20 configuring rsa authentication, 20 configuring rsa, Authentication – H3C Technologies H3C Intelligent Management Center User Manual
Page 427: Configuring rsa authentication
409
20 Configuring RSA authentication
RSA authentication uses an RSA server to authenticate users. The commonly used RSA server is RSA
RADIUS server.
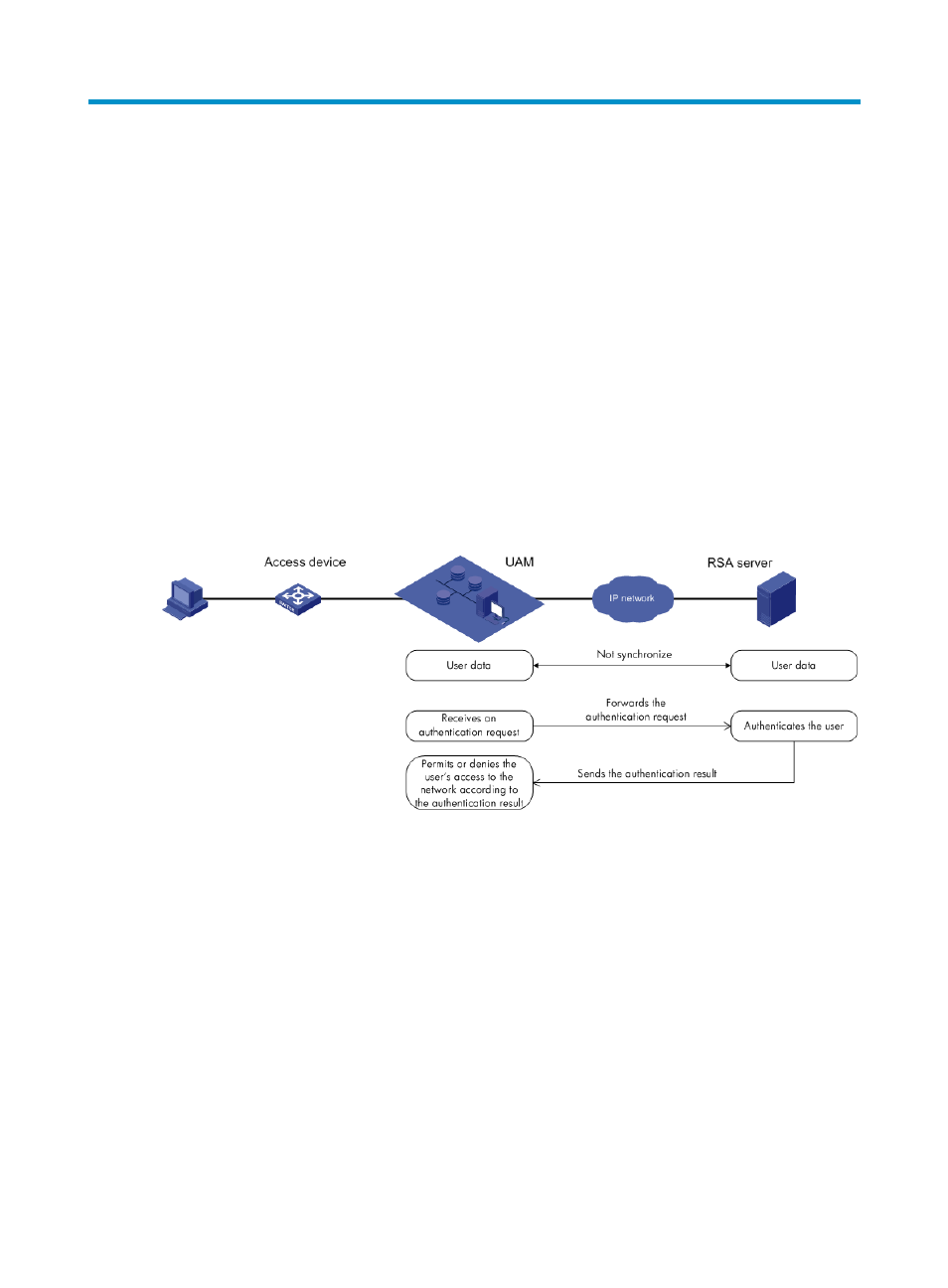
Both UAM and RSA servers are used in RSA authentication. RSA authentication is implemented as shown
in
•
UAM receives an authentication request from a user.
•
UAM searches for the user in the local user database and the services, checking whether RSA
authentication is enabled in the services.
{
If RSA authentication is disabled, UAM performs local authentication.
{
If RSA authentication is enabled, UAM forwards the request to the RSA server.
•
The RSA server authenticates the user and sends the authentication result to UAM.
•
UAM permits or denies the user's access to the network according to the authentication result and
uses access control policies to control the permitted user's access to the network.
Figure 107 RSA authentication involving UAM and the RSA server
When both the UAM and RSA servers save the user information for authentication, they work together to
implement RSA authentication for the user. The user information on the two servers cannot be
automatically synchronized; it must be maintained by the administrator separately on each server.
For UAM to implement RSA authentication with the RSA server, configure the following in UAM:
•
Add access devices. See "
."
•
Add access conditions. See "
7 Configuring access conditions
•
Add access policies and enable RSA authentication in access policies. See "
•
Add services and associate the services with access conditions and policies. See "
•
Add access users.
Common access users and guests support RSA authentication, and mute terminal users and LDAP
users do not support RSA authentication. For more information about access users, see "
."
