5 task-gate descriptor, D section 6.2.5, “task-gate descriptor, See section 6.2.5, “task-gate descriptor”). th – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 253
Vol. 3A 6-11
TASK MANAGEMENT
6.2.5
Task-Gate Descriptor
A task-gate descriptor provides an indirect, protected reference to a task (see Figure 6-6). It can
be placed in the GDT, an LDT, or the IDT. The TSS segment selector field in a task-gate
descriptor points to a TSS descriptor in the GDT. The RPL in this segment selector is not used.
The DPL of a task-gate descriptor controls access to the TSS descriptor during a task switch.
When a program or procedure makes a call or jump to a task through a task gate, the CPL and
the RPL field of the gate selector pointing to the task gate must be less than or equal to the DPL
of the task-gate descriptor. Note that when a task gate is used, the DPL of the destination TSS
descriptor is not used.
A task can be accessed either through a task-gate descriptor or a TSS descriptor. Both of these
structures satisfy the following needs:
•
Need for a task to have only one busy flag — Because the busy flag for a task is stored in
the TSS descriptor, each task should have only one TSS descriptor. There may, however,
be several task gates that reference the same TSS descriptor.
•
Need to provide selective access to tasks — Task gates fill this need, because they can
reside in an LDT and can have a DPL that is different from the TSS descriptor's DPL. A
program or procedure that does not have sufficient privilege to access the TSS descriptor
for a task in the GDT (which usually has a DPL of 0) may be allowed access to the task
through a task gate with a higher DPL. Task gates give the operating system greater
latitude for limiting access to specific tasks.
•
Need for an interrupt or exception to be handled by an independent task — Task gates
may also reside in the IDT, which allows interrupts and exceptions to be handled by
handler tasks. When an interrupt or exception vector points to a task gate, the processor
switches to the specified task.
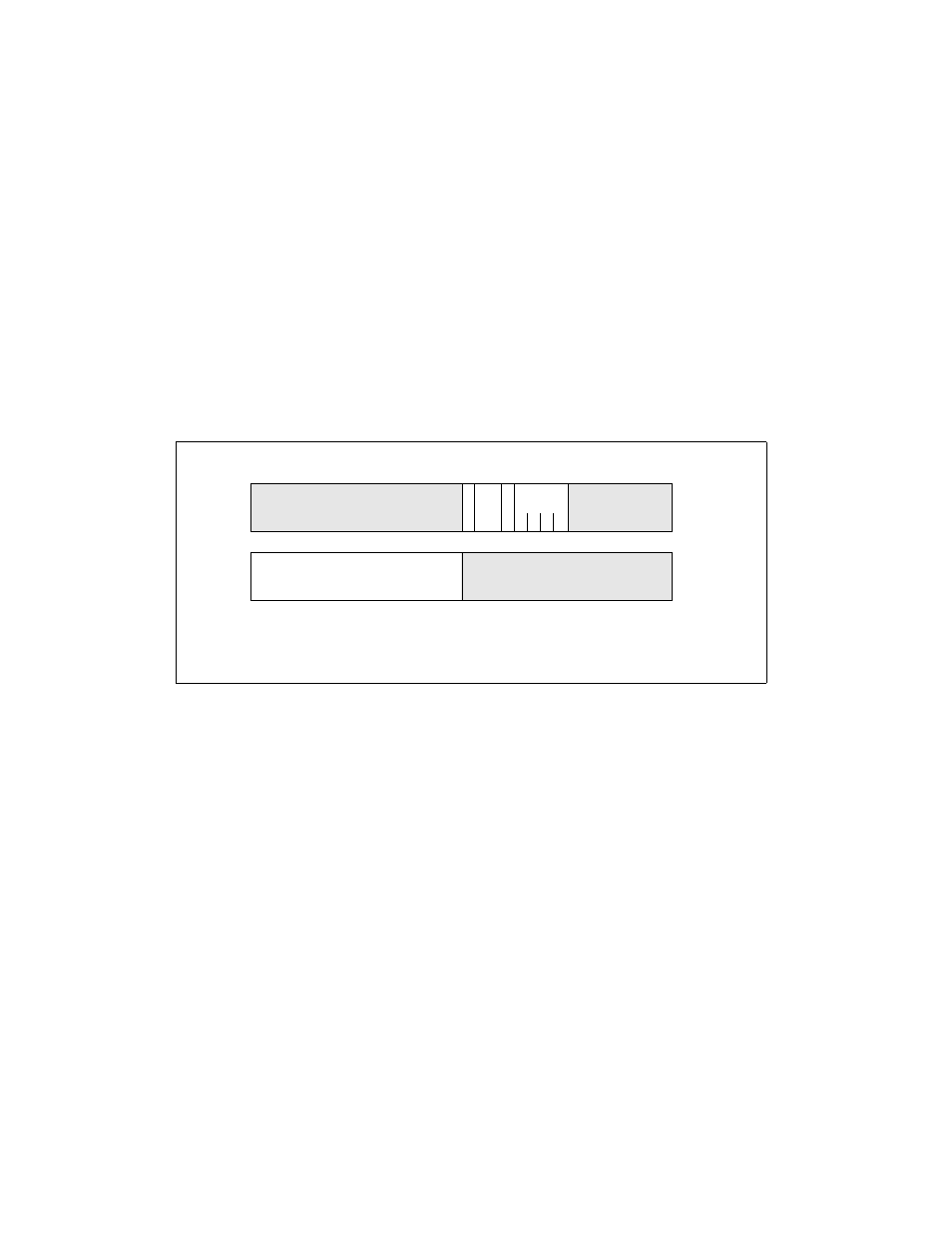
Figure 6-6. Task-Gate Descriptor
31
16 15
13
14
12 11
8 7
0
P
D
P
L
Type
0
31
16 15
0
TSS Segment Selector
1
0
1
0
DPL
P
TYPE
Descriptor Privilege Level
Segment Present
Segment Type
4
0
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
