Snmp settings, Snmp settings -52, Able – Verilink XEL XSP-100 SHARK IAP (9SA-USRS-9.0R1.02) Product Manual User Manual
Page 106: Inhole, Rotocol options
Chapter 5: Graphical User Interface (GUI/WEB) Configuration Pages
Chapter 5-52
XEL P/N & Release: 9SA-USRS-9.0R1.02
SHARK™ IAD User's Guide
pinhole definitions. The SHARK™ IAD system will return to the IP/Routing
configuration
menu.
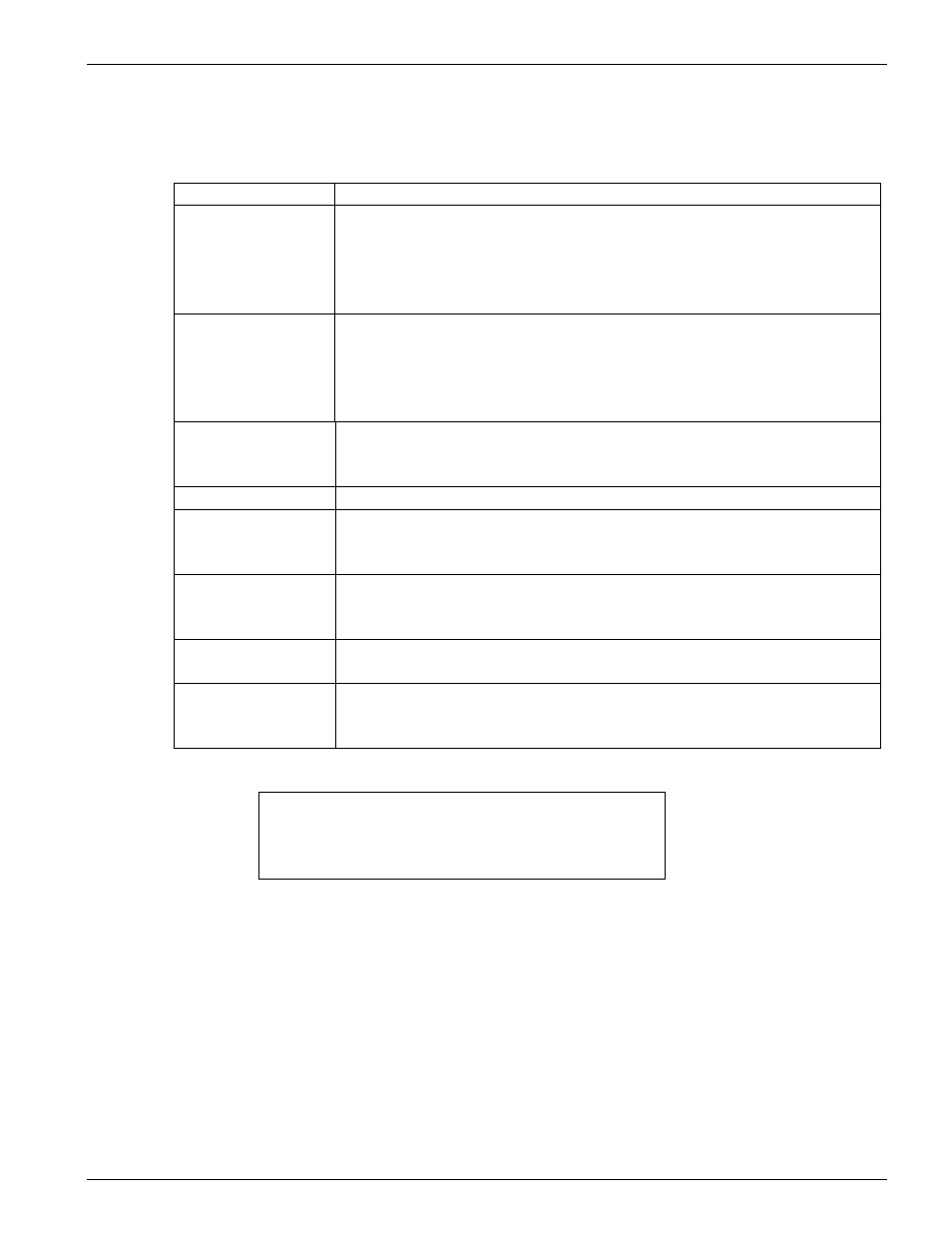
Table 18:
IP Router Server Configuration parameter definitions
Web HTTP Port:
Specifies the port number for HTTP (web) communication with the
SHARK™ IAD. Because port numbers in the range 0-1024 are used
by other protocols, you should use numbers in the range 2000-32767
when assigning new port numbers to the SHARK™ IAD web
configuration interface.
Telnet TCP Port
Specifies the port number for Telnet (CLI) communication with the
SHARK™ IAD. Because port numbers in the range 0-1024 are used
by other protocols, you should use numbers in the range 2000-32767
when assigning new port numbers to the SHARK™ IAD Telnet
configuration interface.
Name
Specifies the number identifying the entry in the router's pinhole table.
You can identify table entries sequentially (1, 2, 3), by port number
(21, 80, 23), or by some other naming scheme.
Protocol options
Specifies the type of protocol being redirected. See Table 19.
External Port Start
Specifies the start port number of the external port over which
incoming traffic will be received. For example, you would enter 21 to
indicate you want FTP traffic forwarded to another host.
External Port End
Specifies the end port number of the external port over which
incoming traffic will be received. For example, you would enter 21 to
indicate you want FTP traffic forwarded to another host.
Internal IP Address Specifies the IP address of the internal host to which traffic of the
specified type should be transferred.
Internal IP Port
Specifies the port number your XEL router should use when
forwarding traffic of the specified type. Under most circumstances,
you would use the same number for the external and internal port.
Table 19:
Pinhole Protocol options
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol.
UDP
User Datagram Protocol.
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol.
PPTP
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol.
SNMP Settings
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) lets a network
administrator monitor problems on a network by retrieving settings on remote
network devices. The network administrator typically runs an SNMP
management station program on a local host to obtain information from an
SNMP agent such as the SHARK™ IAD. The SNMP setup page lets you enter
SNMP configuration information for your SHARK™ IAD. To display the
SNMP setup page click the SNMP button on the SHARK™ IAD IP/Routing
configuration
menu. The SNMP Configuration menu is displayed as shown in
Figure 50.
