Comtech EF Data CDM-625 User Manual
Page 394
CDM-625 Advanced Satellite Modem
Revision 15
Ethernet Network Configuration
MN-CDM625
16–16
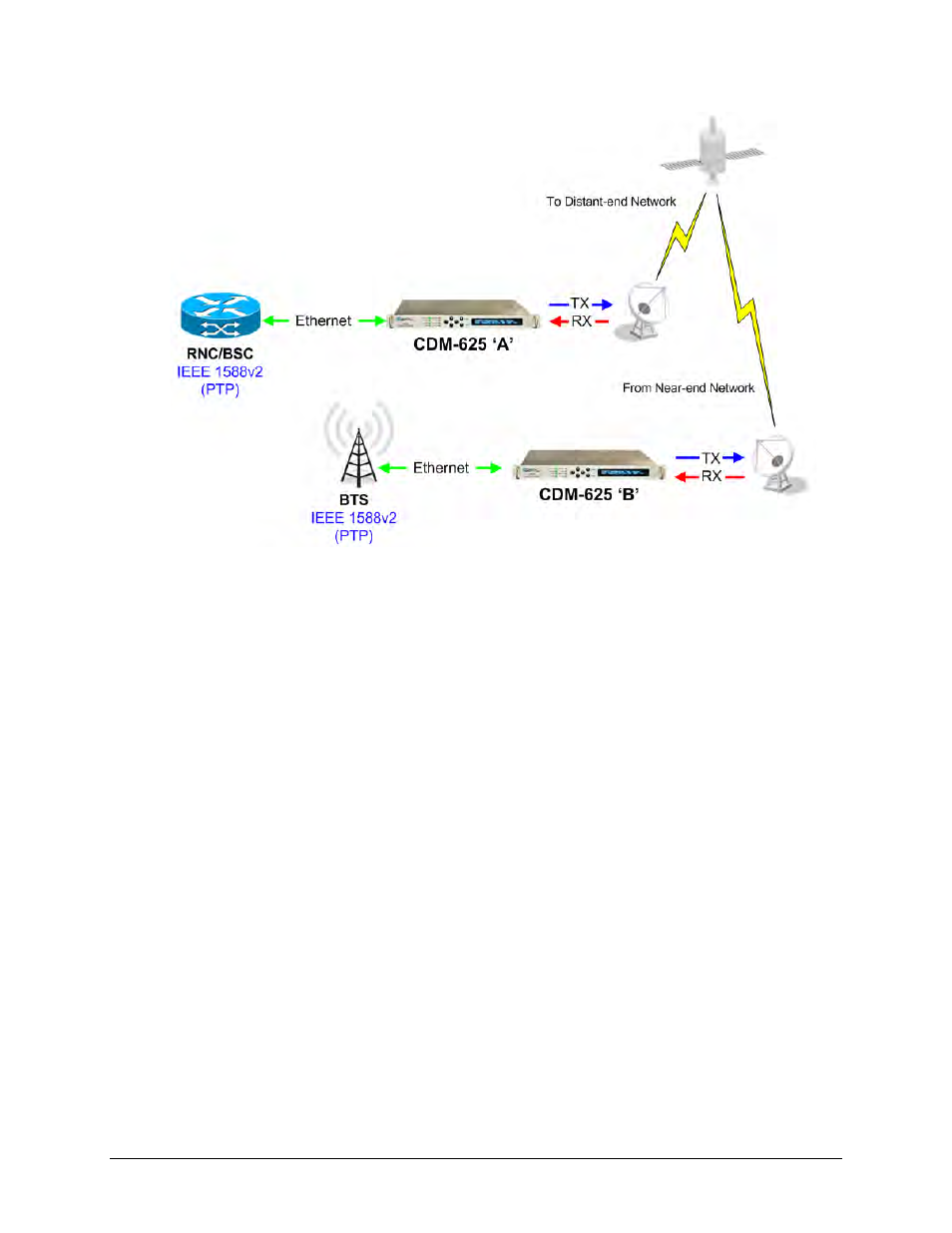
Figure 16-13. Configuration Example – Point-to-Point Network with PTP
Without PTP implementation and support in the modem, it is very difficult to achieve PTP end-
to-end (RNC
► BTS) time synchronization in nanosecond range due to the presence in the
network of variable delay components such as QoS (Quality of Service) buffer, Rx/Tx FIFOs,
Satellite Doppler, etc.
The CDM-625 bridges PTP from LAN to WAN and vice versa, and uses 2-step synchronization
(i.e., it sends both Sync and Follow-up messages when acting as a master). When negotiating
with devices over the LAN interface, the modem uses UDP multicast PTP messages on UDP Port
319 for events, and UDP Port 320 for general packets. On the WAN interface, the modem uses
UDP Port 59319 for events, and UDP Port 59320 for general packets.
Some devices use the Announce message to negotiate which is the PTP master, a process known
as the Best Master Clock (BMC) algorithm. This algorithm allows PTP devices to vote on which
device has the best clock resolution. The CDM-625 will become a PTP master if there is no
Grandmaster device or the Grandmaster is not reachable.
You must configure the modem for the Grandmaster location:
•
When the modem can reach the Grandmaster device only through its LAN interface, set
Grandmaster to LAN.
When Grandmaster is LAN, then the modem knows it must become a slave to the
Grandmaster on the LAN interface, and will set its PTP Clock Priority1 value to 255 (the
lowest).
