Security association, Encapsulation modes – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 362
348
Both AH and ESP provide authentication services, but the authentication service provided by AH is
stronger. In practice, you can choose either or both security protocols. When both AH and ESP are used,
an IP packet is encapsulated first by ESP and then by AH.
shows the format of IPsec packets.
Security association
A security association is an agreement negotiated between two communicating parties called IPsec
peers. It comprises a set of parameters for data protection, including security protocols, encapsulation
mode, authentication and encryption algorithms, and shared keys and their lifetime. SAs can be set up
manually or through IKE. The WX series access controllers support setting up SAs only through IKE.
An SA is unidirectional. At least two SAs are needed to protect data flows in a bidirectional
communication. If two peers want to use both AH and ESP to protect data flows between them, they
construct an independent SA for each protocol.
An SA is uniquely identified by a triplet, which consists of the security parameter index (SPI), destination
IP address, and security protocol identifier (AH or ESP).
An SPI is a 32-bit number for uniquely identifying an SA. It is transmitted in the AH/ESP header. A
manually configured SA requires an SPI to be specified manually for it; an IKE created SA will have an
SPI generated at random.
A manually configured SA never ages out. An IKE created SA has a specified period of lifetime, which
comes in two types:
•
Time-based lifetime, which defines how long the SA can be valid after it is created.
•
Traffic-based lifetime, which defines the maximum traffic that the SA can process.
The SA becomes invalid when either of the lifetime timers expires. Before the SA expires, IKE negotiates
a new SA, which takes over immediately after its creation.
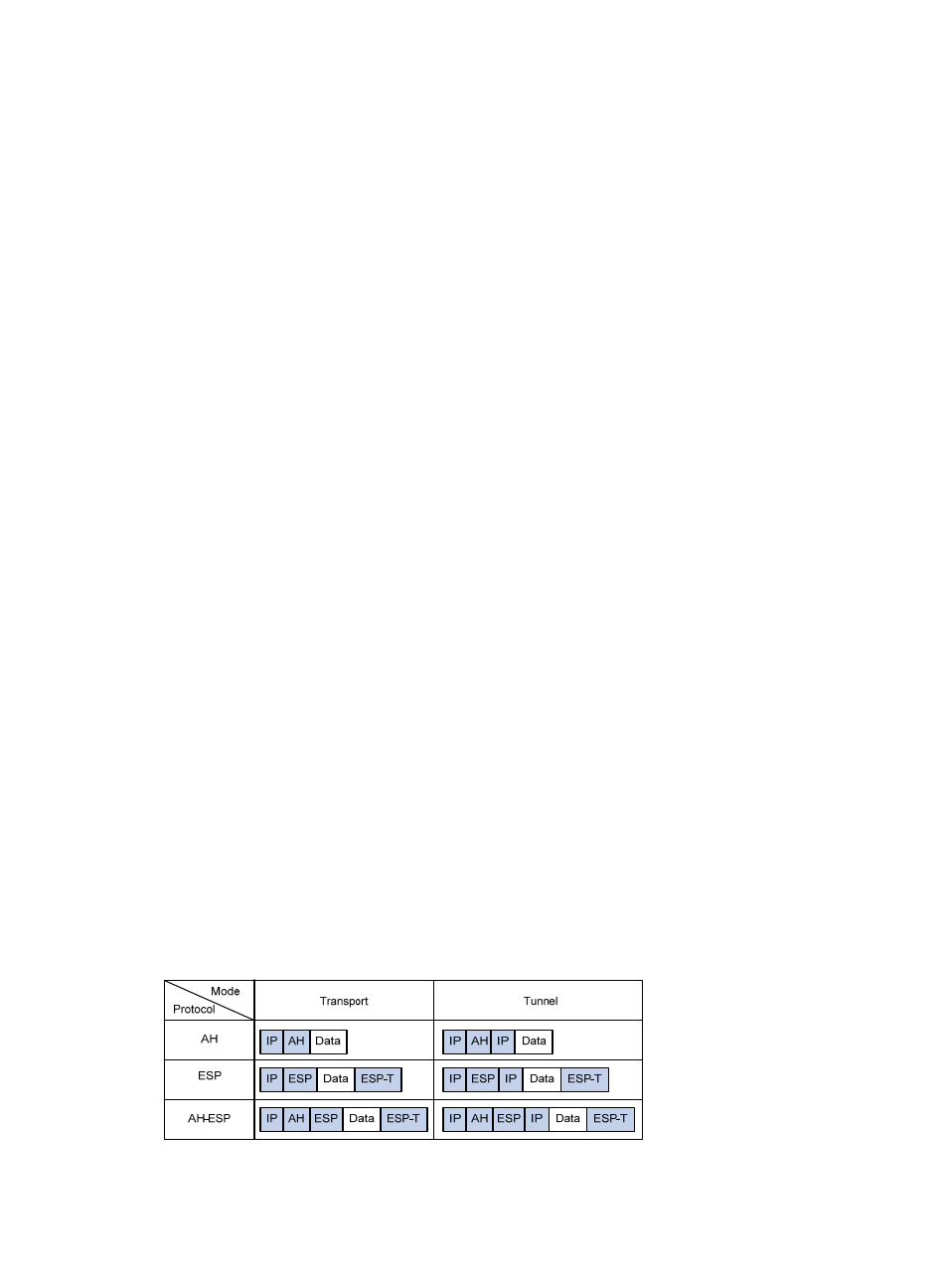
Encapsulation modes
IPsec supports the following IP packet encapsulation modes:
•
Tunnel mode—IPsec protects the entire IP packet, including both the IP header and the payload. It
uses the entire IP packet to calculate an AH or ESP header, and then encapsulates the original IP
packet and the AH or ESP header with a new IP header. If you use ESP, an ESP trailer is also
encapsulated. Tunnel mode is typically used for protecting gateway-to-gateway communications.
IPsec between AC and AP supports only the tunnel mode.
•
Transport mode—IPsec protects only the IP payload. It uses only the IP payload to calculate the AH
or ESP header, and inserts the calculated header between the original IP header and payload. If
you use ESP, an ESP trailer is also encapsulated. The transport mode is typically used for protecting
host-to-host or host-to-gateway communications.
shows how the security protocols encapsulate an IP packet in different encapsulation modes.
Figure 146 Encapsulation by security protocols in different modes
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C WA3600 Series Access Points H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points H3C S10500 Series Switches H3C S5800 Series Switches H3C S5820X Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C S9500E Series Switches H3C MSR 5600 H3C MSR 50 H3C MSR 3600 H3C MSR 30 H3C MSR 2600 H3C MSR 20-2X[40] H3C MSR 20-1X H3C MSR 930 H3C MSR 900 H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C SecPath F5020 H3C SecPath F5040 H3C VMSG VFW1000
