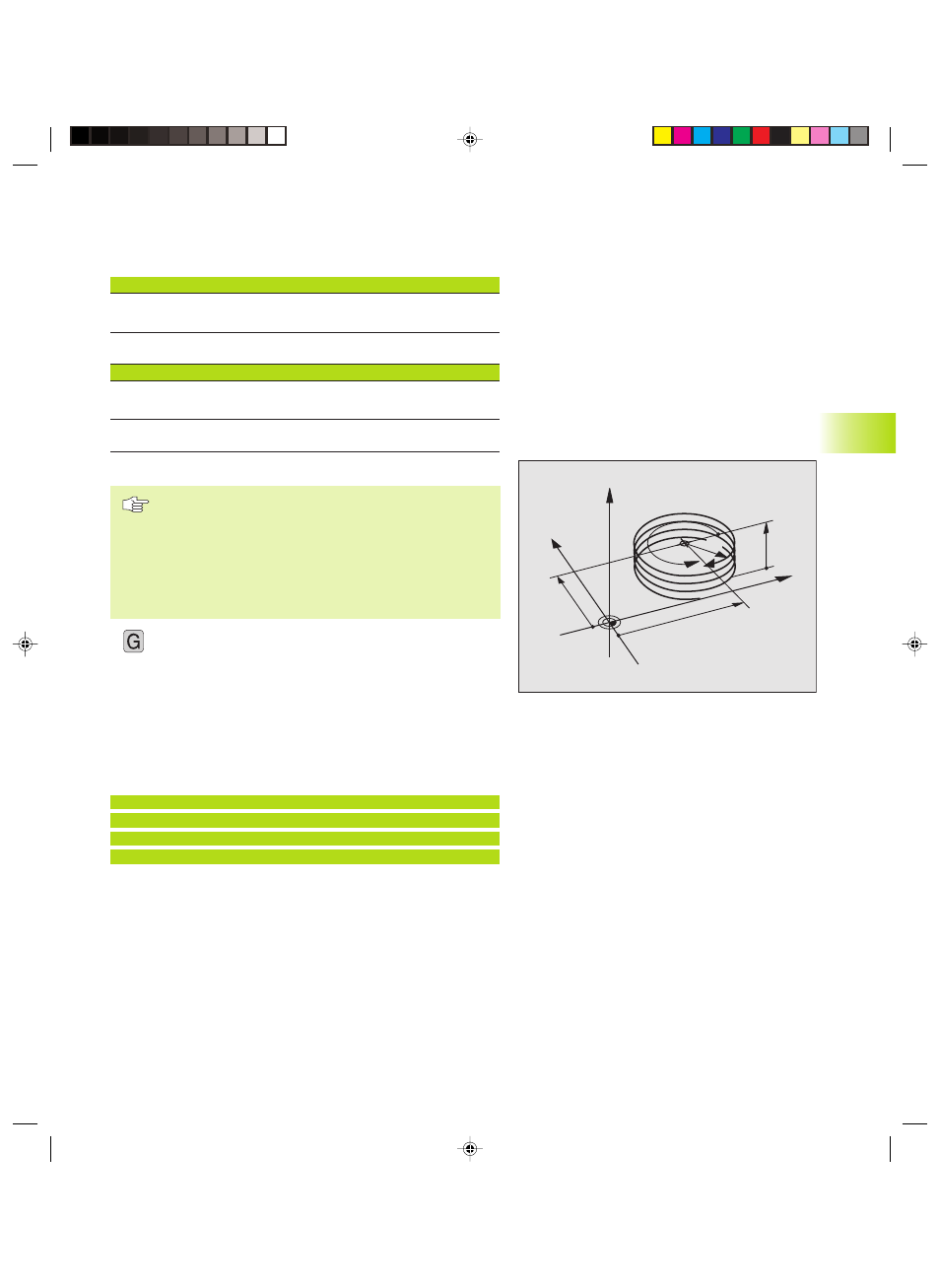
Shape of the helix
The table below illustrates in which way the shape of the helix is
determined by the work direction, direction of rotation and radius
compensation.
Internal thread Work direct. Direct. of rot. Radius comp.
Right-handed
Z+
G13
G41
Left-handed
Z+
G12
G42
Right-handed
Z–
G12
G42
Left-handed
Z–
G13
G41
External thread
Right-handed
Z+
G13
G42
Left-handed
Z+
G12
G41
Right-handed
Z–
G12
G41
Left-handed
Z–
G13
G42
Programming a helix
Always enter the same algebraic sign for the direction of
rotation and the incremental total angle G91 H. The tool
may otherwise move in a wrong path and damage the
contour.
For the total angle G91 H, you can enter a value from
5400° to +5400°. If the thread has of more than 15
revolutions, program the helix in a program section
repeat (see section 9.2 ”Program Section Repeats”).
12
ú
Polar coordinates angle H: Enter the total angle (G91)
of tool traverse along the helix in incremental
dimensions. After entering the angle, identify the
tool axis with an axis selection key.
ú
Enter the coordinate for the height of the helix in
incremental dimensions.
ú
Enter radius compensation G40/G41/G42
Example NC blocks
N120 I+40 J+25 *
N130 G01 Z+0 F100 M3 *
N140 G11 G41 R+3 H+270 *
N150 G12 G91 H-1800 Z+5 F+50 *
Gkap6.pm6
29.06.2006, 08:06
115
