Control overview, Direct vector control, 18 overview of drive – Rockwell Automation 7000A PowerFlex Medium Voltage Drive (A-Frame) - Classic Control User Manual
Page 36
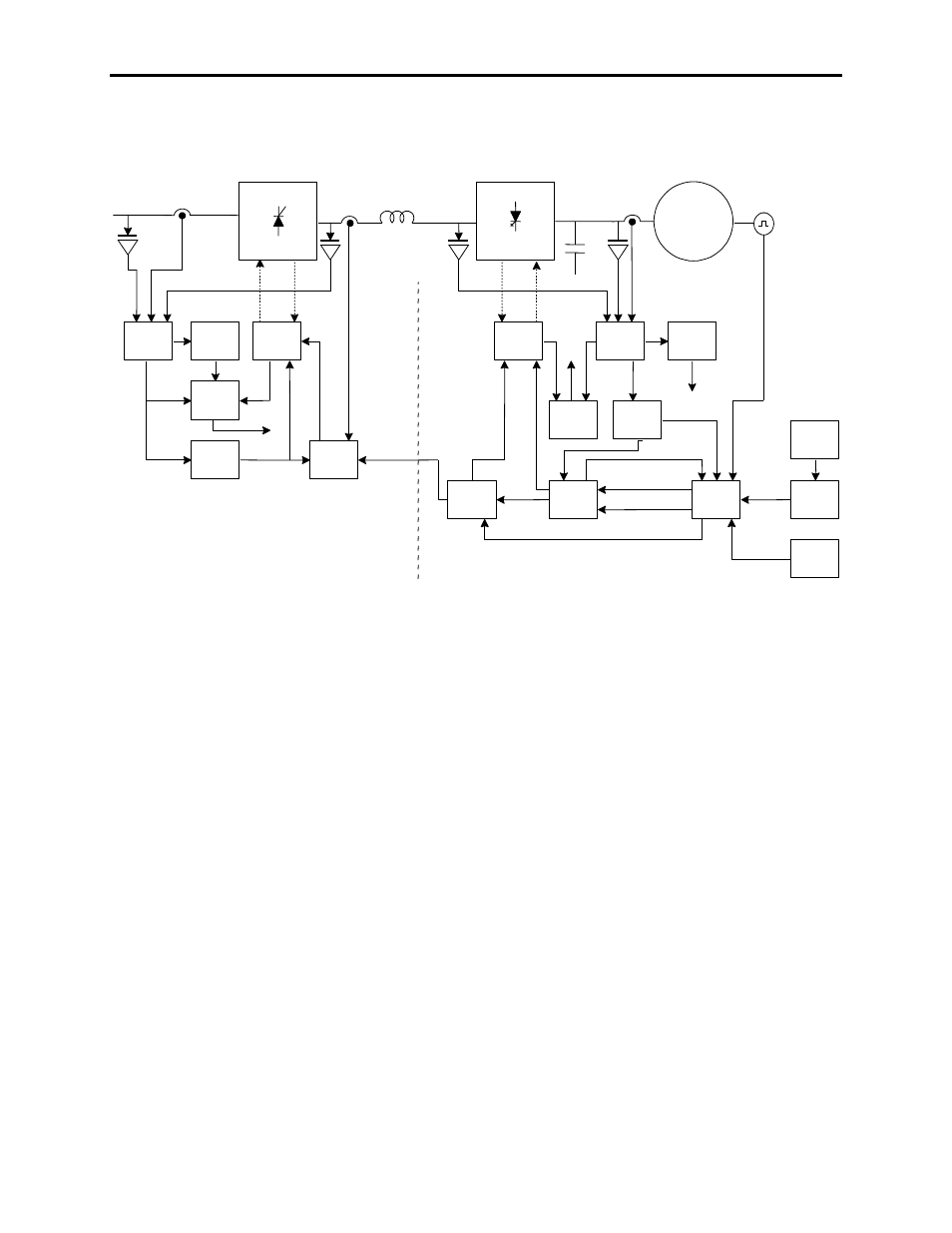
1-18
Overview of Drive
7000A-UM150F-EN-P – June 2013
7000 “A” Frame
Control Overview
Line
Converter
Feedback
Line
Converter
Protection
(HW)
Line gating
and
diagnostic
feedback
Line
Converter
Protection
Line
Side
Control
Machine
Side
Control
Line Converter
Faults
Line
Synch
Current
Control
Li
ne
c
on
verte
r fi
ring
a
ng
le
Idc ref.
Ref.
Current and
phase shift
calculator
Flux
Control
Mag.Current
command
Torque current command
Speed
Control
Torque
Speed Feedback
Machine
Converter
Protection
(SW)
Motor
Model
Synch.
Transfer
Skip Speed
and Speed
Ramp
Speed
Command
Speed Ref.
Tac
h. Fe
ed
ba
ck
Motor
Machine
Converter
Protection
(HW)
Machine
Converter
Feedback
Machine
gating and
diagnostic
feedback
Faults
Motor fil. Cap.
Machine Converter
DC Link
Inductor
M
ac
hi
ne
c
on
verte
r
fi
ring
a
ng
le
Sy
nc
. a
ng
le
Fau
lts
Flux
Figure 1.7 – PowerFlex 7000 “A” Frame Function Block Diagram
Direct Vector Control
The method of control in the PowerFlex 7000 “A” Frame medium
voltage AC drive is called sensorless direct vector control, meaning
that the stator current is divided into torque producing and flux
producing components, allowing the motor torque to be changed
quickly without affecting motor flux. This method of control is used
without tachometer feedback for applications requiring continuous
operation above 6 Hertz and less than 100% starting torque.
Full vector control can also be achieved with tachometer feedback
for applications requiring continuous operation down to 0.2 Hertz
with up to 150% starting torque. Vector control offers superior
performance over volts/hertz type drives. The speed bandwidth
range is 5-25 radians per second, while the torque bandwidth range is
15-50 radians per second.
