1 mtrr feature identification, Es; figure 10-3 – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 466
10-26 Vol. 3A
MEMORY CACHE CONTROL
10.11.1 MTRR Feature Identification
The availability of the MTRR feature is model-specific. Software can determine if MTRRs are
supported on a processor by executing the CPUID instruction and reading the state of the MTRR
flag (bit 12) in the feature information register (EDX).
If the MTRR flag is set (indicating that the processor implements MTRRs), additional informa-
tion about MTRRs can be obtained from the 64-bit IA32_MTRRCAP MSR (named MTRRcap
MSR for the P6 family processors). The IA32_MTRRCAP MSR is a read-only MSR that can
be read with the RDMSR instruction. Figure 10-4 shows the contents of the IA32_MTRRCAP
MSR. The functions of the flags and field in this register are as follows:
•
VCNT (variable range registers count) field, bits 0 through 7 — Indicates the number
of variable ranges implemented on the processor. The Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6
family processors have eight pairs of MTRRs for setting up eight variable ranges.
•
FIX (fixed range registers supported) flag, bit 8 — Fixed range MTRRs
(IA32_MTRR_FIX64K_00000 through IA32_MTRR_FIX4K_0F8000) are supported
when set; no fixed range registers are supported when clear.
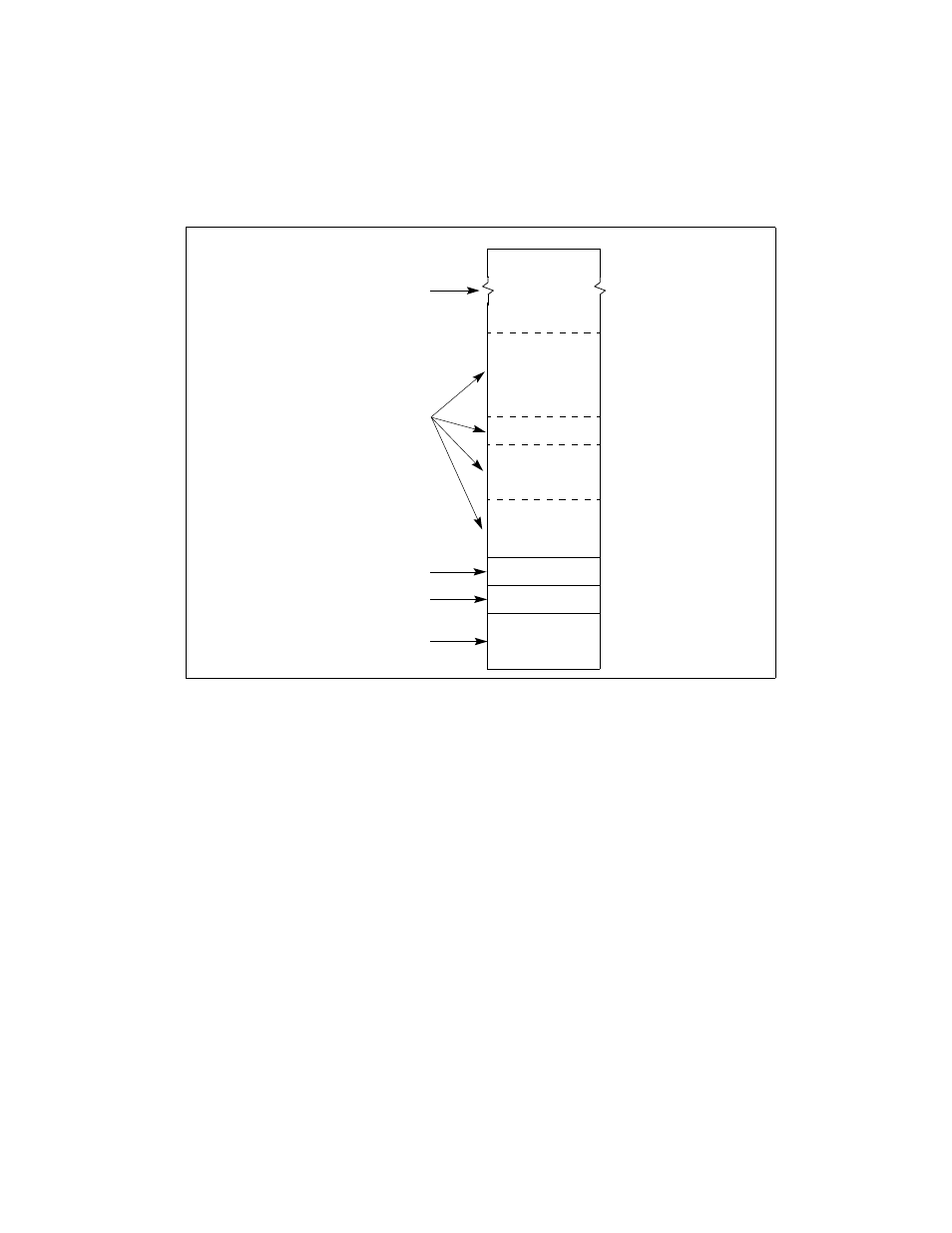
Figure 10-3. Mapping Physical Memory With MTRRs
0
FFFFFFFFH
80000H
BFFFFH
C0000H
FFFFFH
100000H
7FFFFH
512 KBytes
256 KBytes
256 KBytes
8 fixed ranges
16 fixed ranges
64 fixed ranges
8 variable ranges
(64-KBytes each)
(16 KBytes each)
(4 KBytes each)
(from 4 KBytes to
maximum size of
Address ranges not
Physical Memory
mapped by an MTRR
are set to a default type
physical memory)
