5 stack switching, Occurs (see section 4.8.5, “stack switching”) – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 153
Vol. 3A 4-23
PROTECTION
Call gates allow a single code segment to have procedures that can be accessed at different priv-
ilege levels. For example, an operating system located in a code segment may have some
services which are intended to be used by both the operating system and application software
(such as procedures for handling character I/O). Call gates for these procedures can be set up
that allow access at all privilege levels (0 through 3). More privileged call gates (with DPLs of
0 or 1) can then be set up for other operating system services that are intended to be used only
by the operating system (such as procedures that initialize device drivers).
4.8.5
Stack Switching
Whenever a call gate is used to transfer program control to a more privileged nonconforming
code segment (that is, when the DPL of the nonconforming destination code segment is less than
the CPL), the processor automatically switches to the stack for the destination code segment’s
privilege level. This stack switching is carried out to prevent more privileged procedures from
crashing due to insufficient stack space. It also prevents less privileged procedures from inter-
fering (by accident or intent) with more privileged procedures through a shared stack.
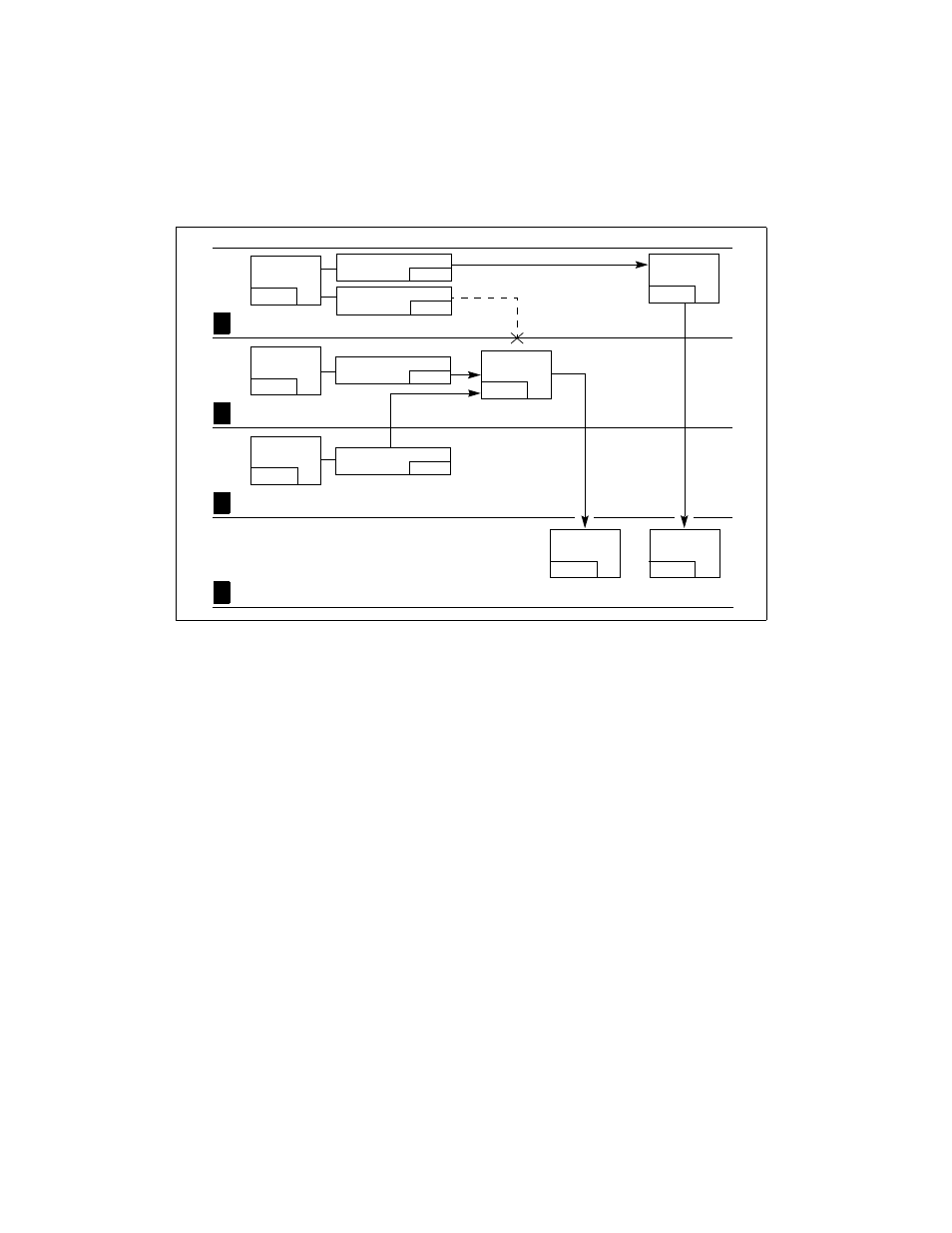
Figure 4-12. Example of Accessing Call Gates At Various Privilege Levels
Code
Segment A
Stack Switch
No Stack
Switch Occurs
Occurs
Lowest Privilege
Highest Privilege
3
2
1
0
Call
Gate A
Code
Segment B
Call
Gate B
Code
Segment C
Code
Segment D
Code
Segment E
Nonconforming
Code Segment
Conforming
Code Segment
Gate Selector A
RPL=3
Gate Selector B1
RPL=2
Gate Selector B2
RPL=1
CPL=3
CPL=2
CPL=1
DPL=3
DPL=2
DPL=0
DPL=0
Gate Selector B3
RPL=3
