Pki architecture, Entity, Pki repository – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 282
268
statement (CPS). A CA policy can be acquired through out-of-band means such as phone, disk, and
email. As different CAs might use different methods to check the binding of a public key with an entity,
make sure that you understand the CA policy before selecting a trusted CA for certificate request.
PKI architecture
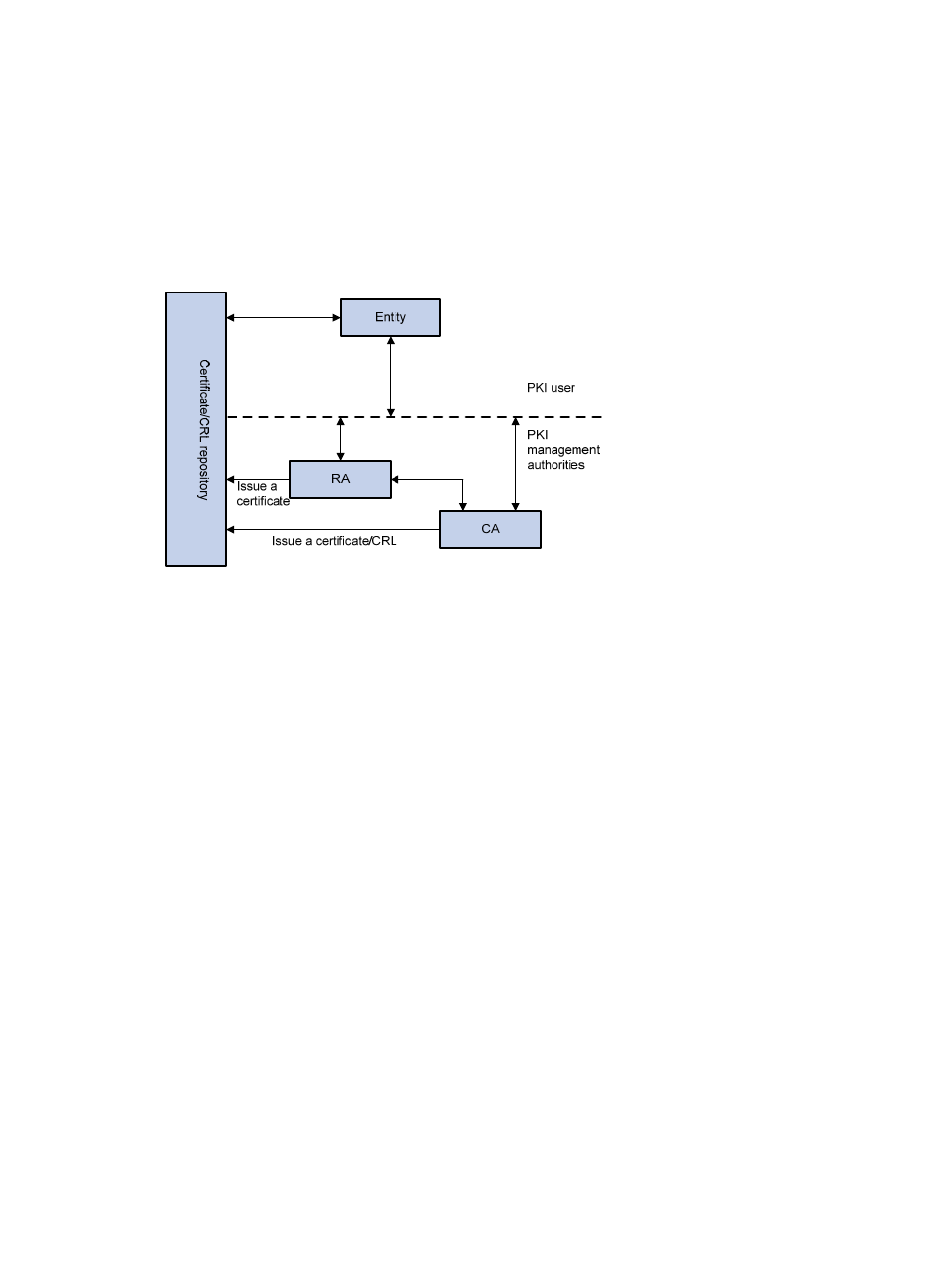
A PKI system consists of entities, a CA, a registration authority (RA), and a PKI repository.
Figure 122 PKI architecture
Entity
An entity is an end user of PKI products or services, such as a person, an organization, a device like a
router or a switch, or a process running on a computer.
CA
A CA is a trusted authority responsible for issuing and managing digital certificates. A CA issues
certificates, specifies the validity periods of certificates, and revokes certificates as needed by publishing
CRLs.
RA
A registration authority (RA) is an extended part of a CA or an independent authority. An RA can
implement functions including identity authentication, CRL management, key pair generation and key
pair backup. The PKI standard recommends that an independent RA be used for registration
management to achieve higher security.
PKI repository
A PKI repository can be a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server or a common database.
It stores and manages information like certificate requests, certificates, keys, CRLs and logs when it
provides a simple query function.
LDAP is a protocol for accessing and managing PKI information. An LDAP server stores user information
and digital certificates from the RA server and provides directory navigation service. From an LDAP server,
an entity can retrieve local and CA certificates of its own as well as certificates of other entities.
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C WA3600 Series Access Points H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points H3C S10500 Series Switches H3C S5800 Series Switches H3C S5820X Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C S9500E Series Switches H3C MSR 5600 H3C MSR 50 H3C MSR 3600 H3C MSR 30 H3C MSR 2600 H3C MSR 20-2X[40] H3C MSR 20-1X H3C MSR 930 H3C MSR 900 H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C SecPath F5020 H3C SecPath F5040 H3C VMSG VFW1000
