C.7 message format, Message content, Slave address – Yaskawa L1000E AC Drive Technical Manual for CIMR-LE Models for Elevator Applications User Manual
Page 427: Function code, Data, Message content slave address function code data, Common_ tmonly
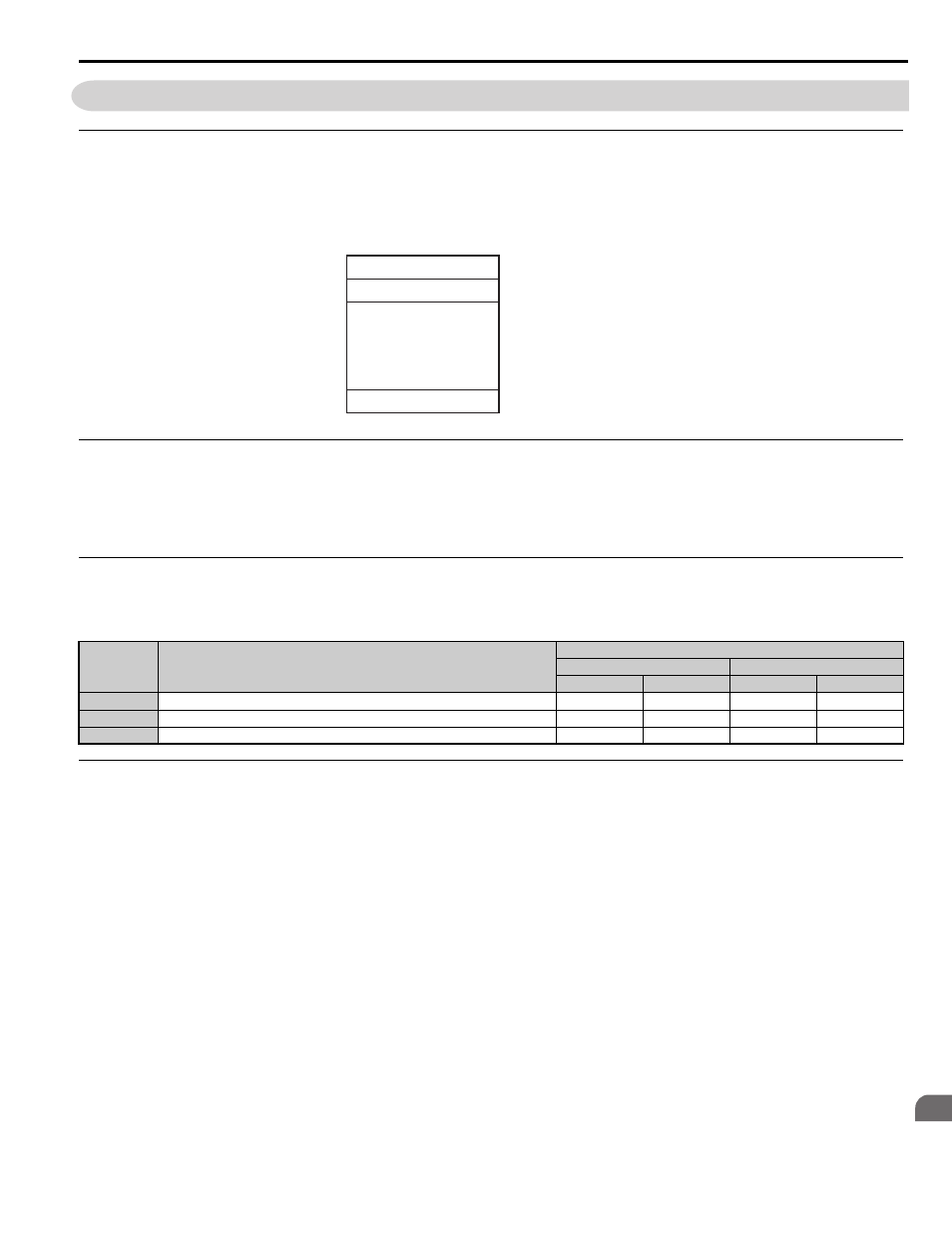
C.7 Message Format
YASKAWA ELECTRIC SIEP YAIL1E 01A YASKAWA AC Drive L1000E Technical Manual
427
MEMOBUS
/Mo
dbu
s
C
o
m
m
u
ni
ca
ti
on
s
C
C.7 Message Format
◆ Message Content
In MEMOBUS/Modbus communications, the master sends commands to the slave, and the slave responds. The message
format is configured for both sending and receiving as shown below, and the length of data packets depends on the
command (function) content.
◆ Slave Address
The slave address in the message defines the note the message is sent to. Use addresses between 0 and FF (hex). If a
message with slave address 0 is sent (broadcast), the command from the master will be received by all slaves. The slaves
do not provide a response to a broadcast type message.
◆ Function Code
The three types of function codes are shown in the table below.
◆ Data
Configure consecutive data by combining the MEMOBUS/Modbus register address (test code in case of a loopback test)
and the data the register contains. The data length changes depending on the command details.
A drive MEMOBUS/Modbus register always has a data length of two bytes. Therefore data written into drive registers
must also always have a length of two bytes. Register data read out from the drive will always consist of two bytes.
Function
Code
Function Name
Data Length (bytes)
Command Message
Response Message
Minimum
Maximum
Minimum
Maximum
03H
Read MEMOBUS/Modbus registers
8
8
7
37
08H
Loopback test
8
8
8
8
10H
Write to multiple MEMOBUS/Modbus registers
11
41
8
8
SLAVE ADDRESS
FUNCTION CODE
DATA
ERROR CHECK
common_
TMonly
