Finding management processors – HP Integrated Lights-Out 4 User Manual
Page 287
•
Windows 7
•
Windows 2012
HP Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors package
The migration software, schema extender, and management snap-ins are included in the HP
Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors package. You can download the installer
from
. To complete the migration of your management processors,
you must extend the schema and install the management snap-ins before running the migration
tool.
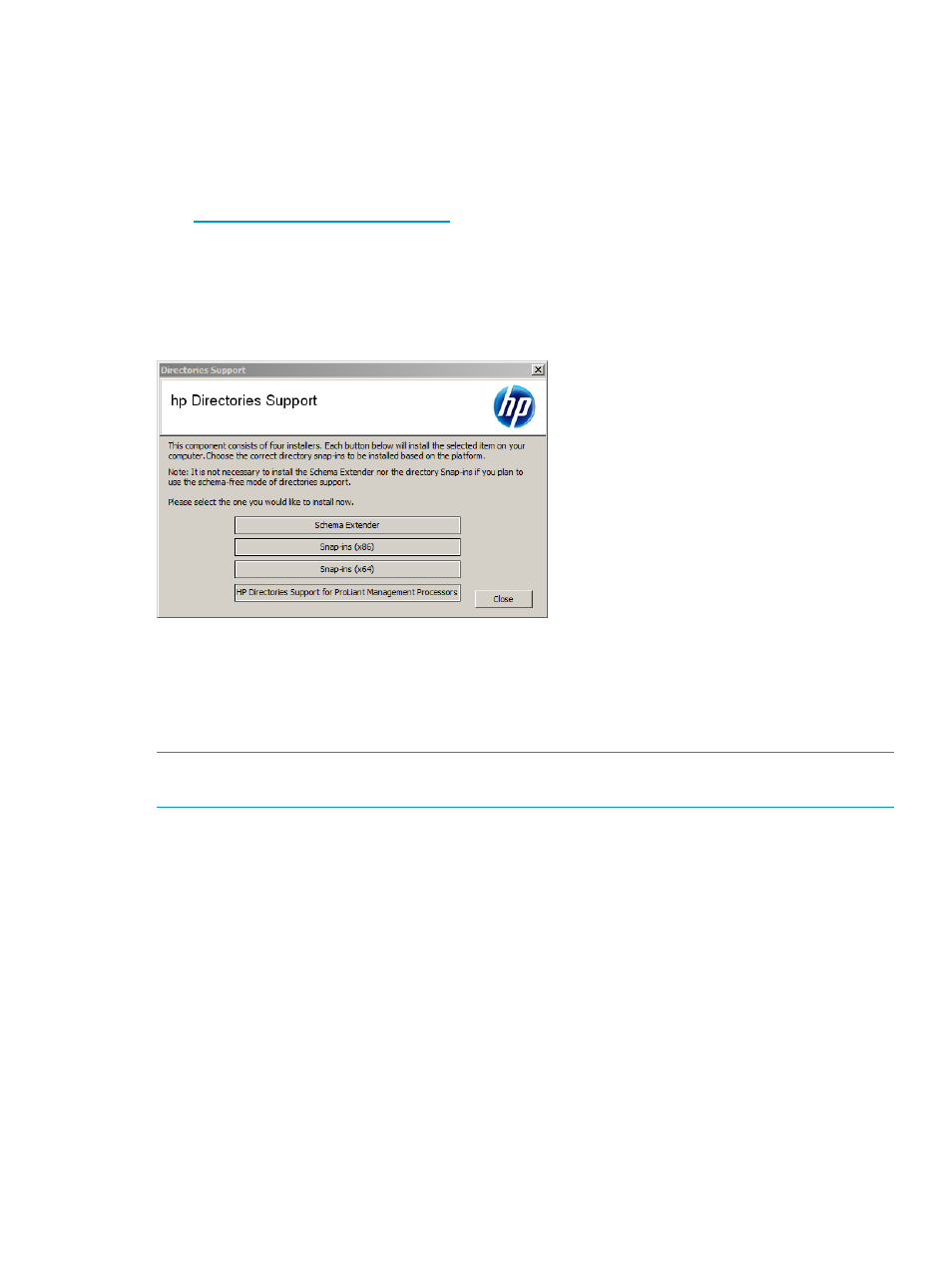
To install the migration utilities, start the installer, and then click HP Directories Support for ProLiant
Management Processors, as shown in
Figure 155 HP Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors installer
The HPLOMIG.exe file, the required DLLs, the license agreement, and other files are installed in
the directory C:\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP Directories Support for
ProLiant Management Processors
. You can select a different directory. The installer creates
a shortcut to HP Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors on the Start menu and
installs a sample XML file.
NOTE:
If the installation utility detects that the .NET Framework is not installed, it displays an
error message and exits.
Using HP Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors
The HP Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors utility automates the process of
migrating management processors by creating objects in the directory that correspond to each
management processor and associating them with a role. HP Directories Support for ProLiant
Management Processors has a GUI and provides a wizard for implementing or upgrading multiple
management processors.
Finding management processors
The first migration step is to discover all management processors that you want to enable for
directory services. You can search for management processors by using DNS names, IP addresses,
or IP address wildcards. The following rules apply to the values entered in the Addresses box:
•
DNS names, IP addresses, and IP address wildcards must be delimited with semicolons.
•
The IP address wildcard uses the asterisk (*) character in the third and fourth octet fields. For
example, IP address 16.100.*.* is valid, and IP address 16.*.*.* is invalid.
HP Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors utility 287
