6 hyper-threading and multi-core technology, Figure 7-2 – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 291
Vol. 3A 7-23
MULTIPLE-PROCESSOR MANAGEMENT
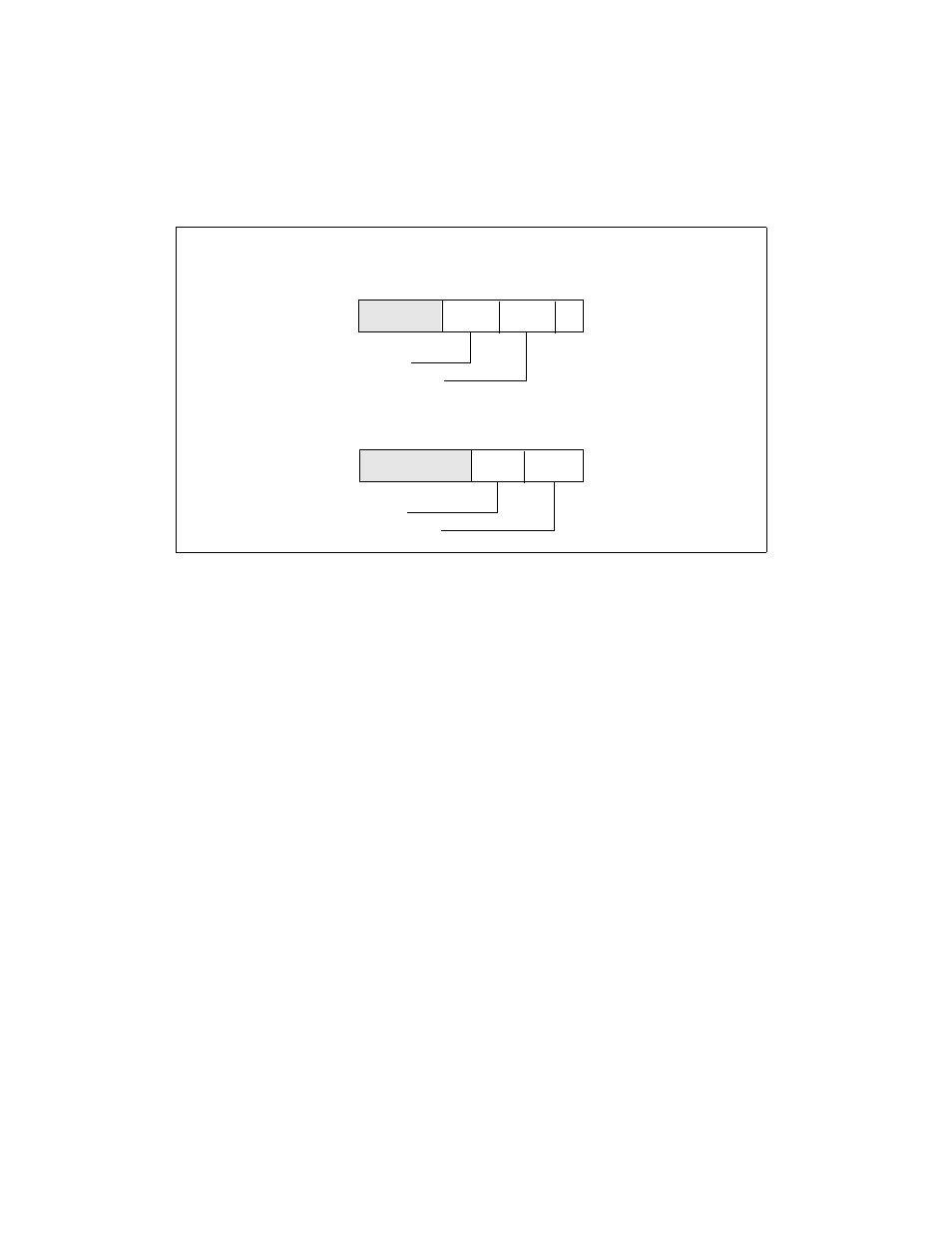
For P6 family processors, the APIC ID that is assigned to a processor during power-up and
initialization is 4 bits (see Figure 7-2). Here, bits 0 and 1 form a 2-bit processor (or socket) iden-
tifier and bits 2 and 3 form a 2-bit cluster ID.
7.6
HYPER-THREADING AND MULTI-CORE TECHNOLOGY
Hyper-Threading Technology and multi-core technology are extensions to IA-32 architecture
that enable a single physical processor to execute two or more separate code streams (called
threads) concurrently. In Hyper-Threading Technology, a single processor core provides two
logical processors that share execution resources (see Section 7.8, “Intel
Technology Architecture”). In multi-core technology, a physical processor package provides
two or more processor cores. Both configurations require chipsets and a BIOS that support the
technologies.
Software should not rely on IA-32 processor names to determine whether a processor supports
Hyper-Threading Technology or multi-core technology. Use the CPUID instruction to deter-
mine processor capability (see Section 7.7.2, “Initializing Dual-Core IA-32 Processors”).
Figure 7-2. Interpretation of APIC ID in Early MP Systems
0
Processor ID
1
7
4
3
2
Cluster
Reserved
0
Processor ID
1
7
4
3
2
5
Cluster
Reserved
APIC ID Format for Intel Xeon Processors that
APIC ID Format for P6 Family Processors
0
do not Support Hyper-Threading Technology
