Comtech EF Data CDM-625 User Manual
Page 337
CDM-625 Advanced Satellite Modem
Revision 15
DoubleTalk
Carrier-in-Carrier Option
MN-CDM625
10–7
must be kept in mind when troubleshooting a system that utilizes the DoubleTalk Carrier-in-
Carrier technique for signal suppression.
One possible way to mitigate false peaks is to narrow the correlation window. For example, if
the delay is known to be around 240ms, set the minimum search delay to 230ms and the
maximum search delay to 250ms.
As all advances in modem technologies – including advanced modulation and FEC techniques –
approach their theoretical limits of power and bandwidth efficiencies, DoubleTalk Carrier-in-
Carrier allows satellite users to achieve spectral efficiencies (bps/Hz) that cannot be achieved
with modulation and FEC alone. Table 10-1 illustrates how DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier, when
used with 16-QAM, approaches the bandwidth efficiency of 256-QAM (8bps/Hz).
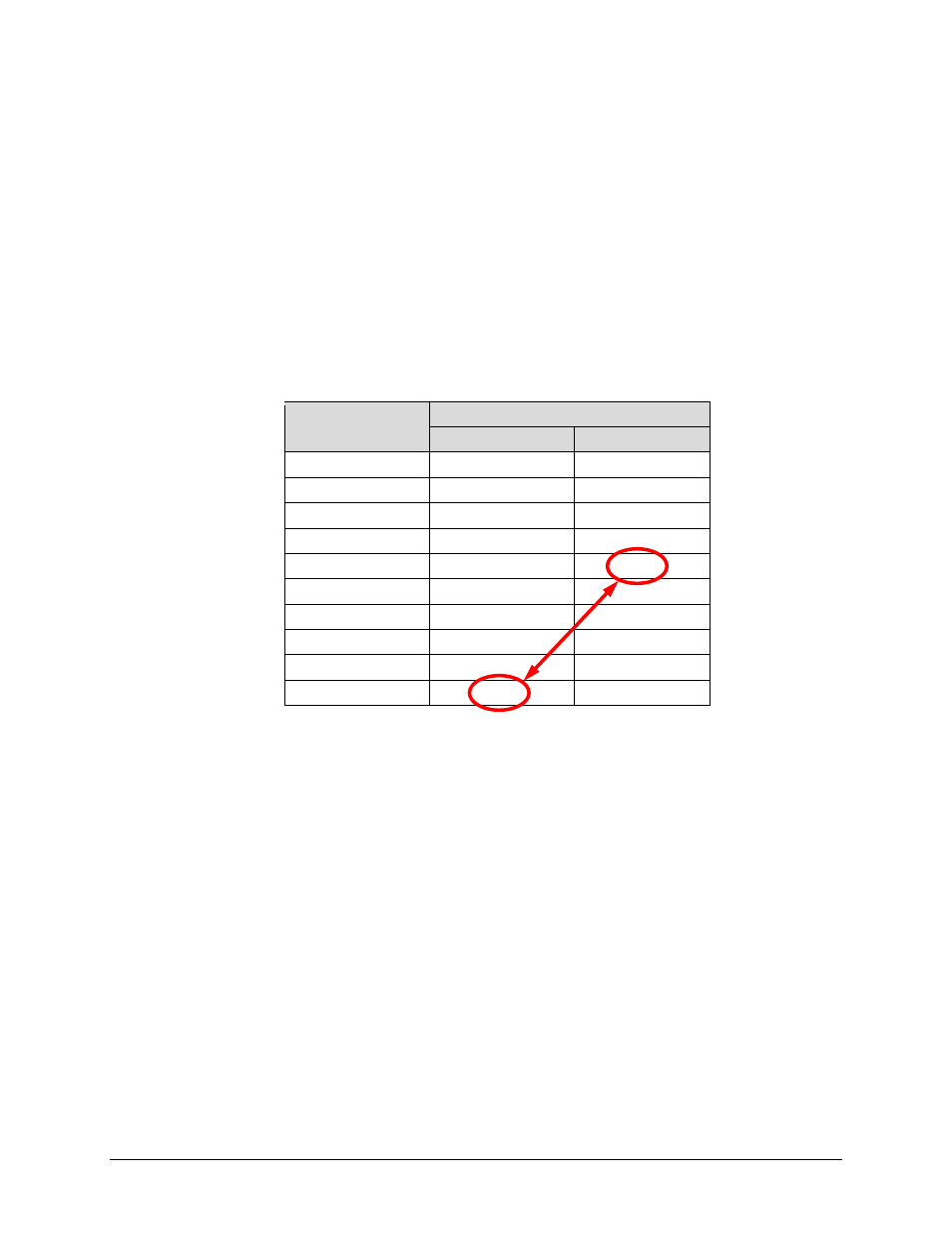
Table 10-1. Spectral Efficiency using DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier
Modulation
and Code Rate
Spectral Efficiency (bps/Hz)
TraditionalSCPC
Carrier-in-Carrier
BPSK 1/2
0.50
1.00
QPSK 1/2
1.00
2.00
QPSK 2/3
1.33
2.67
QPSK 3/4
1.50
3.00
QPSK 7/8
1.75
3.50
8-QAM 2/3
2.00
4.00
8-QAM 3/4
2.25
4.50
8-QAM 7/8
2.63
5.25
16-QAM 3/4
3.00
6.00
16-QAM 7/8
3.50
7.00
As shown here, DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier allows equivalent spectral efficiency using a lower
order modulation and/or FEC Code Rate; CAPEX is therefore reduced by allowing the use of a
smaller BUC/HPA and/or antenna. And, as DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier can be used to save
transponder bandwidth and/or transponder power, it can be successfully deployed in
bandwidth-limited as well as power-limited scenarios.
10.4.1 DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier Cancellation Process
The state-of-the-art signal processing technology employed via DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier
continually estimates and tracks all parametric differences between the local uplink signal and
its image within the downlink. Through advanced adaptive filtering and phase locked loop
implementations, it dynamically compensates for these differences by appropriately adjusting
the delay, frequency, phase and amplitude of the sampled uplink signal, resulting in excellent
cancellation performance.
When a full duplex satellite connection is established between two sites, separate satellite
channels are allocated for each direction. If both directions transmitted on the same channel,
each side would normally find it impossible to extract the desired signal from the aggregate due
