Figure 52 pcr, scr and mbs in traffic shaping – ZyXEL Communications IES-708-22A User Manual
Page 121
Chapter 14 xDSL Profiles Setup
IES-708-22A User’s Guide
121
14.5.2.2 Sustained Cell Rate (SCR)
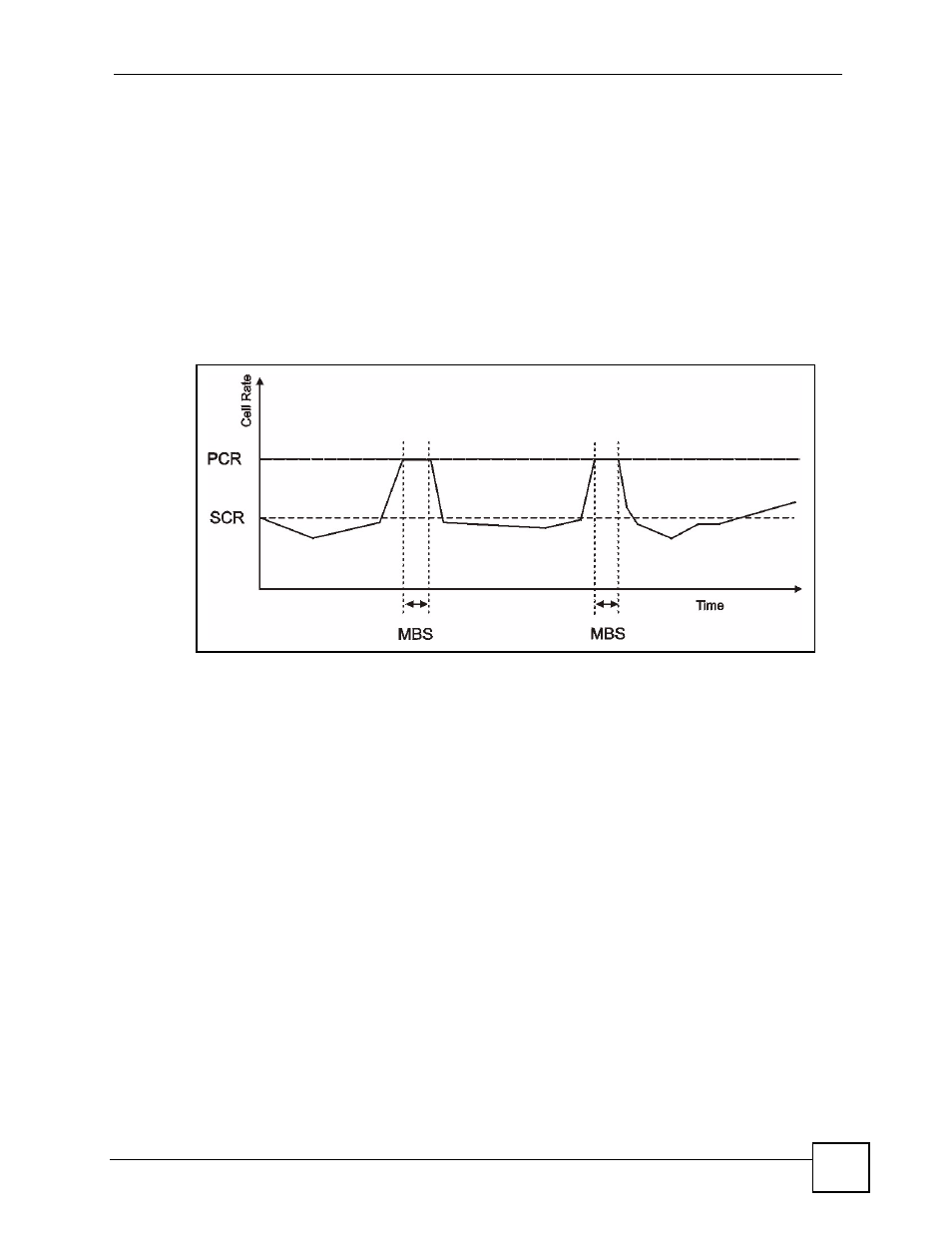
Sustained Cell Rate (SCR) is the mean cell rate of each bursty traffic source. It specifies the
maximum average rate at which cells can be sent over the virtual connection. SCR may not be
greater than the PCR.
14.5.2.3 Maximum Burst Size (MBS)
Maximum Burst Size (MBS) is the maximum number of cells that can be sent at the PCR.
After MBS is reached, cell rates fall below SCR until cell rate averages to the SCR again. At
this time, more cells (up to the MBS) can be sent at the PCR again.
The following figure illustrates the relationship between PCR, SCR and MBS.
Figure 52 PCR, SCR and MBS in Traffic Shaping
14.5.2.4 Cell Delay Variation Tolerance (CDVT)
Cell Delay Variation Tolerance (CDVT) is the accepted tolerance of the difference between a
cell’s transfer delay and the expected transfer delay. CDVT controls the time scale over which
the PCR is enforced. CDVT is used to determine if a cell arrived too early in relation to PCR.
14.5.2.5 Burst Tolerance (BT)
Burst Tolerance (BT) is the maximum number of cells that the port is guaranteed to handle
without any discards. BT controls the time scale over which the SCR is enforced. BT is used to
determine if a cell arrived too early in relation to SCR. Use this formula to calculate BT: (MBS
– 1) x (1 / SCR – 1 / PCR) = BT.
14.5.2.6 Theoretical Arrival Time (TAT)
The Theoretical Arrival Time (TAT) is when the next cell (in an ATM connection’s stream of
cells) is expected to arrive. TAT is calculated based on the PCR or SCR.
The following figure illustrates the relationship between TAT, CDVT and BT. If a cell arrives
at time A, then according to PCR or SCR, the next cell is expected to arrive at time B. If the
next cell arrives earlier than time C, it is discarded or tagged for not complying with the TAT.
Time C is calculated based on the CDVT or BT.
