Prog 4.1: ed–filter1, 1–1: basic, 1–1a: filter1 – KORG TRITON STUDIO music workstation User Manual
Page 25: 1–1b: a (filter a), 1–1c: b (filter b), N 4.1–1d: utility, P.15)
PROG
1.1
2.1
2.2
2.3
3.1
4.1
4.2
5.1
5.2
5.3
6.1
6.2
6.3
6.4
7.1
7.2
7.3
15
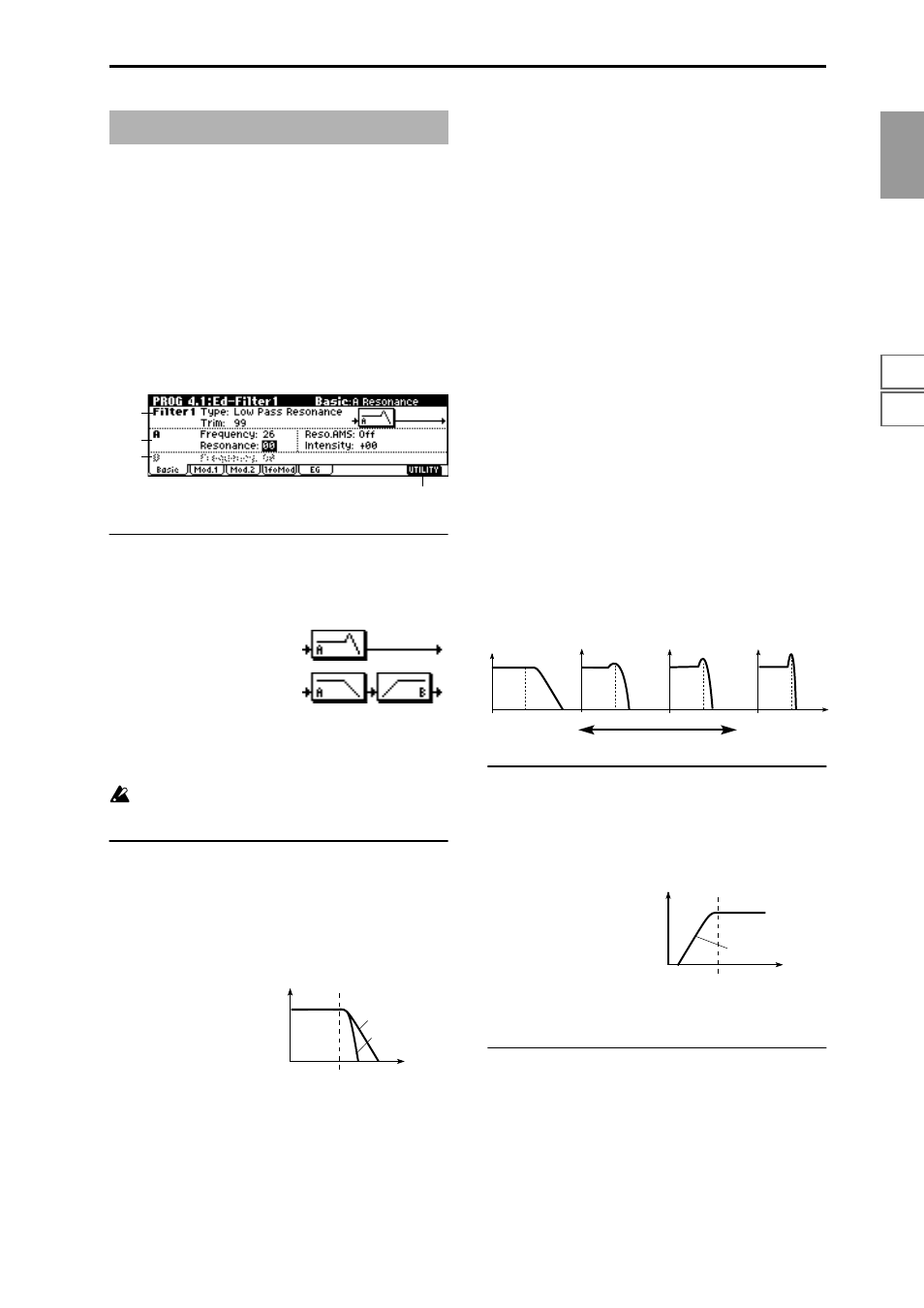
Indicates settings for filter 1 that controls the tone of oscilla-
tor 1. You can select either a 24 dB/oct low pass filter with
resonance, or a 12 dB/oct low pass filter and 12 dB/oct high
pass filter connected in series.
