5 system descriptor types – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 97
Vol. 3A 3-17
PROTECTED-MODE MEMORY MANAGEMENT
3.5
SYSTEM DESCRIPTOR TYPES
When the S (descriptor type) flag in a segment descriptor is clear, the descriptor type is a system
descriptor. The processor recognizes the following types of system descriptors:
•
Local descriptor-table (LDT) segment descriptor.
•
Task-state segment (TSS) descriptor.
•
Call-gate descriptor.
•
Interrupt-gate descriptor.
•
Trap-gate descriptor.
•
Task-gate descriptor.
These descriptor types fall into two categories: system-segment descriptors and gate descriptors.
System-segment descriptors point to system segments (LDT and TSS segments). Gate descrip-
tors are in themselves “gates,” which hold pointers to procedure entry points in code segments
(call, interrupt, and trap gates) or which hold segment selectors for TSS’s (task gates).
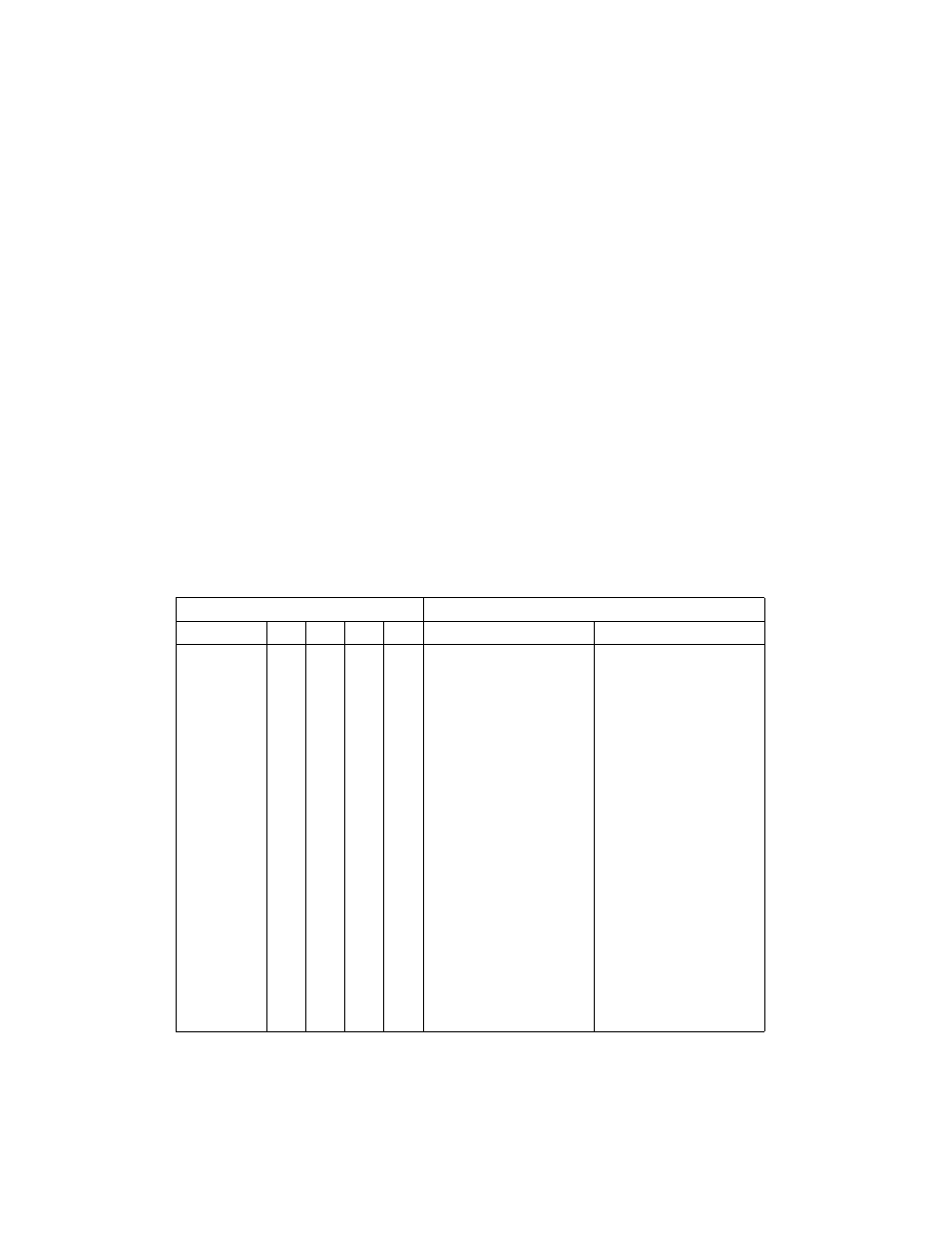
Table 3-2 shows the encoding of the type field for system-segment descriptors and gate descrip-
tors. Note that system descriptors in IA-32e mode are 16 bytes instead of 8 bytes.
Table 3-2. System-Segment and Gate-Descriptor Types
Type Field
Description
Decimal
11
10
9
8
32-Bit Mode
IA-32e Mode
0
0
0
0
0
Reserved
Upper 8 byte of an 16-byte
descriptor
1
0
0
0
1
16-bit TSS (Available)
Reserved
2
0
0
1
0
LDT
LDT
3
0
0
1
1
16-bit TSS (Busy)
Reserved
4
0
1
0
0
16-bit Call Gate
Reserved
5
0
1
0
1
Task Gate
Reserved
6
0
1
1
0
16-bit Interrupt Gate
Reserved
7
0
1
1
1
16-bit Trap Gate
Reserved
8
1
0
0
0
Reserved
Reserved
9
1
0
0
1
32-bit TSS (Available)
64-bit TSS (Available)
10
1
0
1
0
Reserved
Reserved
11
1
0
1
1
32-bit TSS (Busy)
64-bit TSS (Busy)
12
1
1
0
0
32-bit Call Gate
64-bit Call Gate
13
1
1
0
1
Reserved
Reserved
14
1
1
1
0
32-bit Interrupt Gate
64-bit Interrupt Gate
15
1
1
1
1
32-bit Trap Gate
64-bit Trap Gate
