1 membrane isolation valve, 2 mass spectrometer, Section – INFICON HAPSITE ER Chemical Identification System User Manual
Page 34
1 - 6
IP
N 07
4-
47
1-
P1
B
HAPSITE ER Operating Manual
The performance of the column is affected by temperature, therefore, the column
is housed in a temperature controlled oven.
The gas chromatograph performs many operational functions, including injecting
the sample, analyzing the sample, flushing the system, and tuning the system.
GC/MS measurement begins with the Sample Pump drawing the gas to be
analyzed into the Sample Loop. It then uses the pressure of the carrier gas to flush
the sample from the Sample Loop on to the analytical column. This step is termed
injection.
1.6.1.1 Membrane Isolation Valve
Gas exiting the analytical column crosses the face of a membrane mounted in the
membrane isolation valve. This membrane has the special characteristic of
transmitting the flow of organic compounds to the mass spectrometer, while
effectively blocking the flow of inorganic gases (such as the nitrogen carrier gas).
When the membrane isolation valve is opened, the appropriate gases are
permitted to enter the Mass Spectrometer for analysis while the Mass
Spectrometer remains under vacuum. The membrane’s performance is affected by
temperature fluctuations and requires housing in a temperature-controlled zone.
In the Survey mode of operation, in which air samples are passed directly to the
mass spectrometer, the sample pump draws the air sample directly across the
membrane with the isolation valve in the open position.
1.6.2 Mass Spectrometer
The Mass Spectrometer is comprised of three basic physical systems: the ionizer,
the mass selector, and the ion detector. These are mounted together in a vacuum
manifold which also includes an inlet, two vacuum pumps, and a portion of the
vacuum interconnect valve, as shown in
Figure 1-1 on page 1-4
.
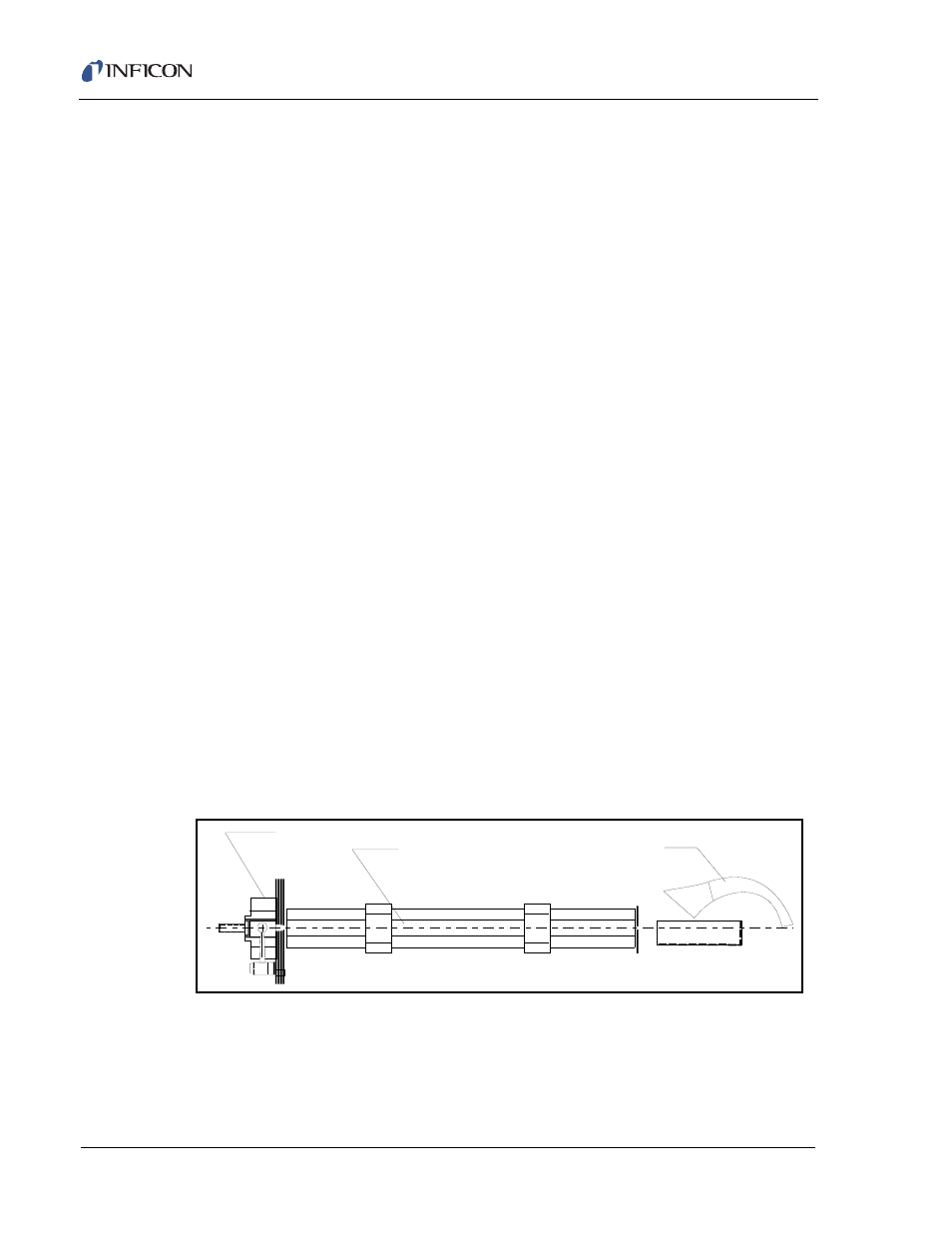
Figure 1-3
is a
representation of the three sub-systems of the mass spectrometer.
Figure 1-3 Three Subsystems of the Mass Spectrometer
The inlet flow from the membrane isolation valve is brought directly to the ionizer.
Within the ionizer, the component introduced from the inlet flow is subjected to a
bombardment of electrons which are boiled off the hot filament. Collisions with the
energetic electrons remove one electron from some of the gas molecules, leaving
them with a net positive charge. This process is termed ionization. Other gas
Mass Selector
Detector
Ionizer