When “Mode (Oscillator Mode)” (2.1–1a) is Single, Drums
you can use filter 1. When it is Double, you can use filters 1
and 2. In the case of Single, Drums the filter 2 pages cannot
be selected.
4.1–1: Basic
Here you can specify the basic type for filter 1 (used by oscil-
lator 1), and set the cutoff frequency and resonance.
4.1–1a: Filter1
Type (Filter1 Type)
[Low Pass Resonance, Low Pass & High Pass]
Indicates the type for filter 1.
Trim
[00…99]
Adjusts the level at which the audio signal output from
OSC1 is input to filter 1A.
If this value is raised, the sound may be distorted if Res-
onance is set to a high value or when you play a chord.
4.1–1b: A (Filter A)
This filter cuts the high-frequency range above the cutoff fre-
quency. This is the most common type of filter, which cuts
the overtone structure to make a bright (sharp) tone darker
(mellow).
When “Type (Filter1 Type)” is Low Pass Resonance, the cut
will have a steeper curve.
Frequency (A Frequency)
[00…99]
Specifies the cutoff frequency of filter 1A.
Resonance (A Resonance)
[00…99]
This emphasizes the overtone components that lie in the
region of the cutoff frequency specified by “Frequency (A
Frequency),” producing a more distinctive sound. Increas-
ing this value will produce a stronger effect.
Reso.AMS (Resonance AMS)
[Off, (PEG, FEG, AEG, LFO, KT, EXT)]
Indicates the source that will control the “Resonance (A Res-
onance)” level (
p.222 “AMS List”).
Intensity (AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that “Reso.
AMS (Resonance AMS)” will have on the resonance level
specified by “Resonance (A Resonance).”
For example, if Velocity has been selected, changes in key-
board velocity will affect the resonance.
With positive (+) values, the resonance will increase as you
play more strongly, and as you play more softly the reso-
nance will approach the level specified by the “Resonance
(A Resonance)” setting.
With negative (–) values, the resonance will decrease as you
play more strongly, and as you play more softly the reso-
nance will approach the level specified by the “Resonance
(A Resonance)” setting.
The resonance level is determined by adding the “Reso-
nance (A Resonance)” and “Intensity (AMS Intensity)” val-
ues.
4.1–1c: B (Filter B)
This will be displayed if “Type (Filter1 Type)” (4.1–1a) is
Low Pass & High Pass
.
This filter cuts the low-frequency range that lies below the
cutoff frequency.
By cutting the lower overtones, it lightens the tone.
Frequency (B Frequency)
[00…99]
Specifies the cutoff frequency of filter 1B.
■
4.1–1d: UTILITY
☞
“Write Program” (1.1–1c), “Copy Oscillator,” “Swap
Oscillator” (2.1–1d)
PROG 4.1: Ed–Filter1
4.1–1a
4.1–1b
4.1–1d
4.1–1c
Low Pass Resonance: 24 dB/octave low
pass filter with resonance
Low Pass & High Pass: 12 dB/octave
low pass filter and 12 dB/octave high pass
filter in series
Frequency
Level
Low Pass
12dB/oct
24dB/oct
The effect of resonance
Low Pass
Level
Low resonance value
High resonance value
Level
Frequency
High Pass
12dB/oct
