Domain-based user management – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 25
11
4.
The LDAP server processes the request. If the bind operation is successful, the LDAP server sends an
acknowledgement to the LDAP client.
5.
The LDAP client uses the username of the Telnet user to send a user DN search request to the LDAP
server.
6.
After receiving the request, the LDAP server searches for the user DN by the base DN, search
scope and filtering conditions. If a match is found, the LDAP server sends a response to notify the
LDAP client of the successful search. There can be one or multiple user DNs found.
7.
The LDAP client uses the obtained user DN and the entered user password as parameters to send
a user DN bind request to the LDAP server, which checks whether the user password is correct.
8.
The LDAP server processes the request, and sends a response to notify the LDAP client of the bind
operation result. If the bind operation fails, the LDAP client uses another obtained user DN as the
parameter to send a User DN Bind Request to the LDAP server. This process goes on until a DN is
bound successfully or all DNs fail to be bound. If all user DNs fail to be bound, the LDAP client
notifies the user of the login failure and denies the user's access request.
9.
The LDAP client and server exchange authorization messages. If another scheme, for example, an
HWTACACS scheme, is expected for authorization, the LDAP client exchanges authorization
messages with the HWTACACS authorization server instead.
10.
After successful authorization, the LDAP client notifies the user of the successful login.
Domain-based user management
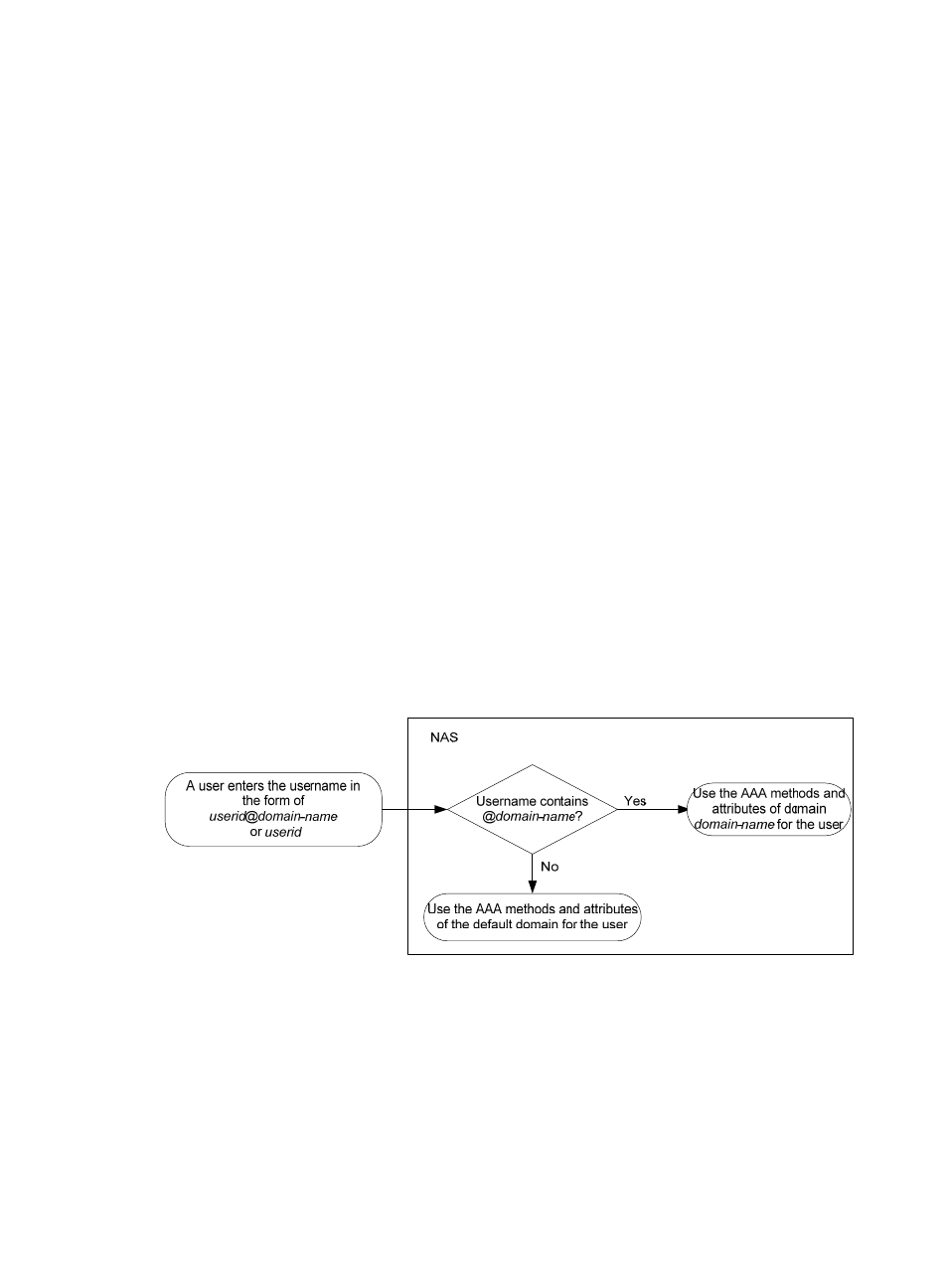
A NAS manages users based on Internet service provider (ISP) domains. In each ISP domain, there are
a collection of users.
On a NAS, each user belongs to one ISP domain. A NAS determines the ISP domain a user belongs to
by the username entered by the user at login.
Figure 8 Determining the ISP domain of a user by the username
The authentication, authorization, and accounting of a user depends on the AAA methods configured for
the domain that the user belongs to. If no specific AAA methods are configured for the domain, the
default methods are used. By default, a domain uses local authentication, local authorization, and local
accounting.
AAA allows you to manage users based on their access types:
•
LAN users—Users on a LAN who must pass 802.1X or MAC address authentication to access the
network.
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C WA3600 Series Access Points H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points H3C S10500 Series Switches H3C S5800 Series Switches H3C S5820X Series Switches H3C S12500 Series Switches H3C S9500E Series Switches H3C MSR 5600 H3C MSR 50 H3C MSR 3600 H3C MSR 30 H3C MSR 2600 H3C MSR 20-2X[40] H3C MSR 20-1X H3C MSR 930 H3C MSR 900 H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C SecPath F5020 H3C SecPath F5040 H3C VMSG VFW1000
