Figure 2-3 sh – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 59
Vol. 3A 2-11
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
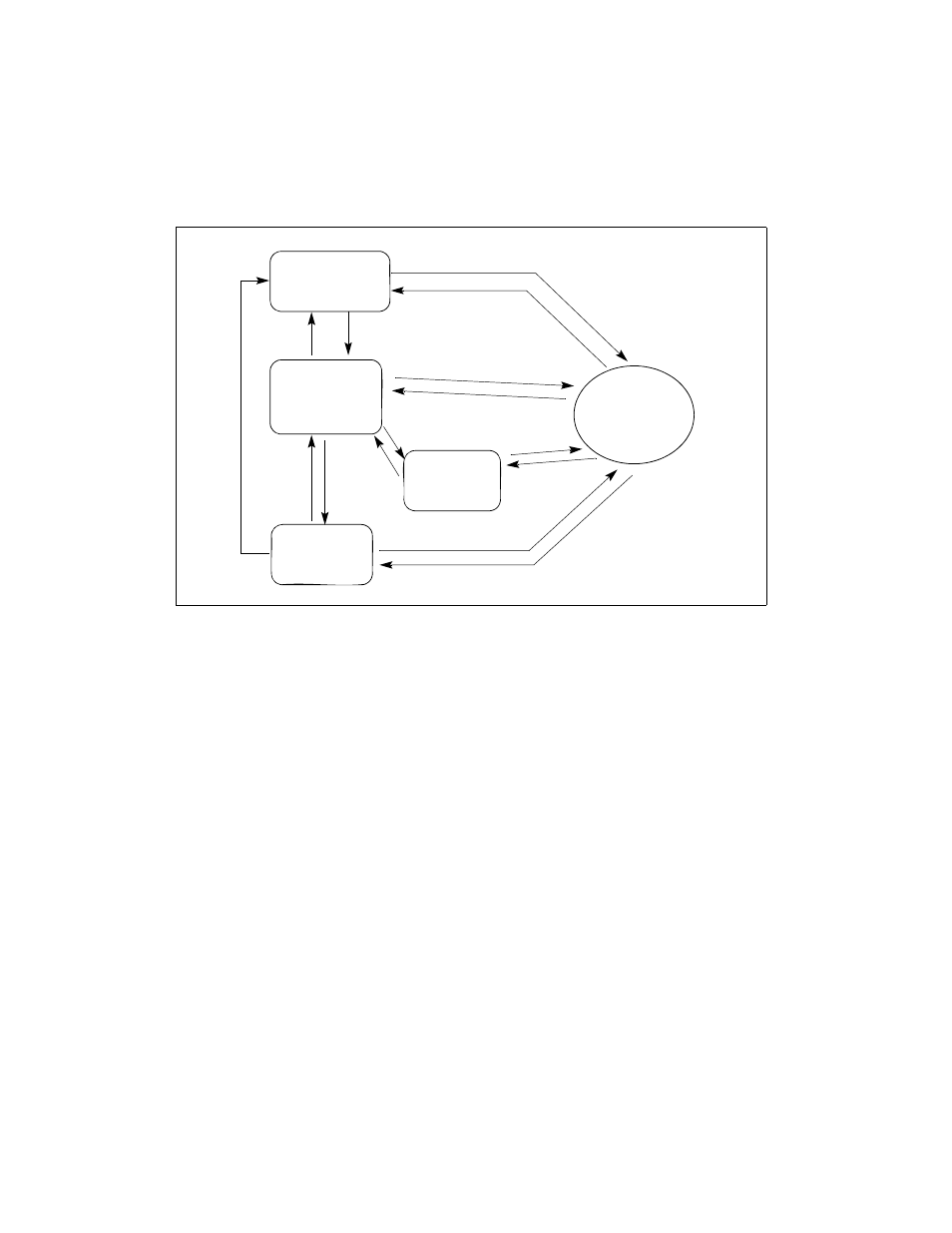
The processor is placed in real-address mode following power-up or a reset. The PE flag in
control register CR0 then controls whether the processor is operating in real-address or protected
mode. See also: Section 9.9, “Mode Switching.”
The VM flag in the EFLAGS register determines whether the processor is operating in protected
mode or virtual-8086 mode. Transitions between protected mode and virtual-8086 mode are
generally carried out as part of a task switch or a return from an interrupt or exception handler.
See also: Section 15.2.5, “Entering Virtual-8086 Mode.”
The LMA bit (IA32_EFER.LMA.LMA[bit 10]) determines whether the processor is operating
in IA-32e mode. When running in IA-32e mode, 64-bit or compatibility sub-mode operation is
determined by CS.L bit of the code segment. The processor enters into IA-32e mode from
protected mode by enabling paging and setting the LME bit (IA32_EFER.LME[bit 8]). See also:
Chapter 9, “Processor Management and Initialization.”
The processor switches to SMM whenever it receives an SMI while the processor is in real-
address, protected, virtual-8086, or IA-32e modes. Upon execution of the RSM instruction, the
processor always returns to the mode it was in when the SMI occurred.
Figure 2-3. Transitions Among the Processor’s Operating Modes
Real-Address
Protected Mode
Virtual-8086
Mode
System
Management
Mode
PE=1
Reset or
VM=1
VM=0
PE=0
Reset
or
RSM
SMI#
RSM
SMI#
RSM
SMI#
Reset
Mode
IA-32e
Mode
RSM
SMI#
LME=1, CR0.PG=1*
See**
* See Section 9.8.5
** See Section 9.8.5.4
