Figure5.1 lvd driver, Lvd driver, Lvd driver scsi signals— sack – Avago Technologies LSI53C1030 User Manual
Page 127: Lvd receiver scsi signals— sack
DC Characteristics
5-3
Version 2.2
Copyright © 2001, 2002, 2003 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
The core voltage must come up before I/O voltage. The following
equation must hold at all times: VDD_I/O
≤
(VDD_CORE + 2 V).
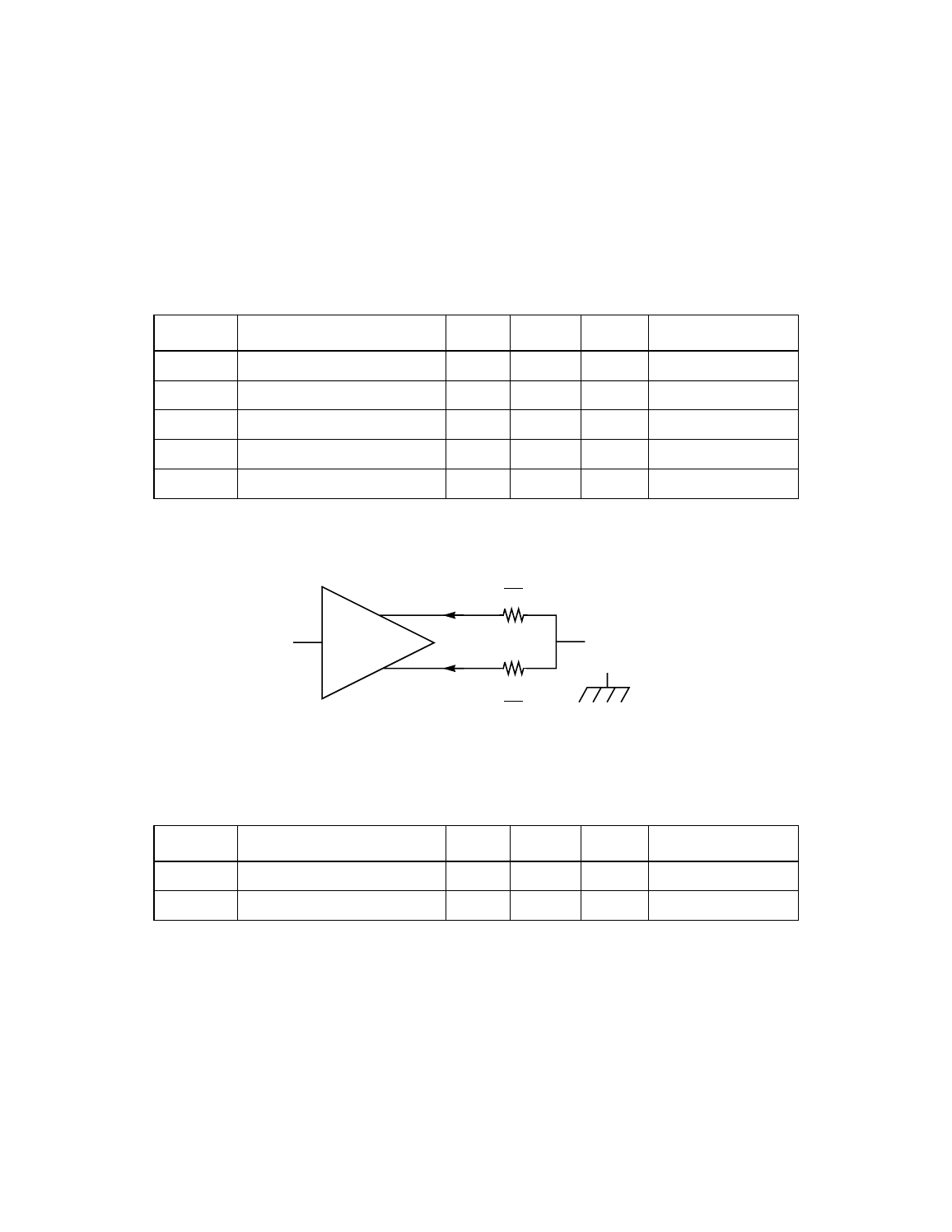
Figure 5.1
LVD Driver
Table 5.3
LVD Driver SCSI Signals
1
— SACK
±
, SATN
±
, SBSY
±
, SCD
±
, SD[15:0]
±
,
SDP[1:0]
±
, SIO
±
, SMSG
±
, SREQ
±
, SRST
±
, SSEL
±
1. V
CM
= 0.7–1.8 V (Common Mode, nominal ~1.2 V), R
bias
= 10.0 k
Ω.
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Units
Test Conditions
I
O
+
Source (+) current
−
6.5
−
13.5
mA
Asserted state
I
O
−
Sink (
−
) current
6.5
13.5
mA
Asserted state
I
O
+
Source (+) current
2.5
9.5
mA
Negated state
I
O
−
Sink (
−
) current
−
2.5
−
9.5
mA
Negated state
I
OZ
3-state leakage
–
20
µ
A
–
R
L
2
V
CM
+
I
O
+
R
L
2
I
O
-
−
+
-
Table 5.4
LVD Receiver SCSI Signals
1
— SACK
±
, SATN
±
, SBSY
±
, SCD
±
, SD[15:0]
±
,
SDP[1:0]
±
, SIO
±
, SMSG
±
, SREQ
±
, SRST
±
, SSEL
±
1. V
CM
= 0.7–1.8 V (Common Mode Voltage, nominal ~1.2 V.)
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Max
Units
Test Conditions
V
I
LVD receiver voltage asserting
|
30
|
-
mV
Differential voltage
V
I
LVD receiver voltage negating
|
30
|
mV
Differential voltage
