Operator’s manual – Teledyne LeCroy WaveExpert 100H Operators Manual User Manual
Page 208
Operator’s Manual
206
WE-OM-E Rev A
0 term.
The first half of the spectrum (Re, Im), from 0 to the Nyquist frequency is kept for further
processing and doubled in amplitude:
R'
n
= 2 x R
n
_0 n < N/2
I'
n
= 2 x I
n
__0 n < N/2
5. The resultant waveform is computed for the spectrum type selected.
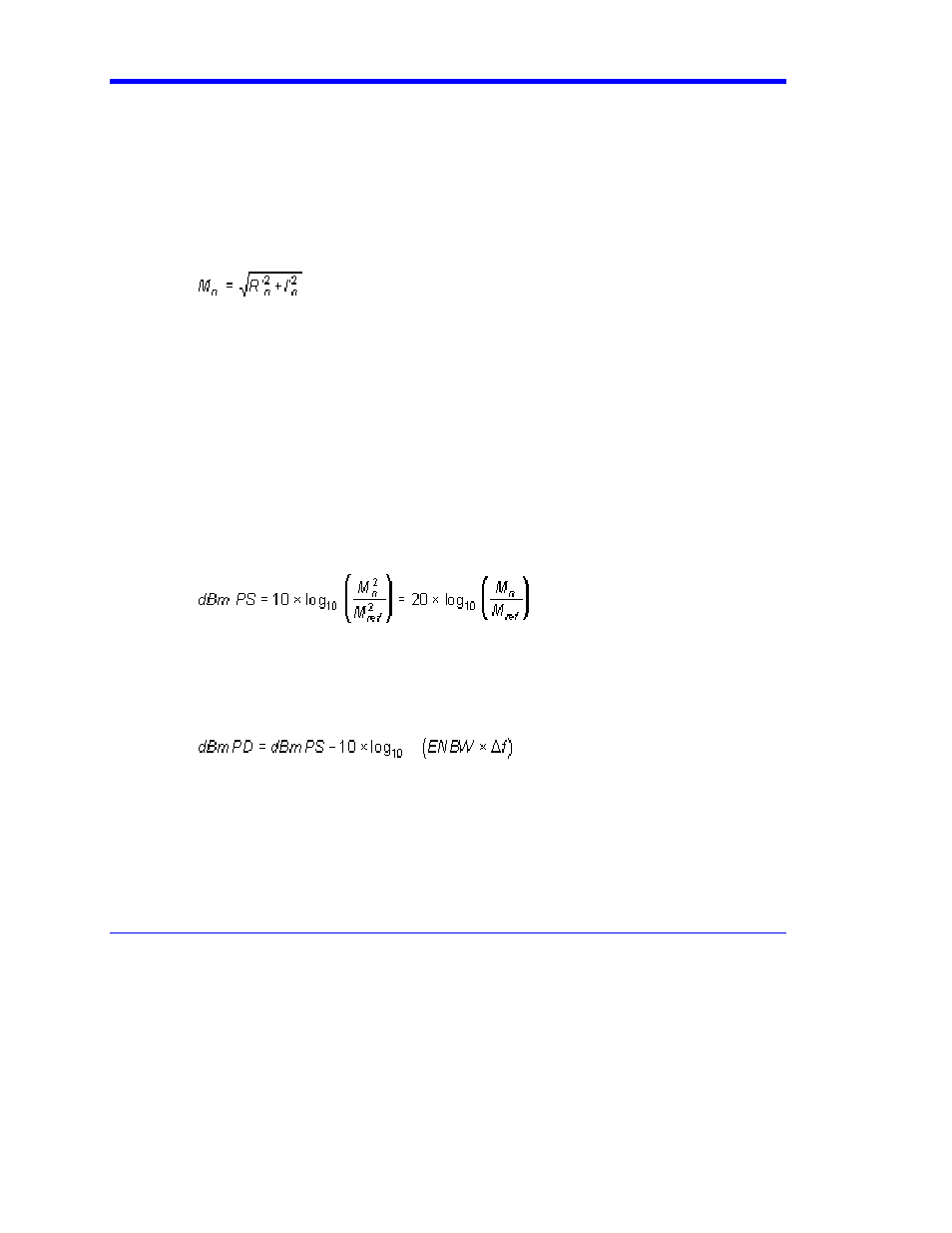
If "Magnitude" is selected, the magnitude of the complex vector is computed as:
Steps 1–5 lead to the following result:
An AC sine wave of amplitude 1.0 V with an integral number of periods N
p
in the time window,
transformed with the rectangular window, results in a fundamental peak of 1.0 V magnitude in the
spectrum at frequency N
p
x Delta f. However, a DC component of 1.0 V, transformed with the
rectangular window, results in a peak of 2.0 V magnitude at 0 Hz.
The waveforms for the other available spectrum types are computed as follows:
Phase: angle = arctan (I
n
/R
n
)_M
n
> M
min
_angle = 0_ M
n
M
min
Where M
min
is the minimum magnitude, fixed at about 0.001 of the full scale at any gain setting,
below which the angle is not well defined.
The dBm Power Spectrum:
where M
ref
= 0.316 V (that is, 0 dBm is defined as a sine wave of 0.316 V peak or 0.224 V rms,
giving 1.0 mW into 50 ohms).
The dBm Power Spectrum is the same as dBm Magnitude, as suggested in the above formula.
dBm Power Density:
where ENBW is the equivalent noise bandwidth of the filter corresponding to the selected window,
and Delta f is the current frequency resolution (bin width).
6. The FFT Power Average takes the complex frequency-domain data R'
n
and I'
n
for each
spectrum generated in Step 5, and computes the square of the magnitude:
M
n
2
= R'
n
2
+ I'
n
2
,
then sums M
n
2
and counts the accumulated spectra. The total is normalized by the
number of spectra and converted to the selected result type using the same formulas as
