2 accessing conforming code segments – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 146
4-16 Vol. 3A
PROTECTION
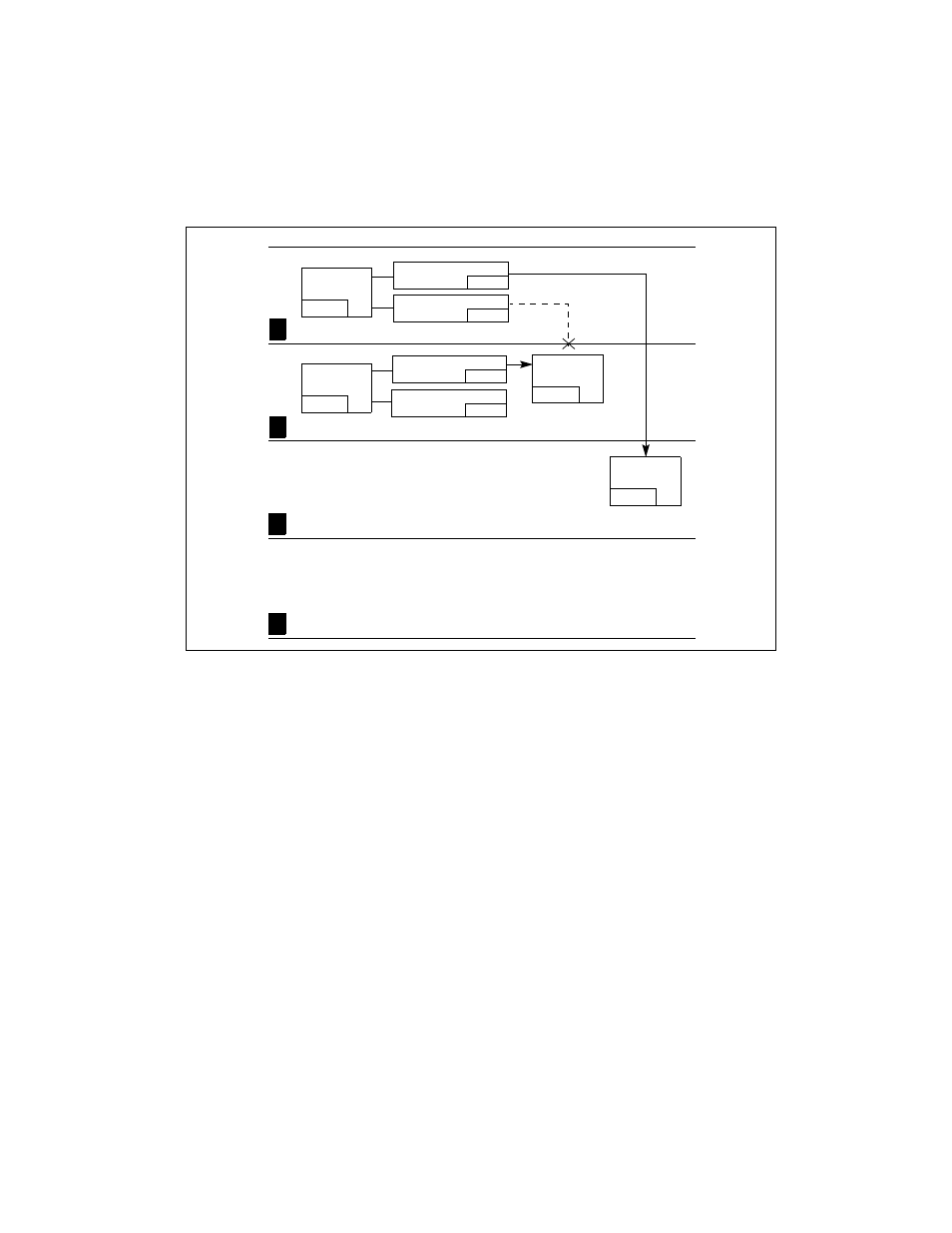
The RPL of the segment selector that points to a nonconforming code segment has a limited
effect on the privilege check. The RPL must be numerically less than or equal to the CPL of the
calling procedure for a successful control transfer to occur. So, in the example in Figure 4-7, the
RPLs of segment selectors C1 and C2 could legally be set to 0, 1, or 2, but not to 3.
When the segment selector of a nonconforming code segment is loaded into the CS register, the
privilege level field is not changed; that is, it remains at the CPL (which is the privilege level of
the calling procedure). This is true, even if the RPL of the segment selector is different from the
CPL.
4.8.1.2
Accessing Conforming Code Segments
When accessing conforming code segments, the CPL of the calling procedure may be numeri-
cally equal to or greater than (less privileged) the DPL of the destination code segment; the
processor generates a general-protection exception (#GP) only if the CPL is less than the DPL.
(The segment selector RPL for the destination code segment is not checked if the segment is a
conforming code segment.)
Figure 4-7. Examples of Accessing Conforming and Nonconforming Code Segments
From Various Privilege Levels
Code
Segment D
Code
Segment C
Code
Segment A
Lowest Privilege
Highest Privilege
CPL=3
Code
Segment B
Nonconforming
Code Segment
Conforming
Code Segment
3
2
1
0
CPL=2
DPL=2
DPL=1
Segment Sel. D1
RPL=2
Segment Sel. D2
RPL=3
Segment Sel. C2
RPL=3
Segment Sel. C1
RPL=2
