Radius, Client/server model, Security and authentication mechanisms – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 16: Basic radius message exchange process
2
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is a distributed information interaction protocol that
uses a client/server model. It can protect networks against unauthorized access and is often used in
network environments where both high security and remote user access are required.
RADIUS uses UDP as the transport protocol. It uses UDP port 1812 for authentication and UDP port 1813
for accounting.
RADIUS was originally designed for dial-in user access. With the addition of new access methods,
RADIUS has been extended to support additional access methods, for example, Ethernet and ADSL.
RADIUS provides access authentication and authorization services, and its accounting function collects
and records network resource usage information.
Client/server model
The RADIUS client runs on the NASs located throughout the network. It passes user information to
designated RADIUS servers and acts on the responses (for example, rejects or accepts user access
requests).
The RADIUS server runs on the computer or workstation at the network center and maintains information
related to user authentication and network service access. It listens to connection requests, authenticates
users, and returns user access control information (for example, rejecting or accepting the user access
request) to the clients.
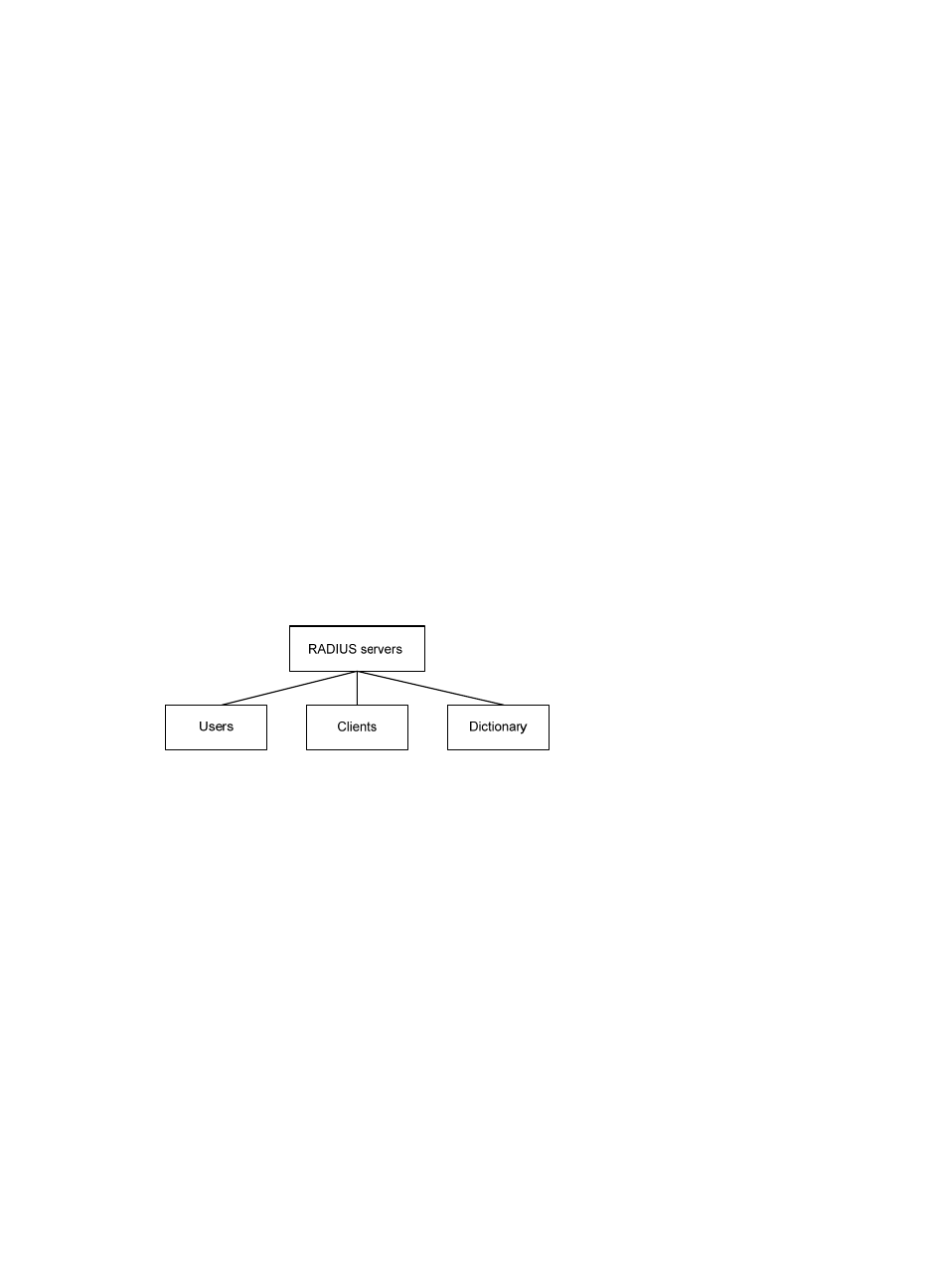
In general, the RADIUS server maintains the following databases: Users, Clients, and Dictionary.
Figure 2 RADIUS server components
•
Users—Stores user information such as the usernames, passwords, applied protocols, and IP
addresses.
•
Clients—Stores information about RADIUS clients, such as shared keys and IP addresses.
•
Dictionary—Stores RADIUS protocol attributes and their values.
Security and authentication mechanisms
Information exchanged between a RADIUS client and the RADIUS server is authenticated with a shared
key, which is never transmitted over the network. This enhances the information exchange security. In
addition, to prevent user passwords from being intercepted on insecure networks, RADIUS encrypts
passwords before transmitting them.
A RADIUS server supports multiple user authentication methods, such as the Password Authentication
Protocol (PAP) and the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) of the Point-to-Point
Protocol (PPP). A RADIUS server can also act as the client of another AAA server to provide
authentication proxy services.
Basic RADIUS message exchange process
illustrates the interactions between the host, the RADIUS client, and the RADIUS server.
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C WA3600 Series Access Points H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points H3C S10500 Series Switches H3C S5800 Series Switches H3C S5820X Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C S9500E Series Switches H3C MSR 5600 H3C MSR 50 H3C MSR 3600 H3C MSR 30 H3C MSR 2600 H3C MSR 20-2X[40] H3C MSR 20-1X H3C MSR 930 H3C MSR 900 H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C SecPath F5020 H3C SecPath F5040 H3C VMSG VFW1000
